Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Abstracts: Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies – Basic and Clinical Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: The ACR recommends a treat-to-target strategy in the management of gout, involving titration of urate lowering therapy (ULT) to a serum urate (SU) goal of < 6.0mg/dL. Limited data exist on factors that predict inability to reach goal SU at maximally-titrated doses of allopurinol or febuxostat. Using data from the STOP Gout Study (O’Dell JR et al. NEJM Evidence 2022), a recently completed multicenter, randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority comparative effectiveness trial of allopurinol versus febuxostat in gout management, we sought to elucidate patient factors associated with response to maximally titrated ULT.
Methods: Participants with gout and SU concentration ≥6.8 mg/dL were randomized 1:1 to receive allopurinol or febuxostat. ULT was titrated during weeks 0-24 (Phase 1) and maintained during weeks 25-48 (Phase 2), with escalation as necessary to reach goal SU of < 6.0 mg/dL or until maximum dosing achieved (800mg allopurinol, 80mg febuxostat after dose reduction from 120mg due to FDA black box warning). Participants were observed on a stable ULT dose during weeks 49-72 (Phase 3). Participants were considered to have achieved a urate-lowering response if mean SU measurement during Phase 2 (mean of weeks 36, 42 and 48) was < 6.0mg/dL. Determinants of response were identified using unadjusted and adjusted logistic regression models.
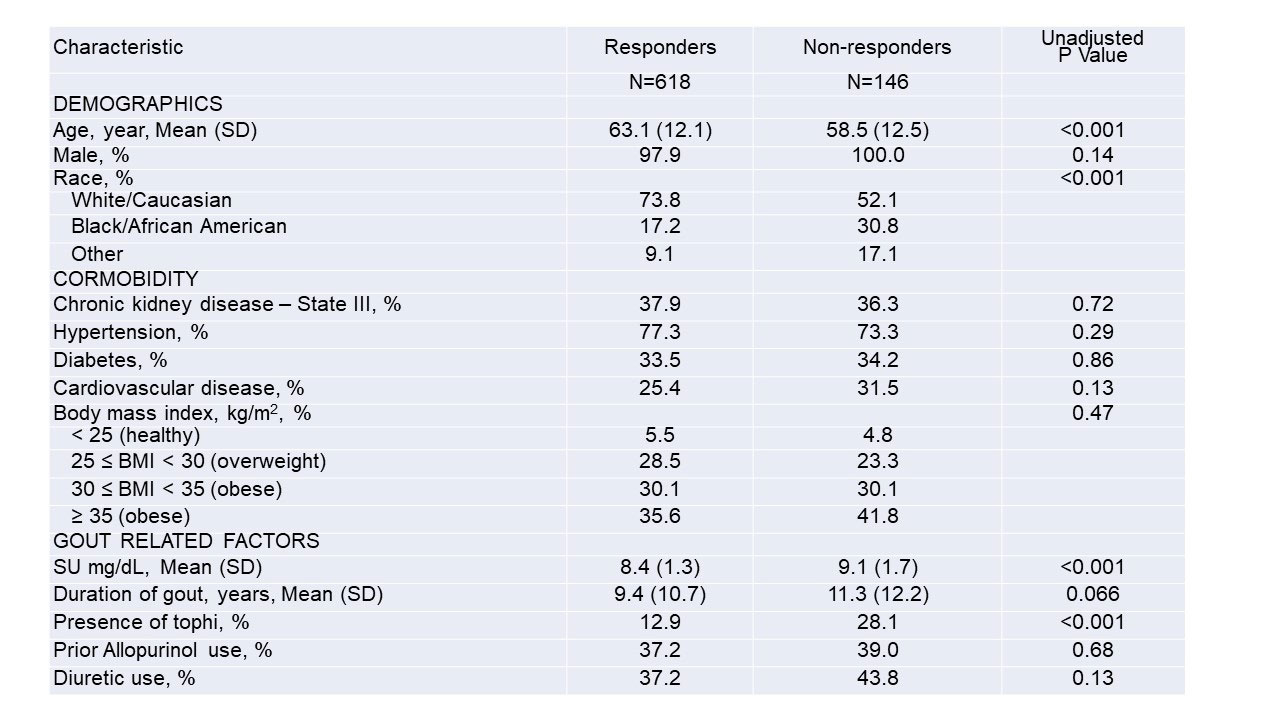
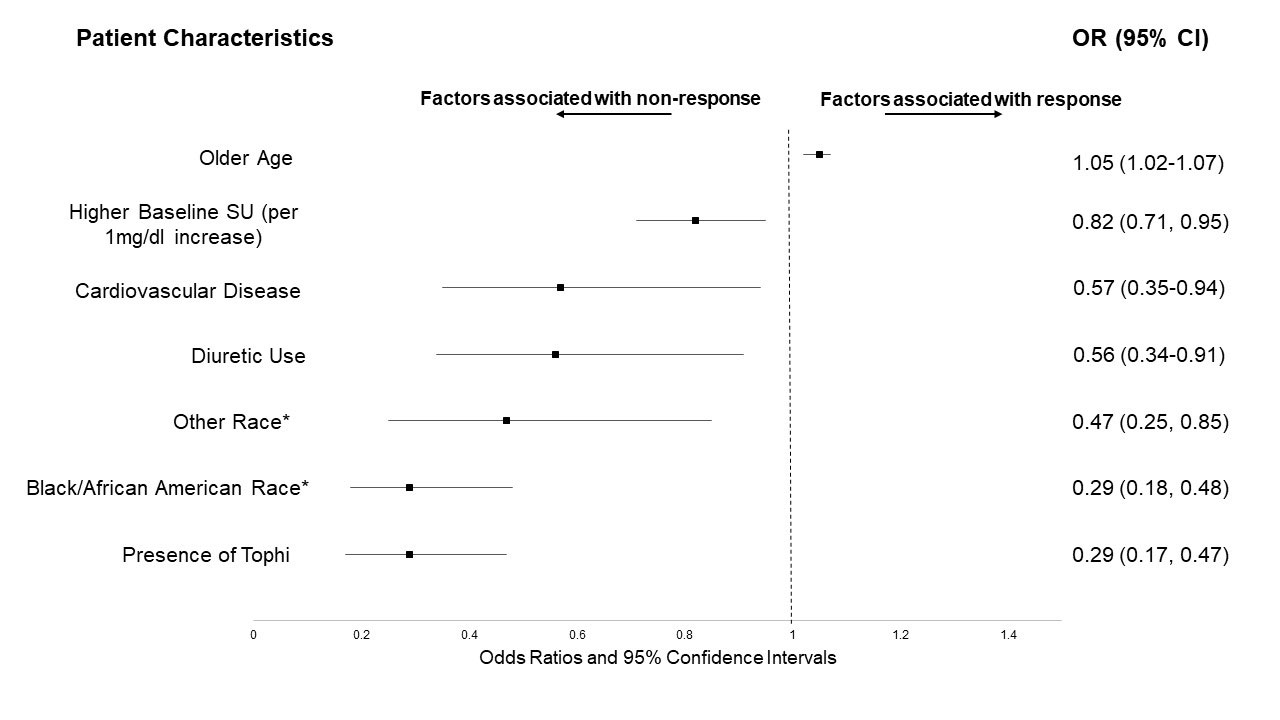
Results: Of 940 trial participants, 764 had SU measures available during Phase 2 and were included in this post-hoc assessment. Of these, 618 (80.9%) were considered ULT responders. Compared to responders, non-responders were younger, more often non-white, more likely to have tophi, and had higher baseline SU values (Table 1). After multivariable adjustment, Black/African Americans were nearly 70% less likely to reach target SU compared to Whites, while races categorized as “other” (a composite of Asian, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and American Indian) were over 50% less likely (Figure 1). Other factors independently associated with a lower likelihood of achieving SU goal included a higher baseline SU, the presence of tophi, cardiovascular disease, and diuretic use. Chronic kidney disease was not associated with response. The multivariable model demonstrated good discriminative ability (c-statistic 0.75).
