Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Predicting outcomes early in the disease course in patients (pts) with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is challenging, owing to heterogeneity of symptoms, varying disease severity, and the various outcome measures being mainly patient-reported, apart from radiographic progression. Using logistic regression analyses and machine learning (ML) techniques to predict the response to therapy may result in improved patient selection for optimized treatment regimens and setting the right expectations for individual patients1,2. We explored whether baseline (BL) disease characteristics could predict the response of secukinumab (SEC) therapy in AS pts, using logistic regression and ML analyses.
Methods: This post hoc analysis was performed on a pooled data of pts treated with SEC 300/150 mg from four phase 3 MEASURE studies (MEASURE 1–4)3-5 in AS (N=860). SEC 300 mg (n=113) group included 76 pts originally randomized to 300 mg and 37 pts initially randomized to placebo and then switched to 300 mg. In SEC 150 mg (n=747) group, 504 pts initially randomized to 150 mg and 243 pts initially randomized to placebo and then switched to 150 mg. A univariate logistic regression analysis was applied to search for potential BL predictors (P < 0.2) commonly collected in the MEASURE trials as demographics, disease activity parameters, prior medications etc. Various BL factors including sex, TNF status (treatment naïve vs inadequate responder), HLA-B27 status, current smoking status, concomitant NSAID use, BMI (< 30 kg/m2 vs ≥30 kg/m2), and hsCRP (elevated ≥5 mg/L vs normal < 5 mg/L) [binary variables], as well as age, MASES score, patient global assessment(PGA), and BASMI parameters [continuous variables] were assessed. Potential predictors identified in the univariate analyses were subsequently included in multivariate logistic regression models for further selection to assess their association with the response to SEC in AS pts on the following outcomes measures: ASAS40, ASDAS-Inactive Disease(ASDAS-ID), and BASDAI50. Additionally, ML Random Forest methods were applied and optimized using a grid search to find the best set of predictors.
Results: The BL factors with a significant (P < 0.05) association with the assessed outcomes of ASAS40, ASDAS-ID and BASDAI50 in multivariate logistic regression at Week 52 are presented in the Table. Age, hsCRP, occiput-to-wall distance score and MASES score were associated with ASAS40 and BASDAI50 responses. BMI, TNF status, occiput-to-wall distance score and PGA were associated with ASAS40 and ASDAS-ID responses. Additional modeling attempts using ML tree-based classification models showed similar results, without demonstrating sufficient predictive power.
Conclusion: The current analysis identified younger age, higher hsCRP, lower BMI, TNF naïve status, lower occiput-to-wall distance score and lower MASES score as factors associated with greater response that could potentially predict outcomes in AS pts treated with SEC.
References:
- Macfarlane, GJ et al. Rheumatology. 2020;0:1-10.
- Vastesaeger N, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:973–981.
- Baeten D, et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2534‒48.
- Pavelka K, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19:285.
- Kivitz A, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2018;5:447‒62.
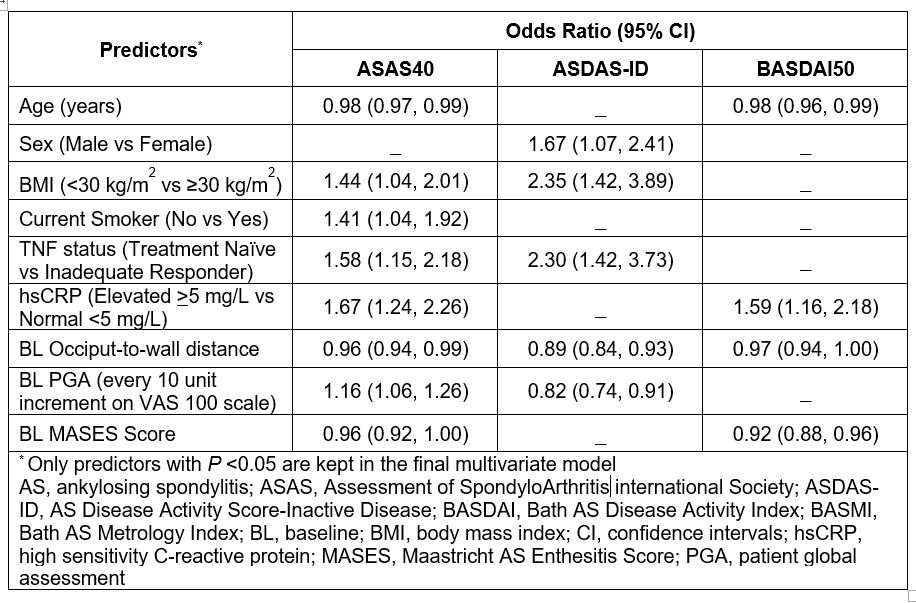 Table: Multivariate Logistic Regression analysis for baseline predictors of ASAS40, ASDAS-ID and BASDAI50 at Week 52: Significant Associations
Table: Multivariate Logistic Regression analysis for baseline predictors of ASAS40, ASDAS-ID and BASDAI50 at Week 52: Significant Associations
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Miceli-Richard C, Poddubnyy D, Deodhar A, Bao W, Parman C, Porter B, Pournara E. Predictors of Response in Secukinumab-treated Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: Logistic Regression and Machine Learning Analyses [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-response-in-secukinumab-treated-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-logistic-regression-and-machine-learning-analyses/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predictors-of-response-in-secukinumab-treated-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-logistic-regression-and-machine-learning-analyses/
