Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II (1364–1390)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Calcinosis cutis (CC) can commonly affect patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc), which is often painful, resulting in functional impairment and morbidity. A radiographic scoring system called SCTC (Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium) hand score1 was developed, which assesses the severity of hand calcinosis in patients with SSc. We aimed to use this scoring system and quality of life measures via patient-reported outcomes (PRO) to assess hand calcinosis in patients with SSc.
Methods: We screened 1104 adult patient charts for diagnosis of SSc and CC based on ICD-10 codes. Diagnosis of SSc was confirmed as per 2013 ACR/EULAR classification criteria, whereas the diagnosis of CC was established as per clinical diagnosis, radiographic evidence, or biopsy. Patients with an overlap syndrome were excluded. Data on patient demographics, serology, and clinical manifestations were collected. SCTC hand score was calculated on patients with available hand radiographs. Patients were invited to participate in a survey utilizing validated, SSc-specific PRO tools. The survey questionnaire included standardized tools such as pain visual analog scale, Scleroderma Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (S-HAQ-DI), Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire (MCQ), and Cochin Hand Function Scale (CHFS). Each survey computed a total score for each PRO tool.
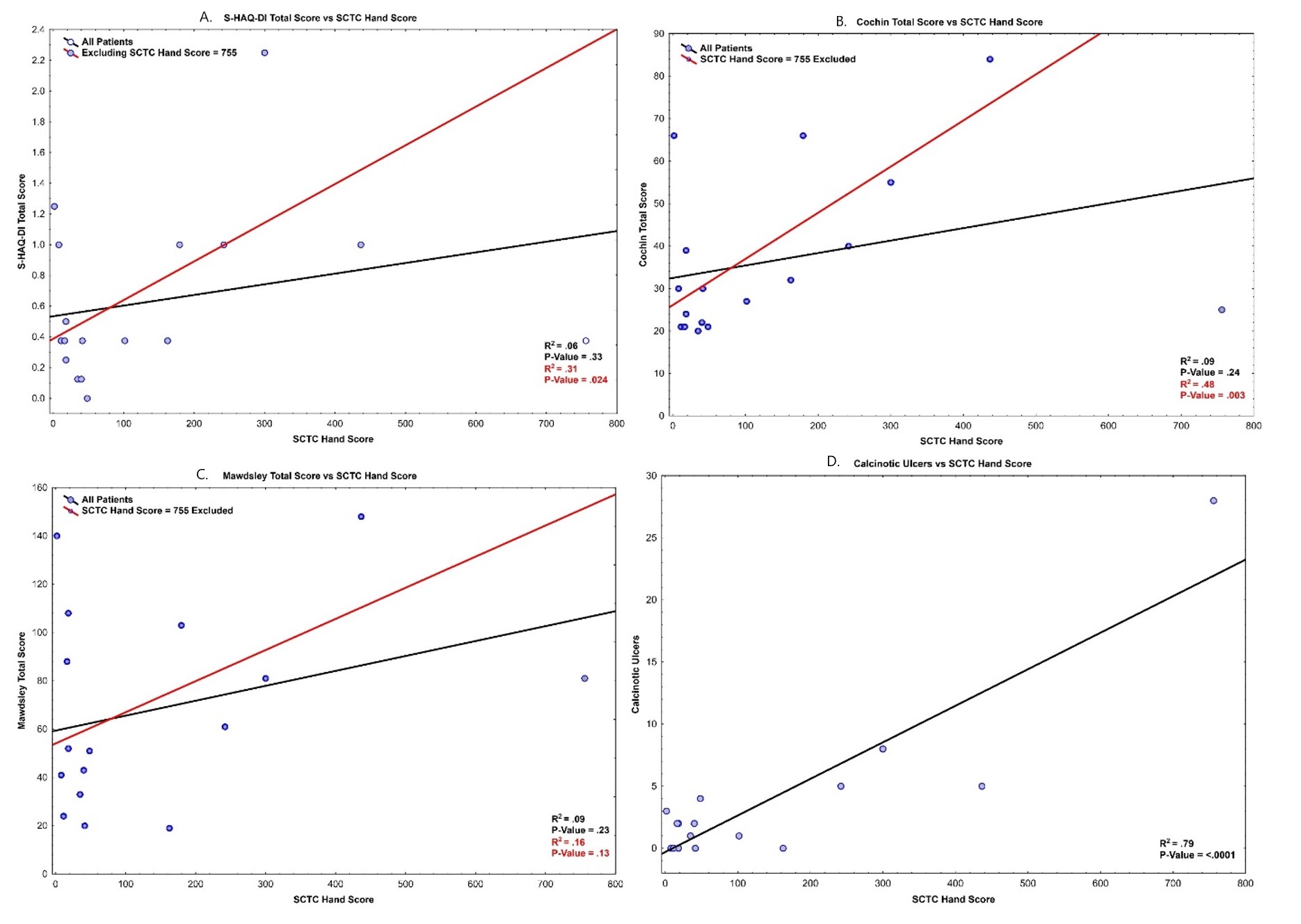
Results: Our cohort included 19 patients with SSc and CC, of which 17 patients had CC in their fingers; 17 patients had hand radiographs available from which SCTC hand scores were calculated. Baseline demographics, disease manifestations, and serology are shown in Table 1. Means, medians, and standard deviations for total scores for each PRO tool were computed, and each total score was regressed against the patient’s SCTC Hand Score, the statistical summary of which is shown in Table 