Conclusion: In this post-hoc analysis from a large randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial comparing the efficacy and safety of allopurinol and febuxostat in the management of gout, several patient factors were associated with inability to reach goal SU on maximally titrated ULT. Outcomes in this study highlight a potentially important health disparity in gout with non-white patients substantially less likely to achieve target treatment goals even in the setting of a controlled clinical trial. To address this disparity, further investigation will be needed to identify the role that social determinants of care and other mechanisms play in driving these observations.
*Values are presented as percentages or means (SD)
**Chronic kidney disease was defined by an eGFR of 30-60 ml/min at trial enrollment
***Cardiovascular disease indicates a history of coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, or heart failure
*Compared to White/Caucasian race
**Results after multivariate analysis; All other variables not shown but displayed in Table 1 were not significant
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Helget L, O'Dell J, Newcomb J, Androsenko M, Brophy M, Davis-Karim A, England B, Ferguson R, Pillinger M, Neogi T, Palevsky P, Wu H, Mikuls T. Race and Disease Severity Predict Reduced Response to Treat-to-Target Urate Lowering Therapy in Gout: Post-hoc Analysis of a Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Non-Inferiority Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/race-and-disease-severity-predict-reduced-response-to-treat-to-target-urate-lowering-therapy-in-gout-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-multicenter-randomized-double-blind-non-inferiority-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/race-and-disease-severity-predict-reduced-response-to-treat-to-target-urate-lowering-therapy-in-gout-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-multicenter-randomized-double-blind-non-inferiority-trial/