Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at an increased risk of venous thromboembolism. Thus far, there have not been any comparative studies investigating the effects of initial antirheumatic treatments in (very) early RA patients. Therefore our objective was to assess the effects of different initial treatments on hemostatic parameters in patients with early RA.
Methods: NORD-STAR is an international, multicentre, open-label, assessor-blinded, phase 4 study where patients with newly diagnosed RA started methotrexate (MTX) and were randomised 1:1:1:1 to a) conventional treatment (either prednisolone tapered to 5mg/day, or sulfasalazine combined with hydroxychloroquine and intra-articular corticosteroids), b) certolizumab pegol, c) abatacept, d) tocilizumab. This study is a spin-off from the main NORD-STAR study extensively investigating hemostatic system in 24 per protocol consecutive Dutch participants at baseline, 12 weeks and 24 weeks after the start of the treatment. Statistical analysis was done using paired samples t-test in SPSS version 28.
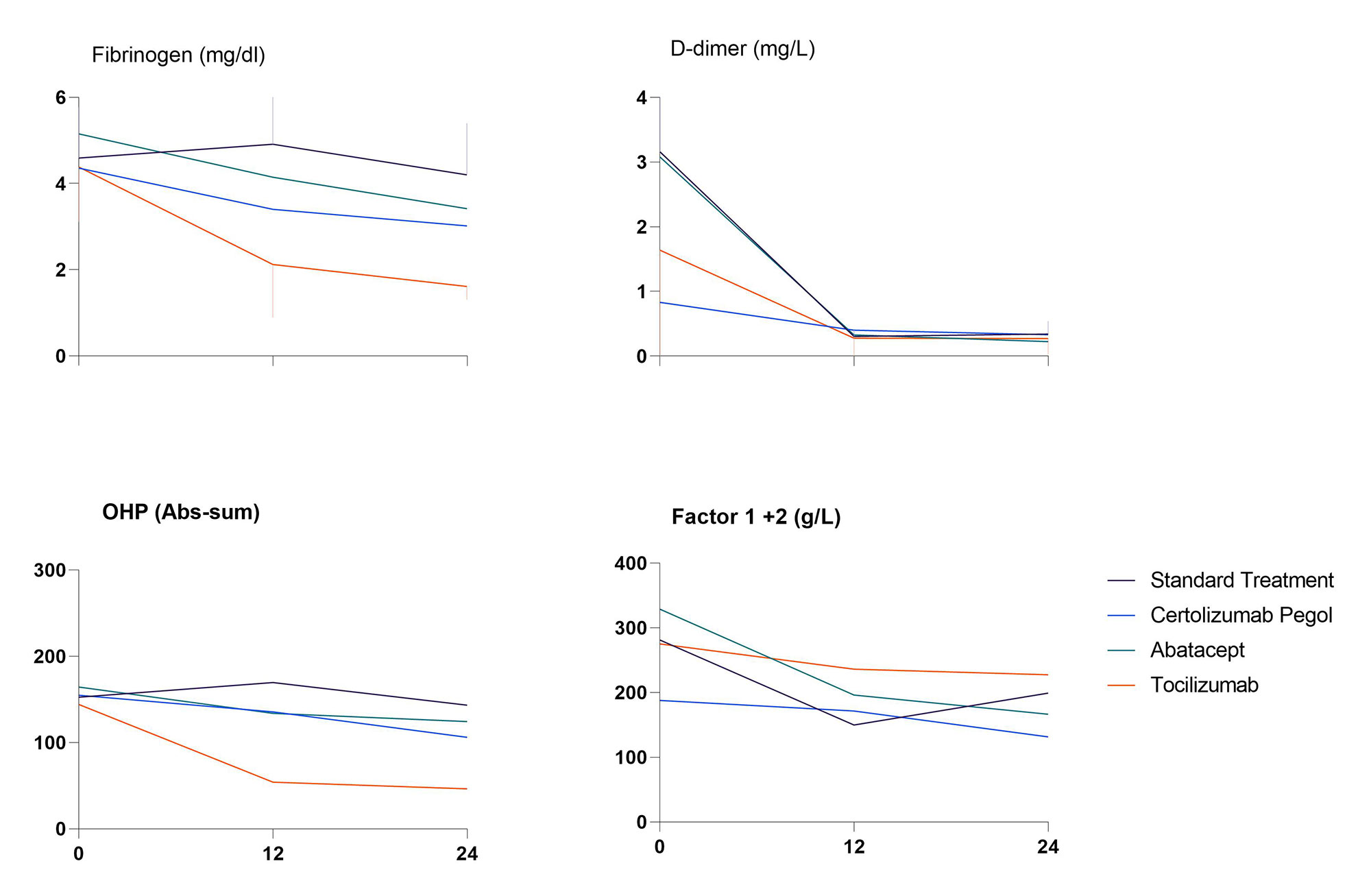
Results: The mean age of investigated patients was 51.8 (± 12.7) years and 58.3% were female. At baseline patients had an average DAS28 score of 4.6 (± 0.9) and had elevated levels of investigated coagulation biomarkers: Factor 1+2, fibrinogen, D-dimer and parameters of the two global hemostatic assays, i.e. endogenous thrombin potential (ETP) and overall hemostasis potential (OHP). These biomarkers decreased significantly at 12 and 24 weeks in patients in all groups (Table 1). Overall fibrinolytic potential (OFP) was decreased and clot lysis time (CLT) was prolonged at baseline, demonstrating impaired fibrinolytic activity in early RA. The reduction of coagulation parameters was significantly higher in biological treatment arms in comparison to the standard MTX treatment arm. In addition, tocilizumab was more effective compared to certolizumab and abatacept, (Figure 1), which was expected considering the direct inhibitory effect of this drug on the IL-6 synthesis and consequently the coagulation activation as well. After 24 weeks of treatment with methotrexate and tocilizumab, the average fibrinogen of patients was reduced by 63% vs 31% and 36% in the certolizumab and abatacept groups, respectively. The changes in DAS-28 and the changes in fibrinogen had a correlation of 0.385 which did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion: Our results indicate an enhanced coagulation and fibrinolytic impairment in newly diagnosed RA patients. Effective antirheumatic treatments reduce this hemostatic imbalance, with significantly more pronounced effects of biologic drugs compared to conventional (MTX+glucocorticoids) treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dijkshoorn B, Vedder D, Rudin A, Nordstrom D, Gudbjornsson B, Lend K, Uhlig T, Haavardsholm E, Grondal G, Hetland M, Heiberg M, Østergaard M, Horslev-Petersen K, Lampa J, van Vollenhoven R, antovic A, Nurmohamed M. Profound Anticoagulant Effects of Initial Antirheumatic Treatments in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients; A NORD-STAR Spin-off Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/profound-anticoagulant-effects-of-initial-antirheumatic-treatments-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-nord-star-spin-off-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/profound-anticoagulant-effects-of-initial-antirheumatic-treatments-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-nord-star-spin-off-study/