Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) related lung manifestations have a significantly impact the morbidity and mortality. Male gender and RF/ACPA positivity are known risk factors but so far, no specific biomarkers, which could predict the future development of lung involvement in RA have been identified. We aimed to explore if proteome signature in peripheral blood and sputum differs in RA patients with and without lung involvement and if possible, biomarkers for RA-related lung disease could be identified.
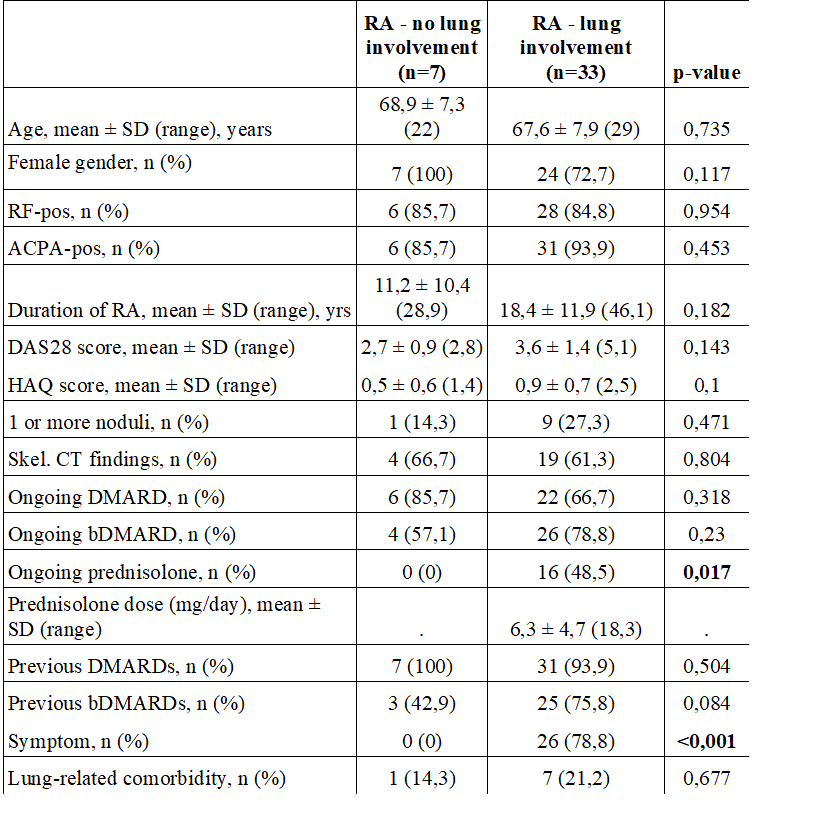
Methods: Peripheral blood and sputum samples were obtained from RA patients with (n=33, 73% female, mean age 68 years, 94% ACPA positive) and without (n=7,100% female, mean age 69 years, 86% ACPA positive) pulmonary manifestations in a single-centre explorative and cross-sectional study. A simultaneous proteome analysis targeting 92-plex inflammatory proteins in peripheral blood and in sputum was performed using proximity extension immunoassay (PEA) (Proteomics, Uppsala, Sweden) (ref). The associations between the levels of possible biomarkers and lung involvement were studied using logistic regression analysis.
Results: Significant differences between the groups were found for the levels of eight proteins in blood and for four proteins in sputum. Separate logistic regression models revealed significantly increased levels of 4 proteins in plasma: IL8, 4EBP1, SIRT2, and ST1A1 with an OR of having RA related lung involvement of 2,9-9,9. Additional 5 proteins (IL12B and FGF19 in plasma, and IL17A, CXCL5 and DNER in sputum) were associated with significantly lower risk of lung involvement (OR 0,1-0,3) (Figure).
Conclusion: The results from this study confirm the feasibility of proximity extension immunoassay (Proteomics) for proteome analysis in peripheral blood and sputum in RA patients with or without lung involvement. The difference in proteomics signature in blood and sputum indicate the analysis may be applied in the search for effective predictors of RA related lung diseases. Despite limitations we identified a number of promising biomarkers of lung involvement in RA in blood and sputum. Ref. Assarsson E, Lundberg M, Holmquist G, et al. Homogenous 96-plex PEA immunoassay exhibiting high sensitivity, specificity, and excellent scalability. PLoS One. 2014 Apr 22;9(4):e95192.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kapetanovic M, Olsson O, Einarsson J, Najibi M, Tufvesson E. Proteomic Signature in Peripheral Blood and Sputum in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with and Without Lung Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-signature-in-peripheral-blood-and-sputum-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-and-without-lung-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-signature-in-peripheral-blood-and-sputum-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-and-without-lung-involvement/