Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Tigulixostat is a potent and highly selective non-purine based xanthine oxidase inhibitor (XOi) being investigated for the management of hyperuricemia in patients with gout. Current gout treatment is not adequately managed for gout patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). To address this unmet need, PK/PD profile of multiple-dose of tigulixostat was investigated in a phase 1 open-label study in participants with various degrees of renal impairment (NCT04066712).
Methods: A total of 37 participants, both male and female, aged 18-80 years were enrolled in four groups based on their renal function according to eGFR calculated by the MDRD equation: normal renal function group (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m², n=13), mild renal impairment group (eGFR 60 to < 90 mL/min/1.73m², n=8), moderate renal impairment group (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min/1.73m², n=8), and severe renal impairment group (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m² and not on hemodialysis, n=8). Tigulixostat 200 mg was orally administered once daily for 7 days. Serial blood and urine samples were collected before dosing and up to 48 or 24 hours after the final dosing for PK/PD assessment. Safety assessments including adverse events, laboratory safety tests, vital signs, and electrocardiograms were collected throughout the study.
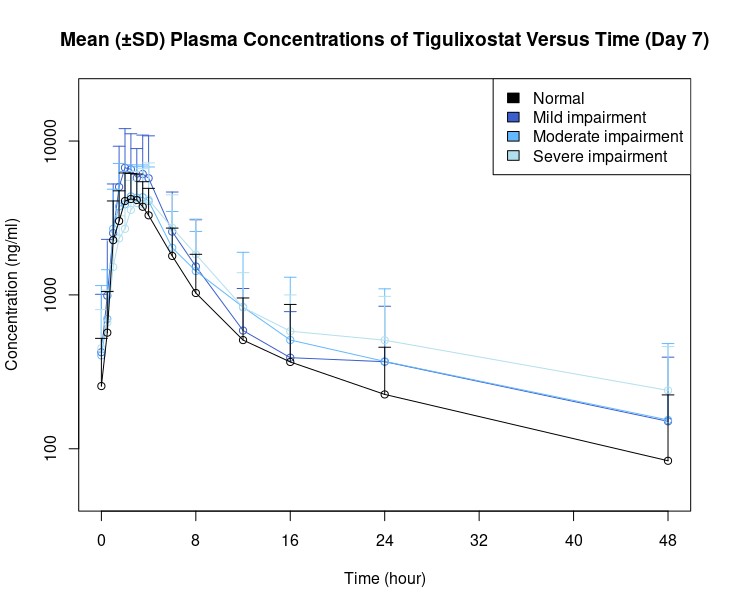
Results: Following repeated administration of 200 mg tigulixostat over 7 days, there was a tendency for slight elevation of Cmax,ss, AUC0-t and AUCtau in all renal impairment groups compared to the normal renal function group, except for a slight decrease in Cmax,ss observed in the severe renal impairment group. However, no clinically meaningful change in PK parameters were observed in participants with mild to severe renal impairment (Figure 1).
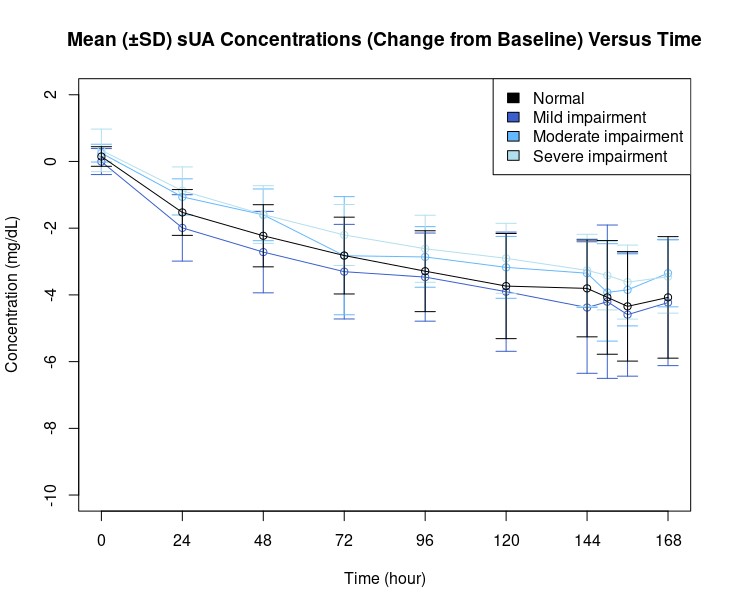
Tigulixostat demonstrated efficacy in reducing serum uric acid (sUA) levels across all renal impairment groups with similar geometric least square mean value of changes from baseline sUA levels (Cmean,24, Emax, and AUEC0-24) (Figure 2).
Overall, 3 TEAEs were reported after administration of tigulixostat. The majority of TEAEs were mild in severity and 1 moderate AE was reported from normal renal function group. There were no deaths or SAEs reported during the study, and no participants were discontinued from the study due to a TEAE.
Conclusion: Tigulixostat exposure and sUA reduction efficacy were not significantly different between participants with various degrees of renal impairment and those with normal renal function. Therefore, tigulixostat is not expected to require dose adjustment in patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment, and multiple doses of tigulixostat were found to be safe and generally well-tolerated in these participants.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kumar A, Hariri A, Lee Y, Lee M. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Tigulixostat in Participants with Mild, Moderate, and Severe Renal Impairment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-tigulixostat-in-participants-with-mild-moderate-and-severe-renal-impairment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-tigulixostat-in-participants-with-mild-moderate-and-severe-renal-impairment/