Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The role of concurrent hyperuricemia as a cardiovascular risk factor in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis (CIA) has yet to be studied. We aim to determine whether hyperuricemia might favor the occurrence of cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), or ankylosing spondylitis (AS) enrolled in the Spanish CARdiovascular in rheuMAtology (CARMA) prospective registry.
Methods: Post-hoc analysis of the CARMA project, a 10-year prospective study of the occurrence of cardiovascular events in patients with CIAs (RA, AS, or PsA) attending outpatient rheumatology clinics from 67 Spanish hospitals. The study spanned from 2010 to 2022, with a two-year recruitment, and included four subsequent visits at 2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 years. Blood tests were performed at baseline, including serum urate (SU) levels; hyperuricemia was defined as SU levels above 6.8 mg/dL. Both were the primary study explanatory variables. On the follow-up, the 10-year cumulative incidence of major cardiovascular events (MACE) was registered, in detail, angina, ischemic heart disease, stroke and transient attacks, renal failure due to arteriosclerotic causes, heart failure, and peripheral arterial disease.
We built a multiple logistic regression model, adjusted for age, sex, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, renal disease, and established cardiovascular disease. The results were reported as odds ratios (OR), 95% confidence intervals (95%CI), and P values. The results were later stratified upon the type of CIA.
Results: Out of 1552 participants, 174 (11.2%) were classified as hyperuricemic, 39 (6.9%) with RA, 78 (15.5%) with AS, and 57 (11.8%) with PsA. Mean SU levels (SD) of the entire cohort were 5.0 (2.3) mg/dL (4.6 (3.1), 5.3 (1.5), and 5.1 (2.0), in RA, AS, and PsA, respectively).
After ten years, 233 MACEs were recorded, 49 (21.0%) occurring in patients with hyperuricemia. By type of arthritis, 14 events (28.6%) occurred in the RA population with hyperuricemia, 23 (46.9%) in AS, and 12 (24.5%) in PsA.
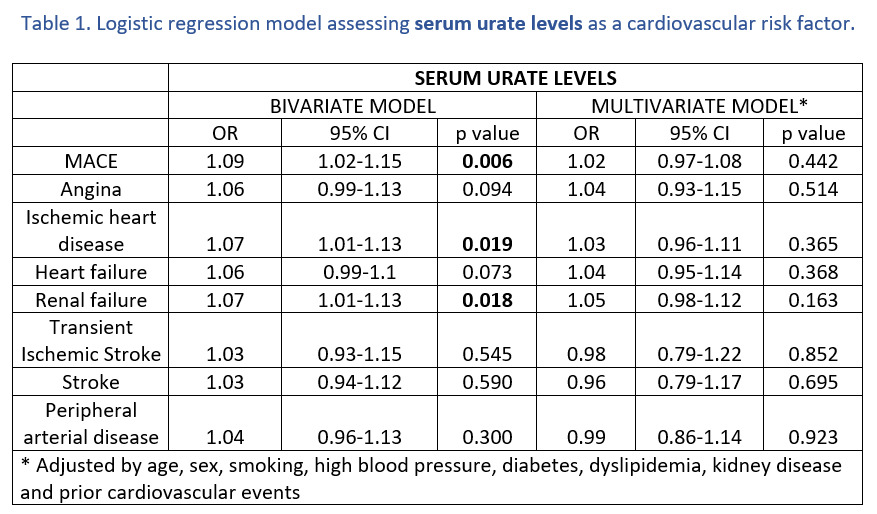
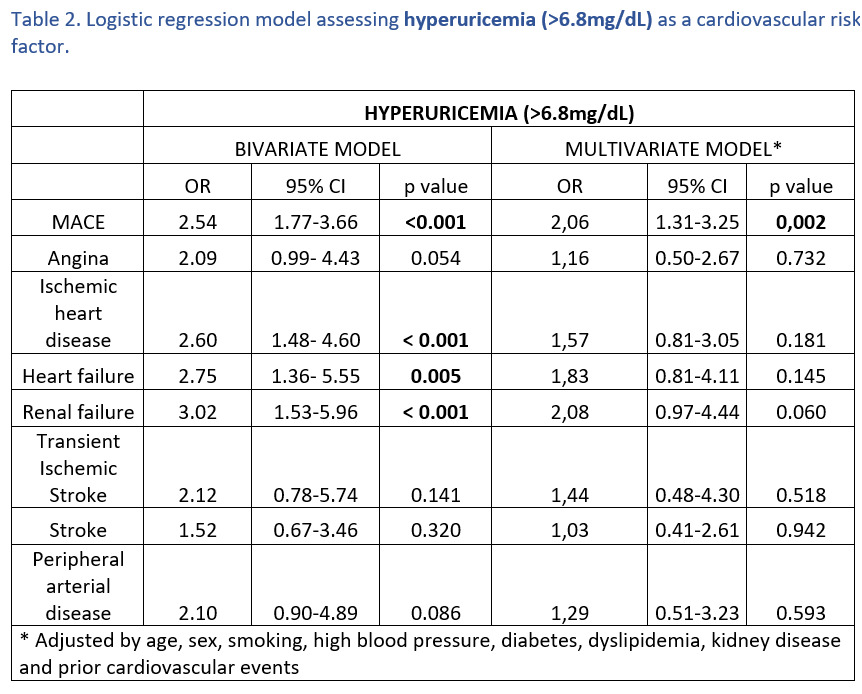
Tables 1 and 2 show the association analysis between baseline urate variables and the occurrence of MACEs and their subtypes. Hyperuricemia, as a dichotomous variable, was independently associated with a higher risk of MACEs. It was confirmed as an independent cardiovascular risk factor (OR 2.06), individually with a trend to a higher risk of vascular kidney disease. Despite being associated in the bivariate analyses, SU levels were not finally linked to the development of MACEs.
When stratified by the type of arthritis, the risk by hyperuricemia persisted increased only in patients with AS (OR 4.02, 95%CI 1.96-8.24), with no significant impact on RA (OR 1.85, 95%CI 0.76-4.49) nor PsA (OR 0.94, 95%CI 0.39-2.26).
Conclusion: In a 10-year prospective cohort, hyperuricemia at baseline and not continuous SU levels showed a prognostic impact on developing cardiovascular events in patients with CIAs, especially in those suffering from AS. Our findings reinforce the need to address comorbidities in this setting adequately.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Avilés A, Plaza Z, Sánchez-Alonso F, Castañeda S, fernandez-Gutierrez B, Díaz C, Font P, Martinez O, Giner E, Senabre J, Rueda A, Perez A, Sanchez G, Gonzalez C, García J, Llorca J, Gonzalez-Gay M, Andres M. Prognostic Value of Hyperuricemia in Developing Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Arthritis: A 10-Year Prospective Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prognostic-value-of-hyperuricemia-in-developing-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-chronic-inflammatory-arthritis-a-10-year-prospective-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prognostic-value-of-hyperuricemia-in-developing-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-chronic-inflammatory-arthritis-a-10-year-prospective-study/