Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: SLE – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: HRES-1/Rab4 or Rab4A, a GTPase responsible for mitochondrial oxidative stress1 and activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin2, is overexpressed in T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients3 and livers of lupus-prone mice4. Therefore, we investigated the impact of Rab4A on hepatitis in spontaneous and pristane-induced mouse models of SLE.
Methods: C57Bl/6J wild-type (B6) mice, strains expressing constitutively active Rab4A (Rab4AQ72L) in all cells, and strains lacking Rab4A in T cells (Rab4ACD4-KO) were injected intraperitoneally (ip) with pristane (500µL/20g body weight). Rab4AQ72L and Rab4ACD4-KO mice were generated on both B6 and lupus prone SLE1.2.3 B6-triple congenic backgrounds (B6.TC). Rapamycin was administered to 27-week-old B6.TC mice (ip) 3 times weekly at a concentration of 3 µg/g for 14 weeks. The number of inflammatory cells, inflammatory foci, cells/foci, and vasculitic lesions were used to measure inflammation normalized to surface area within mouse livers. Vasculitis was scored as earlier described5. Student’s t-test was used to test significance; 2-tailed p values < 0.05 were considered significant for hypothesis testing
Results: Following pristane injection, B6/Rab4ACD4-KO mice had fewer inflammatory foci/mm2 (0.32±0.10 vs 1.62±0.45; p=0.042) and vasculitic lesions (0.22±0.02 vs 1.60±0.46; p=0.033) than WT controls. The average vasculitis score was decreased in B6 Rab4ACD4-KO animals (2±0.324) compared to B6 (3.1±0.11; p=0.0016) and B6 Rab4AQ72L controls (2.9±0.18; p=0.014). Female lupus prone B6.TC mice had more inflammatory foci/mm2 (3.04±0.2) than B6 controls (0.93±0.15; p=0.0052). Male B6.TC mice did not show differences in liver inflammation relative to B6 controls. Rapamycin reduced the number of inflammatory and vasculitic foci irrespective of genetically enforced changes in expression of Rab4A. Among female B6.TC mice, 30-50 weeks of age, rapamycin-treated B6.TC Rab4ACD4-KO had fewer inflammatory cells/mm2 (0.41±0.039) compared to rapamycin-treated B6.TC mice (19.10±6.14; p=0.038) and rapamycin-treated B6.TC Rab4AQ72L mice (4.52±1.21; p=0.020). Vehicle treated B6.TC Rab4ACD4-KO also had less severe vasculitis (1.58±0.16) compared to vehicle treated B6.TC Rab4AQ72L (2.67±0.56; p=0.014). Vehicle treated B6.TC Rab4AQ72L had more severe vasculitis (2.67±0.56) compared to vehicle treated B6.TC mice (1.75±0.14; p=0.047). Among 20-40-week-old females, B6 Rab4ACD4-KO mice had fewer inflammatory foci/mm2 (8.36±2.66) compared to B6 Rab4AQ72L mice (29.56±7.87; p=0.043). B6.TC/Rab4AQ72L mice had moderately increased vasculitis severity (2.019±0.10) compared to B6.TC mice (1.82±0.094; p=0.151). By contrast, vasculitis was reduced in B6.TC/Rab4ACD4-KO mice (1.71±0.075) relative to B6.TC/Rab4AQ72L mice (2.02±0.10; p=0.0428).
Conclusion: Activation of Rab4A predisposes while its T cell-specific deletion protects against inflammation and vasculitis in the livers of mice with spontaneous or pristane-induced SLE. mTOR blockade with rapamycin reduced hepatitis in lupus prone mice.
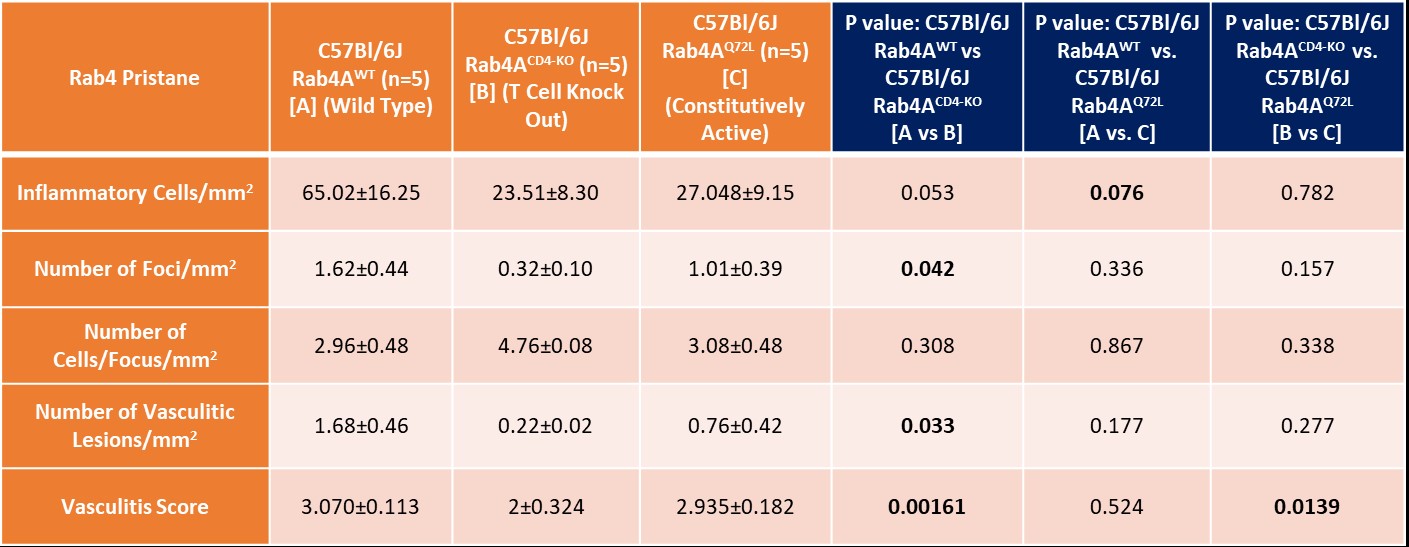 Table summary of Rab4 effect on Pristane-induced SLE liver disease.
