Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Increasing evidence exists that health outcomes are improved when people living with a chronic condition partner with their clinicians to coproduce their care based on their values, preferences, goals, and the best scientific evidence. This partnership may be aided by a data display tool, or dashboard, that presents longitudinal patient-reported outcomes (PROs), clinical data, and medications and is reviewed together to co-assess health status and co-decide next steps in the plan of care. This study assesses the utility of a dashboard to support coproduction of care for adults with RA.
Methods: We pilot tested the rheumatology dashboard with two rheumatologists and their adult RA patients at a rural academic health system. The dashboard resides within the Epic electronic health record and aggregates PROs and clinical data in real-time for review by the patient and clinician together (Figure 1). PRO data include the Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data (RAPID3); and, clinical data include the Clinical Disease Activity Index. RA-specific medications (Biologics, DMARDs, steroids, NSAIDs) map to the dashboard. Consecutive RA patients completed a a 19-item survey following their clinic visit to assess the impact of the dashboard on communication and shared decision making with their clinicians. Data were collected between January and March 2020. Feedback from clinicians was collected during biweekly meetings with the research team.
Results: Nineteen consecutive adult RA patients completed the post-visit survey. Mean (SD) age was 57 (12), 79% were female, 56% had a greater than high school education, and 39% had actively flaring RA (self-assessed). Three-quarters of patients (14 of 19) submitted pre-visit questionnaires (RAPID3) prior to their visit. Of those patients, 74% discussed the RAPID3 results with their clinician, and the clinician shared the dashboard in almost every visit that they discussed the RAPID3 (13 of 14). Two-thirds of patients (9 of 14) felt that the data and information in the dashboard was useful in discussions with their clinicians, helped them talk about what matters most, and helped them work with their clinician to make healthcare decisions. Half (7 of 14) felt that the dashboard helped them create a care plan that they could act on at home. Less than a third (4 of 14) thought that the data and information changed the content or focus of the discussion. Two thirds of patients (9 of 14) would recommend the dashboard to a friend or colleague with RA. Clinicians valued the ability to review and discuss with patients their disease activity over time and the impact of medications on their health status. Limitations included the small sample size as a result of decreased in-clinic visits during the study timeframe due to Covid-19.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that the rheumatology dashboard supports in-person review and discussion of PROs and clinical data and facilitates a meaningful dialogue and shared decision making between RA patients and their clinicians. Additional efforts are ongoing to spread the dashboard use to other clinicians in the department and to determine optimal use of the dashboard during telehealth visits.
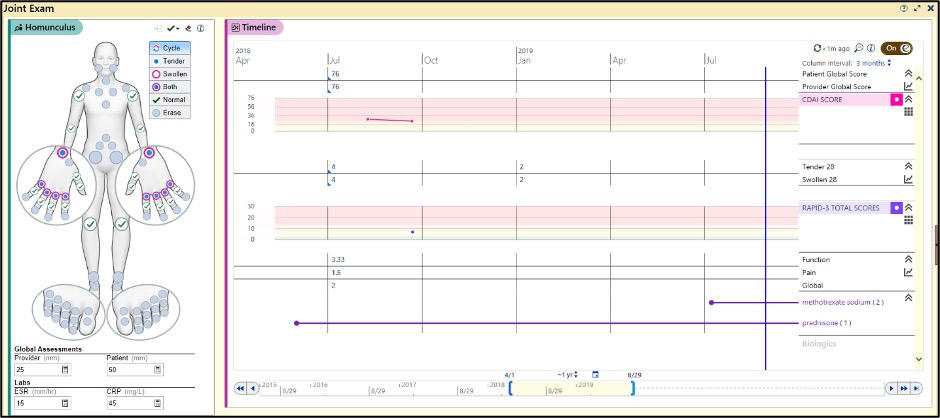 Figure 1. Rheumatology Dashboard (Epic Electronic Health Record) © 2020 Epic Systems Corporation. Used with Permission.
Figure 1. Rheumatology Dashboard (Epic Electronic Health Record) © 2020 Epic Systems Corporation. Used with Permission.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mathew S, Mecchella J, Johnson L, Van Citters A, Courtnay S, Marden J, Ahmad J, Eakin G, Nelson E, Kazi S, Pompa S. Pilot Testing Supports Utility of a Point-of-Care Dashboard to Enhance Patient and Clinician Partnerships in the Management of RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pilot-testing-supports-utility-of-a-point-of-care-dashboard-to-enhance-patient-and-clinician-partnerships-in-the-management-of-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pilot-testing-supports-utility-of-a-point-of-care-dashboard-to-enhance-patient-and-clinician-partnerships-in-the-management-of-ra/
