Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: A pivotal clinical characteristic of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is disease manifestations in several domains (skin, entheses, joints, spine) and multiple domain involvement is prevalent, which complicates therapy. Recent evidence supports a major role for CD8 T cells in the pathogenesis of PsA, however, the role of these cells and serum factors in driving disease in the individual domains is poorly understood. To address this gap, we injected sera and peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC)s from patients with specific phenotypes (psoriasis only, psoriasis and non-erosive arthritis, psoriasis with erosive arthritis, dactylitis) into immunodeficient NSG-SGM3 mice to experimentally evaluate cellular and serum factors that promote domain inflammation in PsA.
Methods: Sera and PBMC were isolated from healthy controls (HC), treatment naïve Psoriasis (Ps) patients with active plaques and PsA. Three groups of NSG-SGM3 mice were intravenously injected with serum and PBMCs collected from healthy (HC), Ps and PsA patients with predominant dactylitis, non-erosive or erosive arthritis. Blood leukocytes, 3-mm skin punch biopsies and synovia (back/front paws) were collected on day 30 post-transfer to quantitate T cells by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. We examined synovial CD8 T cells with GeoMx digital spatial profiler and next-generation sequencing readout, combined with nSolver software, to define their molecular profiles.
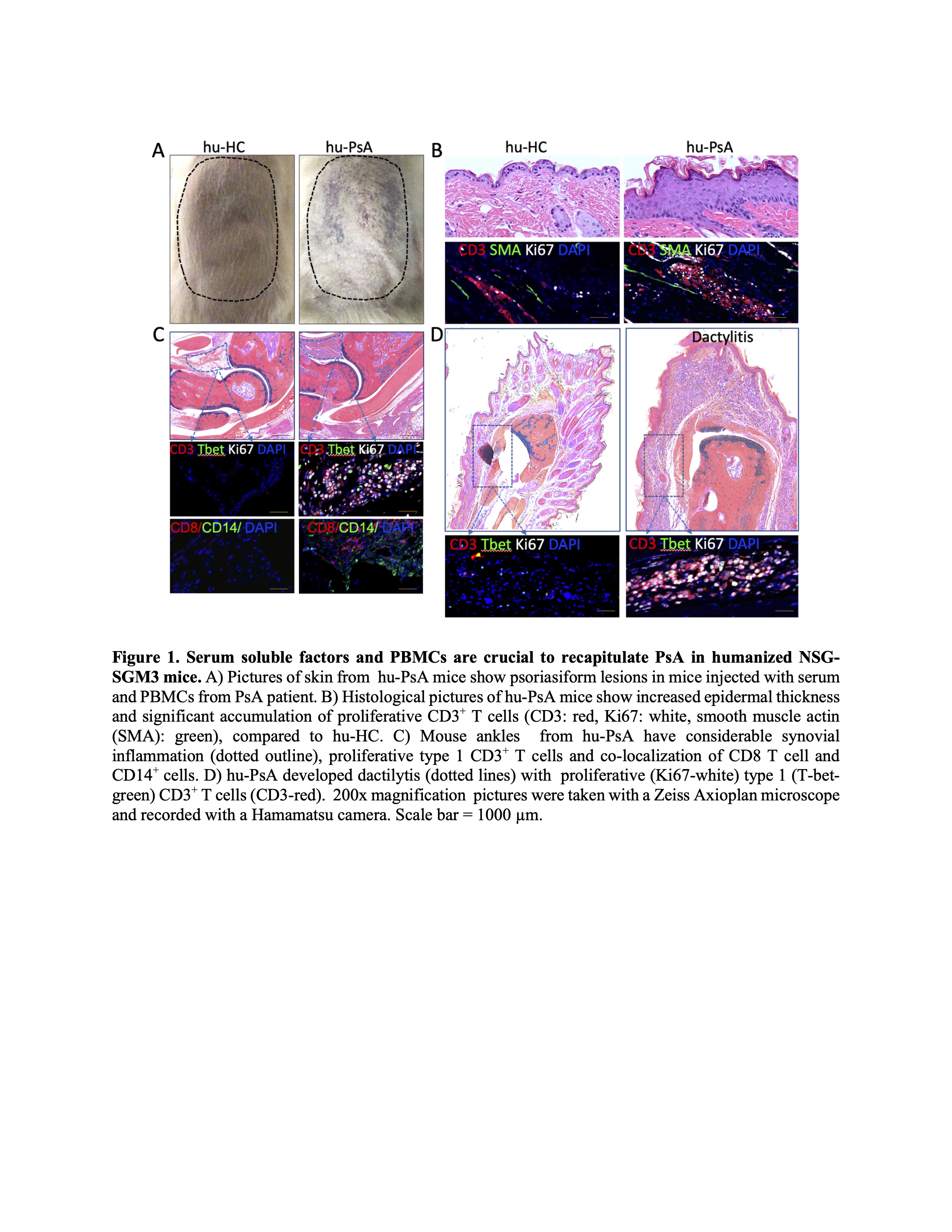
Results: Only NSG-SGM3 injected with serum and PBMCs from PsA patients developed psoriasiform plaques and arthritis (Figure 1). Mice injected with cells and sera from Ps patients showed psoriasiform lesions only. The disease phenotype observed in a patient (predominant dactylitis, erosive or non-erosive arthritis) was also observed in the mouse. Flow cytometry analysis showed an increase of effector memory percentages (hu-Ps; 37.79%, hu-PsA; 22% Vs Ps;16%, PsA 18%) with a decrease in naïve CD8 T cells in the blood of the mice (Ps; 8.91% vs. hu-Ps; 0.48%, hi-PsA; 2.6%). Hu-PsA mice had swollen ankles and developed psoriasiform lesions, dactylitis and pannus infiltration composed of CD8 T cells, macrophages and proliferating CD3 T cells. In contrast, hu-Ps mice had no swollen ankles or dactylitis. All hu-Ps and hu-PsA mice developed skin plaques with increased epidermal thickness (hu-HC 27.6 µm2 vs. hu-PsA 125 µm2, p = 0.025) and numerous proliferating CD3 T cells (hu-HC; 16 cell/ µm2 vs. hu-PsA 204 cells/µm2). GeoMx digital spatial profiler and next-generation sequencing readout showed enrichment of synovial CD8 T cells expressing IL32,GrzK, and GrzA in hu-PsA, but not in hu-HC or hu-Ps. Of note, transfer of serum and PBMCs from a PsA patient showed arthritis and psoriasiform lesion in this model that completely resolved in the patient and murine model following anti-TNF therapy.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that serum factors and CD8 T cells promote domain specific phenotypes. In addition, this model has potential to provide insight into patient specific therapeutics and underlying disease mechanisms.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garcia-Hernandez M, Rangel-Moreno J, Paine A, Bhattacharya S, Fox J, Meyer E, Isett B, Bao R, Bruno T, Ritchlin C. Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Subtypes Mediated by CD8 T Cells Are Phenocopied in a Novel Humanized Murine Model of Psoriasis and Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriatic-arthritis-disease-subtypes-mediated-by-cd8-t-cells-are-phenocopied-in-a-novel-humanized-murine-model-of-psoriasis-and-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/psoriatic-arthritis-disease-subtypes-mediated-by-cd8-t-cells-are-phenocopied-in-a-novel-humanized-murine-model-of-psoriasis-and-arthritis/