Table summary of Rab4 effect on Pristane-induced SLE liver disease.
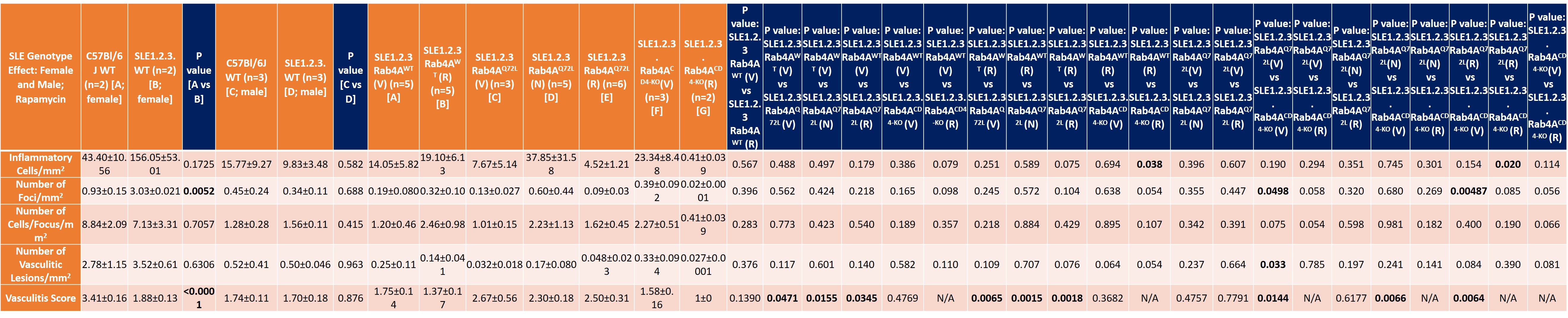 Table summary of liver disease in the following genotypes: Female SLE1.2.3. vs. female C57Bl/6J; Male SLE1.2.3. vs. male C57Bl/6J; Vehicle/NAC/Rapamycin effects on female SLE1.2.3. mice (30-50 weeks of age) with differential Rab4A expression (Wild Type, Q72L, CD4KO).
Table summary of liver disease in the following genotypes: Female SLE1.2.3. vs. female C57Bl/6J; Male SLE1.2.3. vs. male C57Bl/6J; Vehicle/NAC/Rapamycin effects on female SLE1.2.3. mice (30-50 weeks of age) with differential Rab4A expression (Wild Type, Q72L, CD4KO).
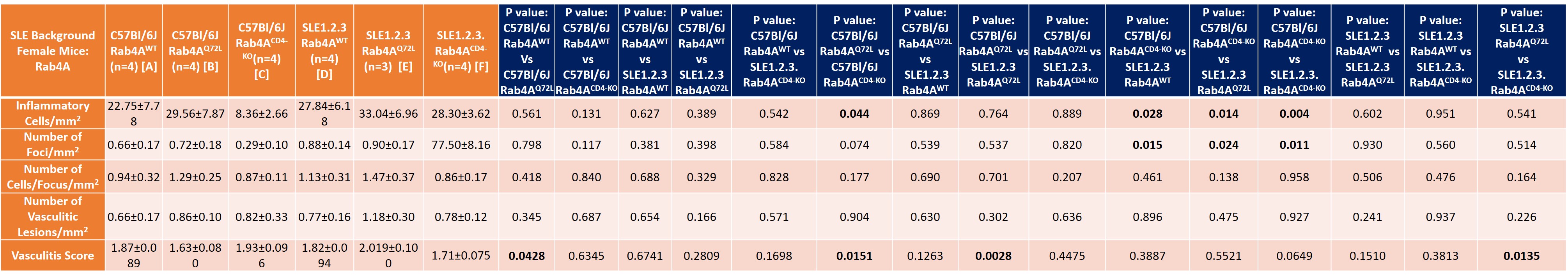 Table summary of liver disease in the following genotypes: Female SLE1.2.3. mice (20-40 weeks of age) with differential Rab4A expression (Wild Type, Q72L, CD4KO).
Table summary of liver disease in the following genotypes: Female SLE1.2.3. mice (20-40 weeks of age) with differential Rab4A expression (Wild Type, Q72L, CD4KO).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huang N, Patel A, Oaks Z, Perl A. Rab4A Activation Predisposes to Hepatitis in Spontaneous and Pristane-Induced Mouse Models of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rab4a-activation-predisposes-to-hepatitis-in-spontaneous-and-pristane-induced-mouse-models-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rab4a-activation-predisposes-to-hepatitis-in-spontaneous-and-pristane-induced-mouse-models-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
