Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease that affects the spine and peripheral joints, and the exact etiology is still unknown. Diagnosis with urinary sample is a fascinate approach without patient’s pain due to its non-invasive nature. In this study, we performed proteomic analysis of AS urinary samples. Our aim is to discover novel diagnostic urinary biomarkers in the AS.
Methods: A total of 50 urine samples from 20 AS and each 10 controls [rheumatoid arthritis (RA), gout, healthy control (HC)] were collected. We collected AS and HC samples only from young males (< 50 years of age). Label-free quantitative proteomics were preformed and the resulting datasets were analyzed by MaxQuant (Ver.1.6.2.3) with Uniprot human database. Differentially expressed proteins were determined based on the fold change and p-value from LFQ(label-free quantitation) intensities log2(fold change >=1.5) and p-value< 0.05.
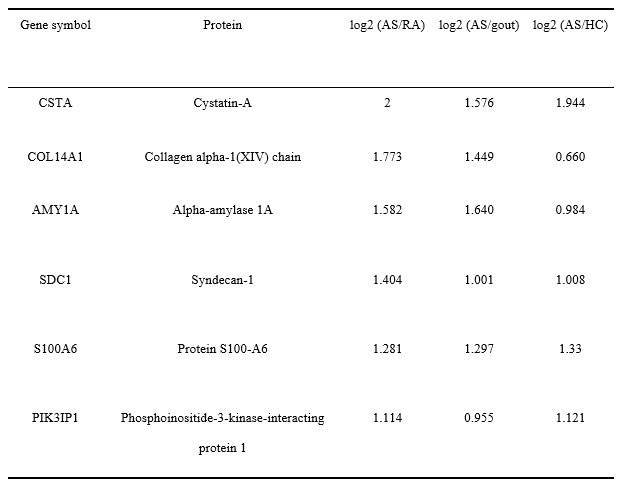
Results: From all urinary samples analyzed by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), we identified 1,975 proteins. Among them, we first found six proteins were differentially upregulated in AS patient group compared to the control group: cystatin-A(CSTA), collagen alpha-1 chain (COL14A1), alpha-amylase 1A(AMY1A), syndecan-1(SDC1), S100-A6(S100A6) and phosphoinositide-3-kinase-interacting protein 1(PIK3IP1) (Table 1). Interestingly, some of these proteins were previously observed as urinary biomarkers in other disease. For example, alpha-amylase 1A was highly expressed in the urine of prostate cancer, S100-A6 in the urine of upper gastrointestinal cancer, and PIK3IP1 in the urine of exertional rhabdomyolysis.
Conclusion: Diagnosing AS based on non-invasive manner still remains a challenge. We performed quantitative proteomic profiling of the respective urine samples from 4 diseases, i.e., AS, RA, gout and HC, and thereby identified six potential urinary biomarkers for AS. We will conduct molecular biological validation studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Kim J, kim S, kim J, son C. Proteomic Investigation to Identify Urinary Biomarker for Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-investigation-to-identify-urinary-biomarker-for-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/proteomic-investigation-to-identify-urinary-biomarker-for-ankylosing-spondylitis/