Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Nipocalimab is a fully human, immunoglobulin G (IgG) 1 monoclonal antibody that blocks the neonatal crystallizable fragment receptor (FcRn), thereby lowering IgG levels. RA is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease with a multitude of pathogenic mechanisms. Anti-citrullinated protein autoantibody (ACPA) is one of the hallmark autoantibodies that may contribute to the pathogenesis and active inflammation in RA. In a phase 2a proof-of-concept study (IRIS-RA; NCT04991753), nipocalimab demonstrated numerically greater improvements in clinical endpoints (reported separately). Here, we report the initial pharmacodynamics of nipocalimab and associated disease biomarkers in the IRIS-RA study.
Methods: IRIS-RA was a phase 2a, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eligible adult patients had active, seropositive RA with prior inadequate response or intolerance to≥1 tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Nipocalimab or placebo was given intravenous every 2 weeks from Weeks 0-10. Blood samples were collected from consenting patients for the measurement of serum immunoglobulin levels, including total IgG and IgG subclasses. Levels of serum ACPA IgG were measured by an anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide 2 (CCP2) assay. Circulating immune complexes (CICs), complement activation markers, and serum inflammatory markers, including cytokines and C-reactive protein (CRP), were also measured. Associations between changes in biomarker levels and clinical responses at Week 12 were assessed.
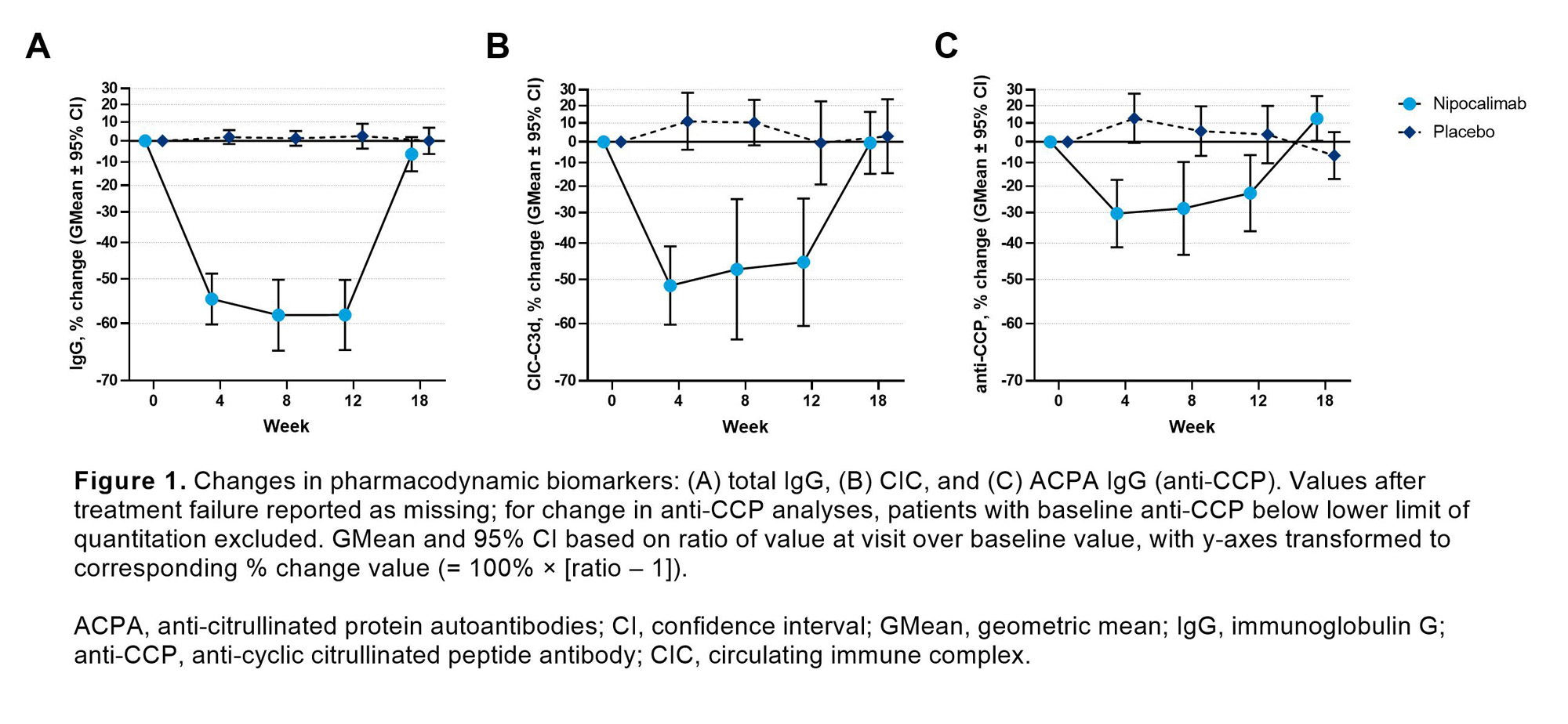
Results: A total of 53 patients (nipocalimab, n=33; placebo, n=20) were enrolled in the study. Baseline biomarker levels were generally comparable between groups. Serum total IgG levels were reduced by nipocalimab from Weeks 4 through 12 and returned to baseline levels at Week 18. At Week 12, there was a 58% reduction (geometric mean) in the total IgG level observed in the nipocalimab group compared to a 2.4% increase in the placebo group (Figure 1). Decreases from baseline in all IgG subclasses were consistent with those observed for total IgG levels. Significant reductions of total CIC and ACPA IgG levels were also observed in the nipocalimab group versus the placebo group (Figure 1), with a trajectory similar to total IgG reduction. Relative to the baseline, no changes in complement activation markers or serum inflammatory markers were observed in either group. In nipocalimab group, those who achieved remission in the Disease Activity Score 28-CRP at Week 12 had numerically greater reduction in ACPA compared to non-responders.
Conclusion: Nipocalimab significantly and reversibly reduced IgG, ACPA, and CICs, consistent with the expected mechanism of action, but did not impact complement activation markers or serum inflammatory markers. Reduction in ACPA by nipocalimab was associated with clinical remission. These findings support the observed clinical response and suggest that combination of nipocalimab and a therapy with an orthogonal mechanism may provide clinical benefits for patients with refractory RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Panchakshari R, Loza M, Huizinga T, Schett G, Ma K, Leu J, Liva S, Ibrahim F, Zhou B, Wang Q, Cella R, Karyekar C, Fei K, Cuff C, Gao S. Pharmacodynamic Effects of Nipocalimab in Patients with Moderate to Severe Active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Results from the Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blinded, Placebo-controlled Phase 2A IRIS-RA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacodynamic-effects-of-nipocalimab-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-results-from-the-multicenter-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-phase-2a-iris/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacodynamic-effects-of-nipocalimab-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-results-from-the-multicenter-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-phase-2a-iris/