Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Nipocalimab is a fully human, immunoglobulin G (IgG) 1 monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the IgG-binding site of the neonatal crystallizable fragment receptor (FcRn), thereby lowering IgG levels. Sjögren’s disease (SjD) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease with a multitude of pathogenic mechanisms. IgG autoantibodies are one of the hallmarks of the disease that may contribute to the pathogenesis and active inflammation. In a phase 2 proof-of-concept study (DAHLIAS), nipocalimab demonstrated significant improvements in clinical endpoints in participants with SjD at Week 24. Here, we report on the pharmacodynamics of nipocalimab and associated disease biomarkers in the DAHLIAS study.
Methods: Adults with active, anti-Ro-positive SjD were eligible for the DAHLIAS study. Patients were randomized to nipocalimab 5 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg or placebo administered intravenously every 2 weeks through Week 22. Blood samples were collected from consenting study participants for the measurement of serum IgG levels, including total IgG and IgG subclasses, as well as IgM and IgA levels. Levels of serum anti-Ro60, -Ro52 and -La IgG were measured along with C3d-bound circulating immune complexes (C3d-CIC) and clinically relevant markers including rheumatoid factor (RF) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
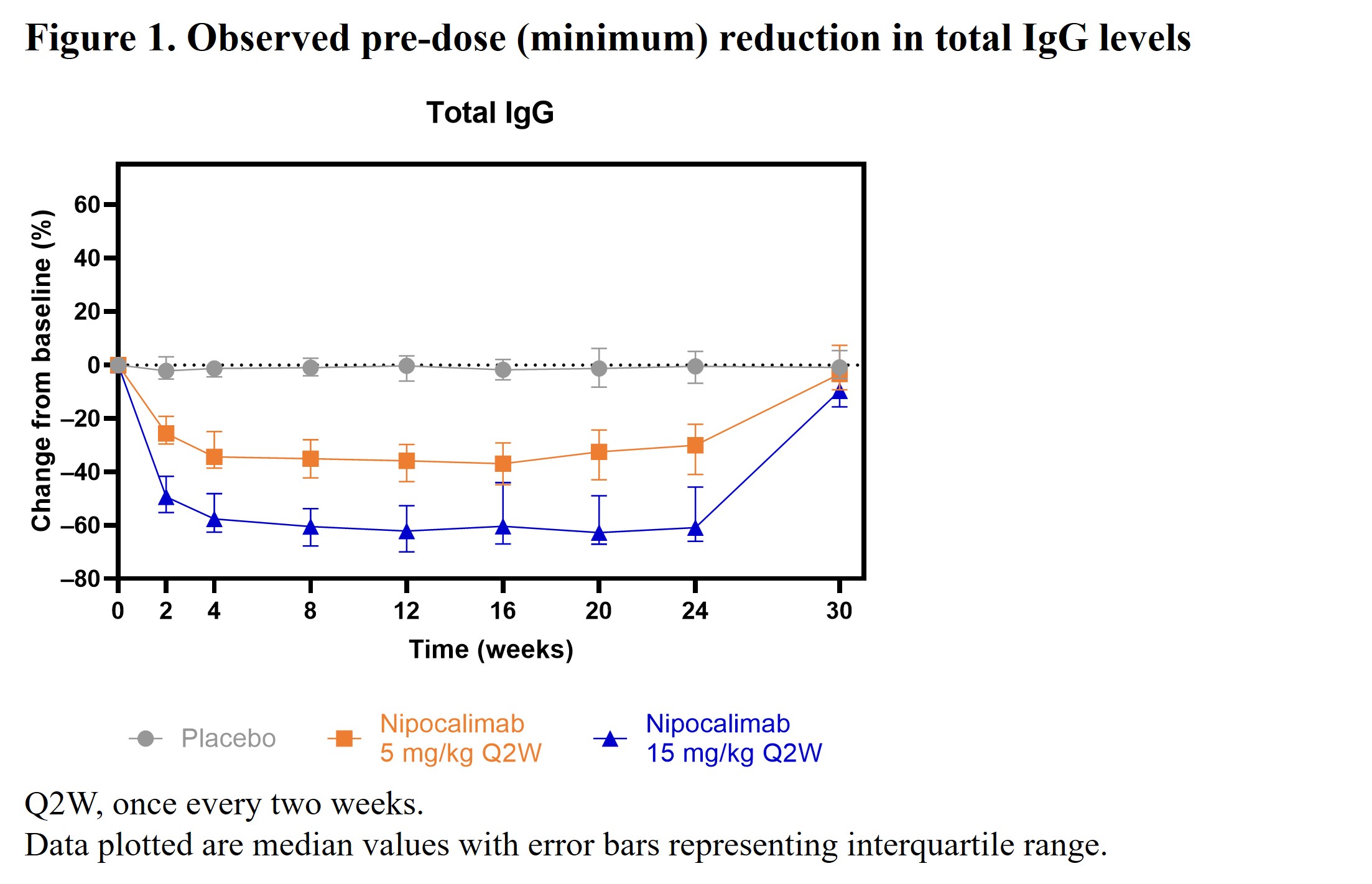
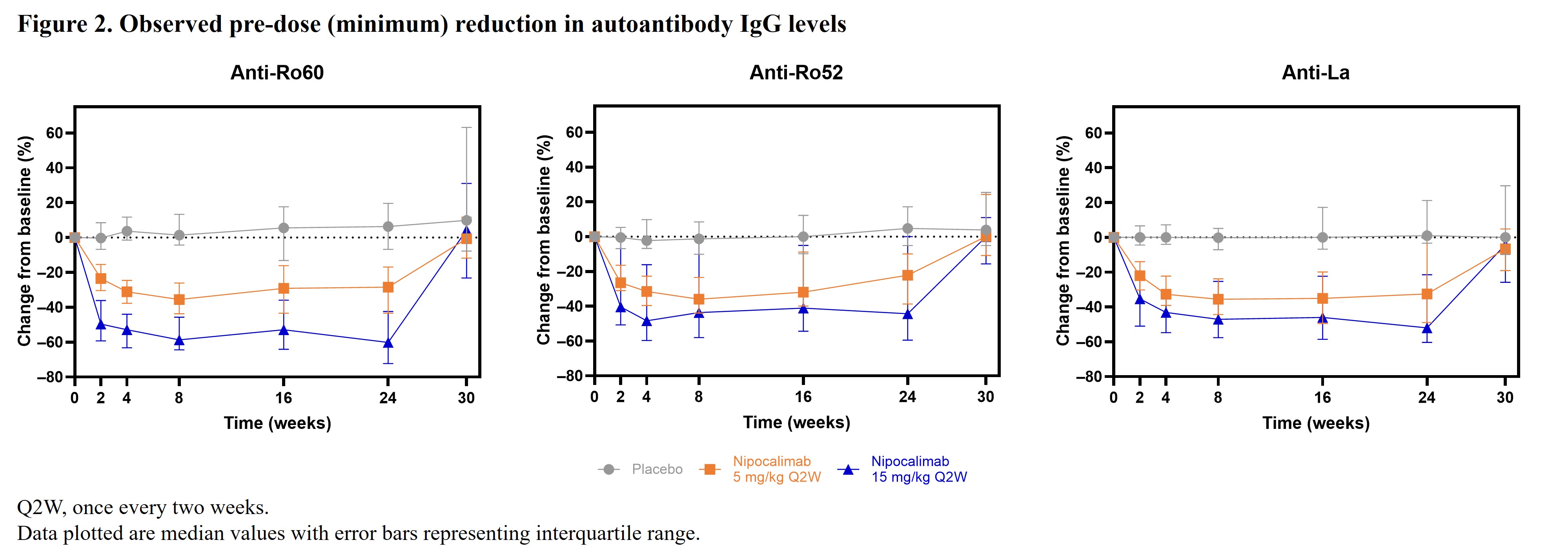
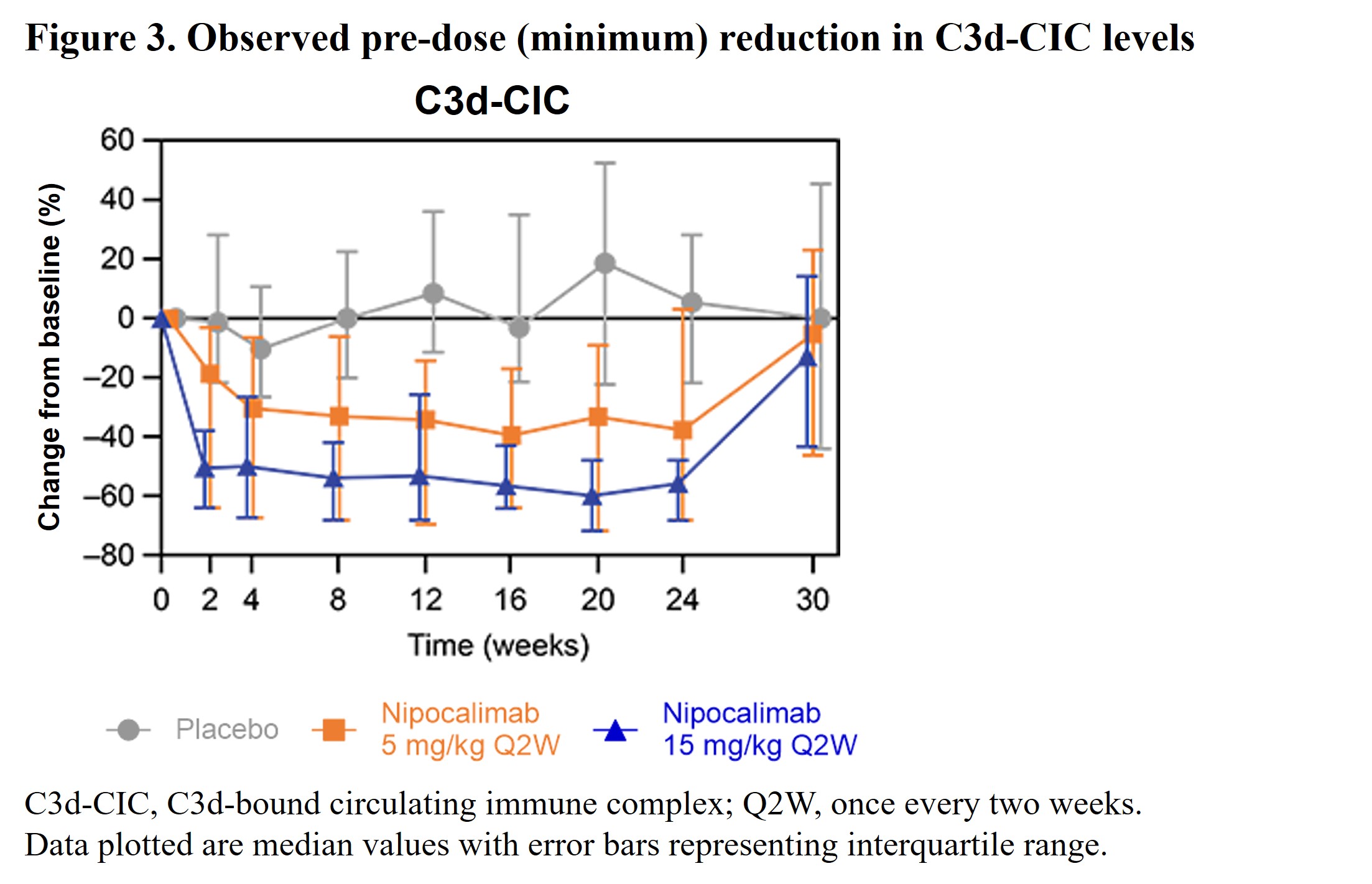
Results: A total of 163 patients (nipocalimab 5 mg/kg, n=53; nipocalimab 15 mg/kg, n=54; placebo, n=56) were enrolled in the study. Baseline biomarker levels were generally comparable between groups. Serum total IgG levels were reduced by nipocalimab from Weeks 2 through 24 and returned to baseline levels at Week 30 (Figure 1). At Week 24, there was an observed median pre-dose (minimum) reduction of 61% (interquartile range [IQR]: –66%, –46%) in the total IgG level in the nipocalimab 15 mg/kg group compared to a 0.5% (IQR: –7%, 5%) reduction in the placebo group. Decreases from baseline in all IgG subclasses were consistent with those observed for total IgG levels. Reductions in autoantibody (Figure 2), RF, and C3d-CIC (Figure 3) levels were also observed in the nipocalimab groups versus the placebo group, with trajectories similar to total IgG reduction. Nipocalimab 15 mg/kg was associated with clinically significant changes from baseline at Week 24 in RF and ESR levels versus placebo. Small changes from baseline in IgM and IgA levels were observed at Week 24. All biomarker changes mentioned above returned to near baseline by Week 30.
Conclusion: Nipocalimab substantially and reversibly reduced total IgG, IgG autoantibodies, and CICs, consistent with its mechanism of action, with clear differences by dose. Furthermore, substantial reductions in clinical biomarkers were observed, whereas IgM and IgA changes did not appear to be clinically significant. These findings suggest that autoantibodies and CICs may play an important role in SjD and support the hypothesis that reducing their levels through FcRn blockade may provide clinical benefits for patients with SjD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sivils K, Leonardo S, Li H, Ma K, Loza M, Hubbard J, Campbell K, Gao S. Pharmacodynamic Effects of Nipocalimab on Disease Biomarkers in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Active Sjögren’s Disease: Results from a Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blinded, Placebo-controlled Phase 2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacodynamic-effects-of-nipocalimab-on-disease-biomarkers-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-sjogrens-disease-results-from-a-multicenter-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-p/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacodynamic-effects-of-nipocalimab-on-disease-biomarkers-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-sjogrens-disease-results-from-a-multicenter-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-p/