Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC) proved to be an effective treatment for patients suffering from ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in randomized clinical trials [1]. There is only limited knowledge on prediction of low disease activity (LDA) and treatment strategy in AS patients under SEC treatment in routine clinical care.
Using real-world data from the German non-interventional study AQUILA [2], the main objectives were (1) to predict LDA in individual AS patients treated with SEC through machine learning methods and (2) to identify the most important predictors and their influence on the prediction using explainable artificial intelligence (XAI).
Methods: Data of 580 AS patients from the AQUILA study were used. Thirty-two demographic, clinical and treatment parameters at baseline (BL) served as input data to develop prediction models. LDA was defined as Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index (BASDAI) ≤ 2.0 at week (w) 16 (+/- 6 w). Samples were divided into training (70%) and validation (30%) cohorts. Ten different prediction models were applied and compared. Model performance was measured using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) which represents the probability that a randomly selected patient with LDA will have higher prediction to achieve LDA than a patient with moderate/high disease activity. Additionally, sensitivity and specificity of the prediction model were computed and express the proportion of correctly identified patients who reach or don’t reach LDA at w16, respectively. Shapley XAI estimated importance and impact of each predictor based on how it affected the change in individual prediction [3].
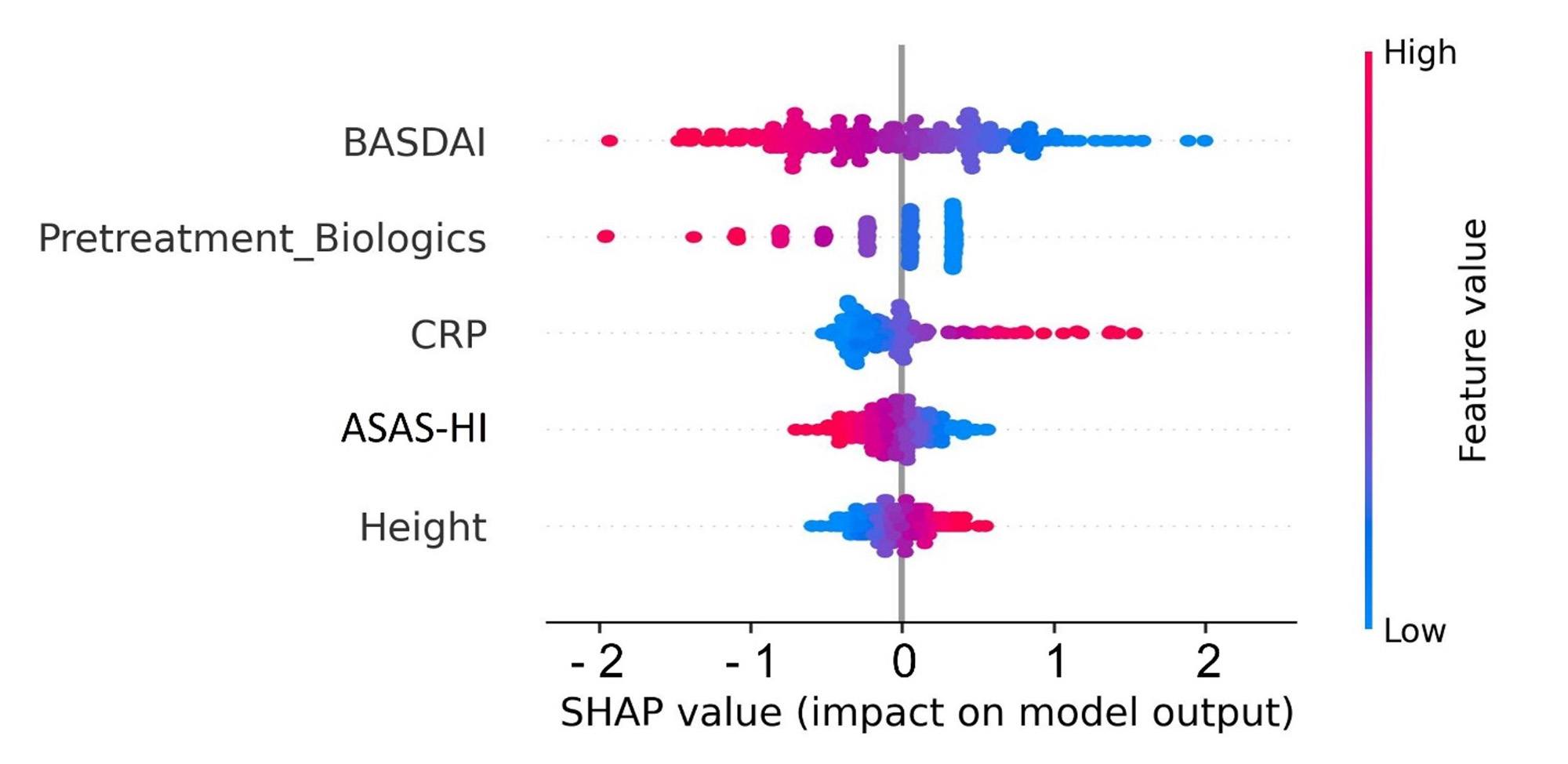
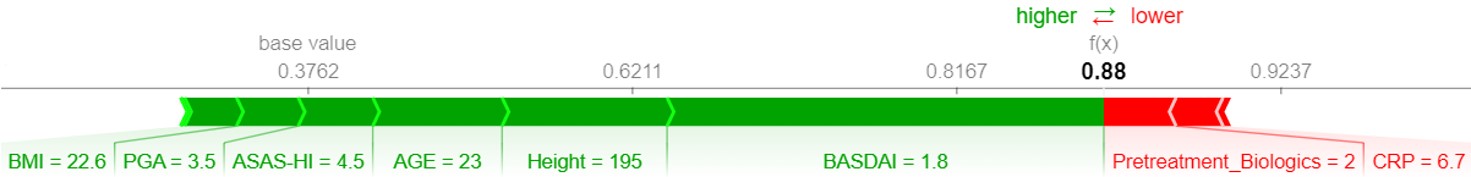
Results: The most influencing predictor was BASDAI at BL, followed by the number of pretreatments with biologics, C-reactive protein (CRP), assessment of spondyloarthritis international society health index (ASAS-HI) and patient height (Figure 1 A). AUROC of the best performing prediction model was 0.84. Sensitivity and specificity were 0.87 and 0.67, respectively. Applied XAI approach showed that the lower the BL values of BASDAI, ASAS-HI and number of pretreatments with biologics were, the higher the probability of reaching LDA at w16 was. The opposite was the case for BL values of CRP and body height (Figure 1 A). The approach also provided visual explanations of patient-individual predictions: Variables with values shown in green color increased probability of reaching LDA at w16, whereas red ones showed the opposite effect (Figure 1 B).
Conclusion: A promising prediction model accuracy of LDA in AS patients treated with SEC could be reached and validated. Identified main predictors at BL, such as BASDAI and number of pretreatments with biologics, and their direction of influence on the prediction of LDA mostly match the existing clinical knowledge [4]. The analysis showed that XAI can provide useful clinical insights into patient-individual predictions, potentially guiding AS treatment decisions in future.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vodencarevic A, Brandt-Juergens J, Peterlik D, Gmeiner B, Kiltz U. Prediction of Low Disease Activity in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Treated with Secukinumab in Real World – Data from a German Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-low-disease-activity-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-treated-with-secukinumab-in-real-world-data-from-a-german-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/prediction-of-low-disease-activity-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-treated-with-secukinumab-in-real-world-data-from-a-german-observational-study/