Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a rare heterogeneous group of autoimmune diseases characterized by immune-mediated muscle injury. We aimed to examine urine proteomic signatures and identify protein biomarkers for early diagnosis of IIM.
Methods: We analyzed the proteome of urine samples using a data-independent acquisition (DIA)-combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS) strategy from 132 patients with IIM and 97 healthy controls. All of the subjects were randomly distributed into training and validation data sets at a ratio of 2:1 to evaluate diagnostic performance.
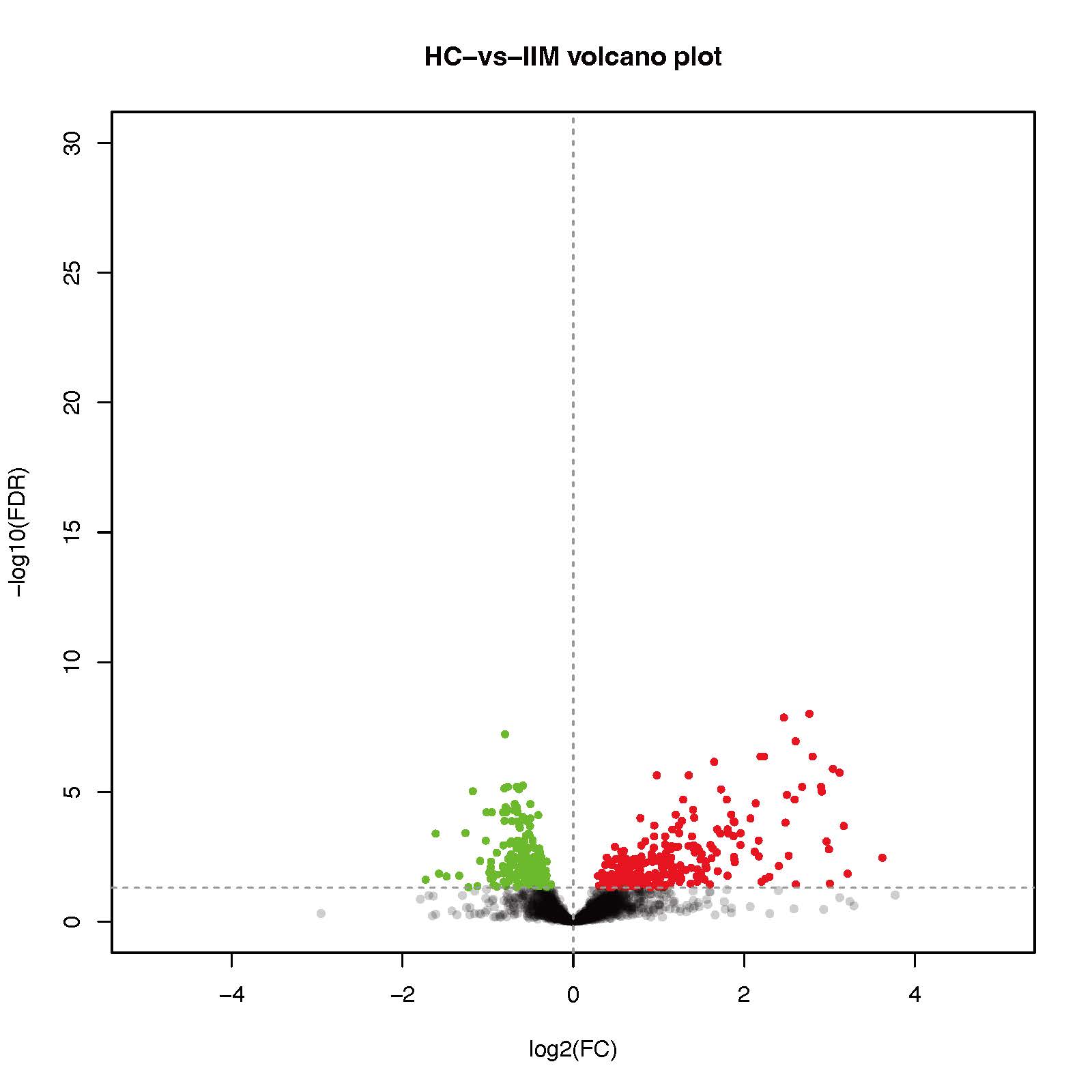
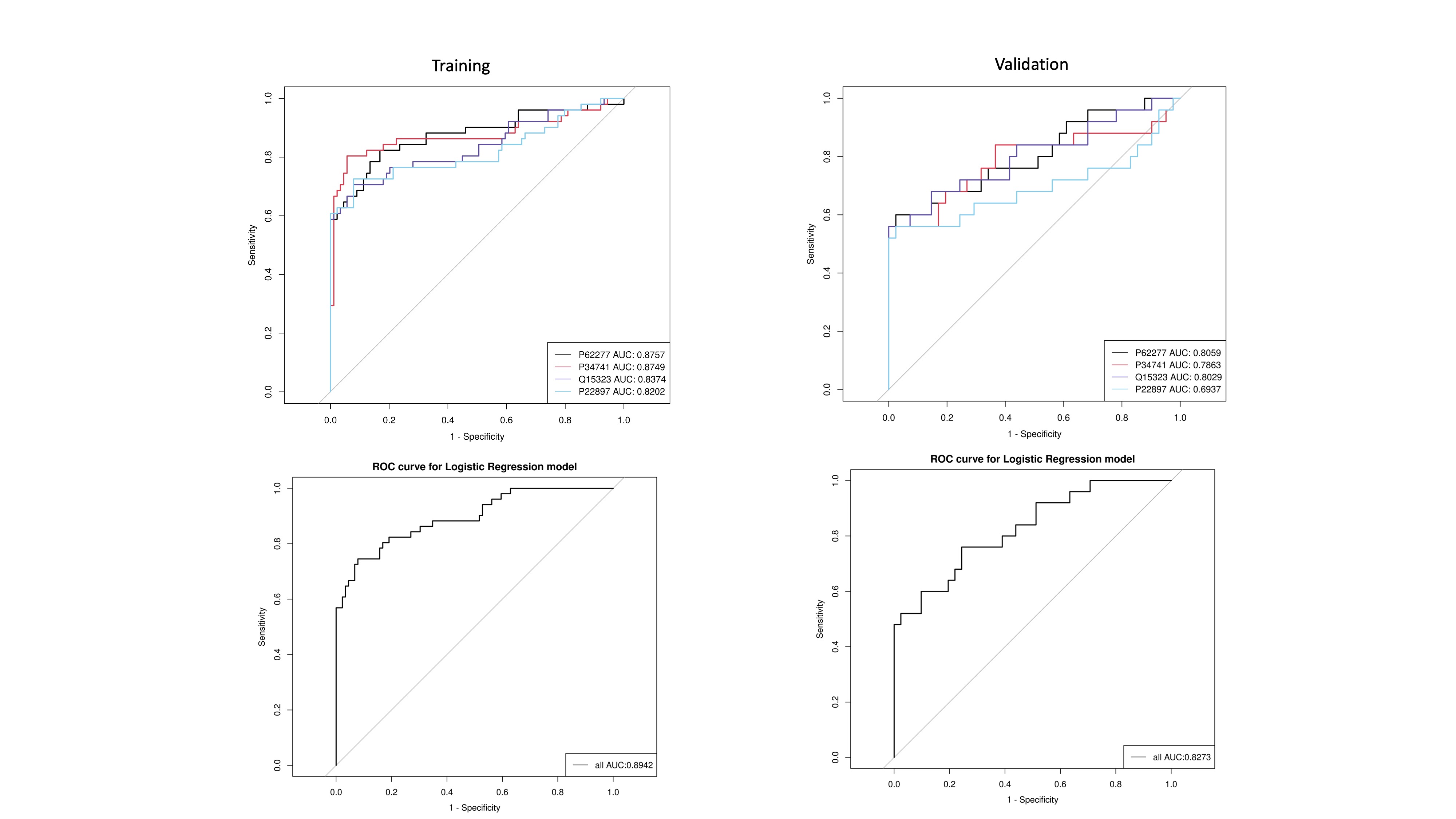
Results: Our data showed that 434 proteins were differentially expressed in the IIM group compared to the control, including 250 up-regulated and 184 down-regulated proteins (Figure 1). GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis indicated that differential urinary proteins are primally involved in cell adhesion molecules, oxidative phosphorylation, and complement and coagulation cascades. Ribosomal protein S13(RPS13), syndecan 2(SDC2), keratin 31(KRT31), and mannose receptor C-type 1(MRC1) were further identified as candidate biomarkers which could effectively distinguish IIM from control. The combined diagnostic efficiency of four indexes had satisfied discrimination in both the training (AUC=0.894) and validation sets (AUC=0.827) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This study revealed distinct urine proteomic profiles and a panel of proteins as novel urinary markers for non-invasive and simple screening of IIM, which may have translational significance and provide unique insights into the disease pathogenesis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yuan X, Guo Z, Shi J, Zhou S, Wu C, Zhao J, Xu D, Li M, Sun W, wang q, Zeng X. Proteomic Profiling of Urine Reveals Biomarker Candidates for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-profiling-of-urine-reveals-biomarker-candidates-for-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-profiling-of-urine-reveals-biomarker-candidates-for-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/