2. In the case of each PRO tool, the total score for a single patient with an SCTC Hand Score of 755 was an extremely influential response. Regressions were run with and without this patient. There were no significant correlations (P < .05) between any of the total scores and SCTC Hand Scores using data from all patients. However, when the influential data point was removed, there was a significant correlation between SCTC Hand Scores and S-HAQ-DI and CHFS total scores. A significant correlation was also found between SCTC Hand Scores and the number of calcinotic digital ulcers. These correlations are shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion: Our study shows a significant correlation between SCTC hand scores and S-HAQ-DI, CHFS, and the number of calcinotic digital ulcers. A higher SCTC hand score may predict a higher likelihood of developing calcinotic ulcers. No significant correlation between SCTC hand scores and MCQ could relate to non-accountability for psychological aspects of CC in SCTC hand scores, highlighting the limitation of using SCTC hand scores alone to assess the quality of life in SSc patients with CC.
Reference:
1. Chung L, Valenzuela A, Fiorentino D, et al. Validation of a Novel Radiographic Scoring System for Calcinosis Affecting the Hands of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014 Aug 22
 Table 1: Baseline demographics, disease manifestations and serology
Table 1: Baseline demographics, disease manifestations and serology
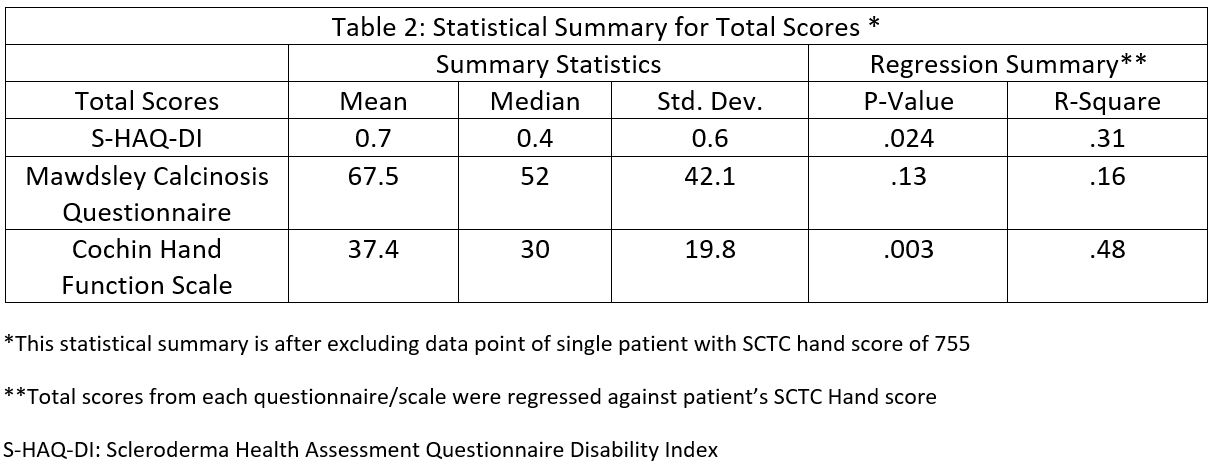 Table 2: Patient-reported outcomes
Table 2: Patient-reported outcomes
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel A, Grewal M, Butler R, Chatterjee S. Quality of Life in Patients with Scleroderma Associated Calcinosis Cutis: A Cross-Sectional Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-in-patients-with-scleroderma-associated-calcinosis-cutis-a-cross-sectional-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quality-of-life-in-patients-with-scleroderma-associated-calcinosis-cutis-a-cross-sectional-study/