Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Multiple lymphocyte subsets like T and B cells have been connected to joint infiltration and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Identification of leucocyte subsets that are dysregulated in arthritis development could provide insight into the aetiology of RA. Elderly-onset RA, EORA, which is defined as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) starting at > 60 years of age, has received less attention than young-onset RA. Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is another common rheumatic disease in the elderly. This study aimed to investigate the composition of the peripheral blood component. We hypothesize that by defining lymphocyte subsets we might be able to define elements of inflammation pathobiology in this population.
Methods: ARTIEL (Arthritis in the Elderly) is a collection cohort with newly diagnosed arthritis in patients older than 60 years, with blood samples collected at baseline (pre-treatment) and 12 months after treatment, along with physician and patient outcome measures through 12 months. They are compared with randomly control individuals of the same age and gender. A thorough clinical examination was conducted. Patients completed a health assessment questionnaire (HAQ). Disease activity score (DAS)28CRP was calculated. Absolute numbers of lymphocyte subsets in whole EDTA blood were determined with complete blood counts and flow cytometry fluorescent labelled antibodies for T and B cell subsets. Data processing and statistical analysis were performed in SPSS.
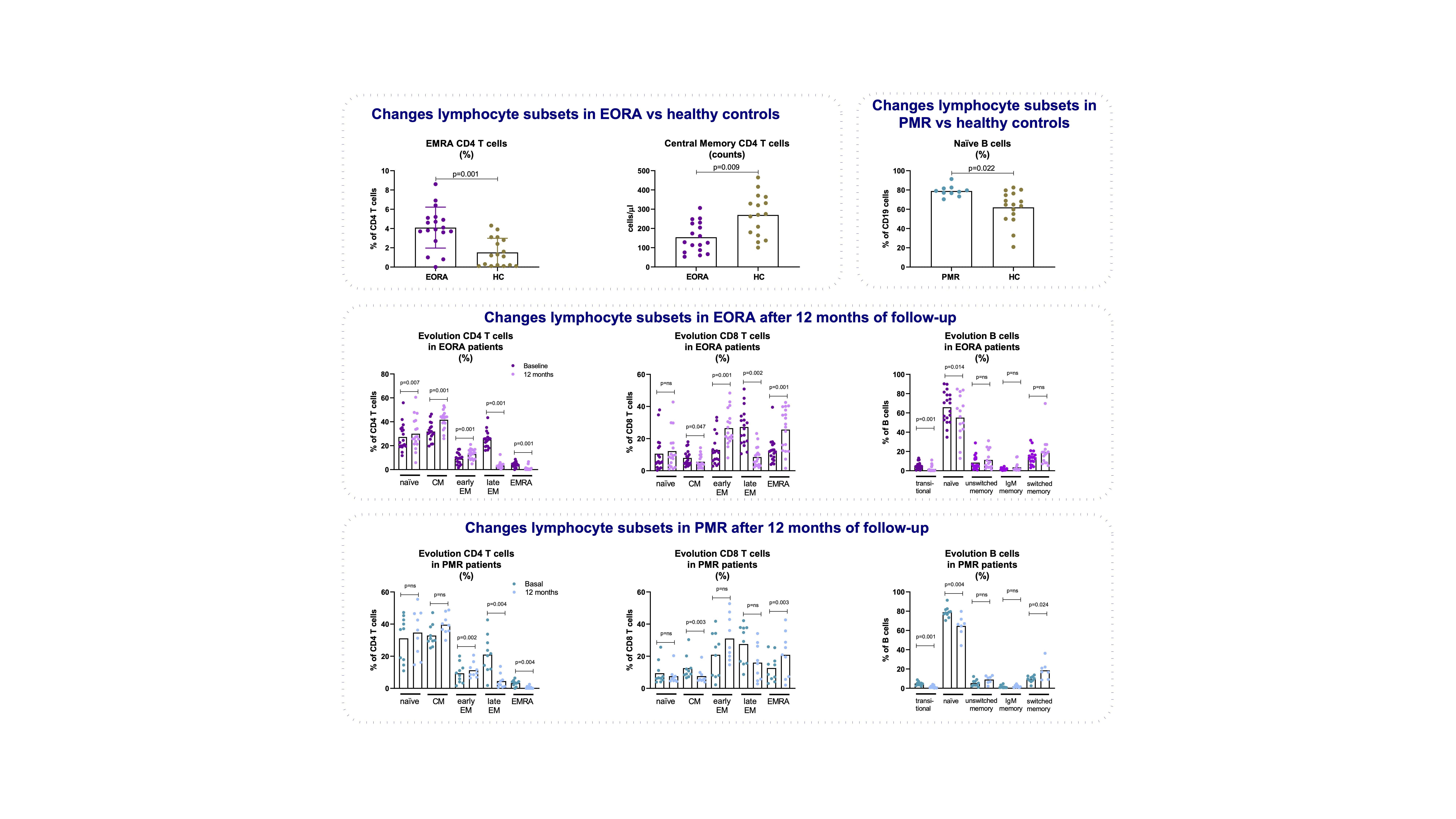
Results: 29 patients (average: 75.15, standard deviation (SD) 6.80) and 18 controls (C; average: 75.39, SD, 6.04) were analyzed. Of these, 19 were diagnosed with RA and 10 with PMR. At the start of the study, patients had a mean DAS28CRP of 5.72 (SD, 1.05), mean HAQ was 1.64 (SD, 0.73). In addition, 84% of the patients reported scapular pain, and 56% of the patients reported pelvic pain at baseline. Several lymphocyte subsets were different between populations. In patients with EORA, significant increase in percentage and numbers of CD4+ effector subset (EMRA; defined as CD3+CD4+CD45RA+CCR7–CD27–) and significantly decrease in numbers of CD4+ central memory (CM; defined as CD3+CD4+CD45RA–CCR7+CD27+). In patients with PMR, a trend towards different B cell subsets were observed with an increase in percentage of naïve B cells (CD19+CD27–IgM+IgD+) was observed compared to HC and a significant increase in percentage and numbers of CD8 + CM (CD3+CD8+CD45RA+CCR7–CD27–). Longitudinal analysis showed that several B and T cell subsets were significantly different at 12 months in both EORA and PMR patients (see figure) suggesting an effect of therapy in the lymphocyte subsets.
Conclusion: This study revealed that patients with EORA and PMR demonstrate a change in cellular immune parameters apparent in the periphery. More studies are needed to show whether these subsets before and after treatment might be related to clinical and therapeutic outcomes in these populations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Teniente-Serra A, Mateo L, Prior A, Guma M, Martinez-Caceres E, Martinez-Morillo M. Peripheral Blood T and B Lymphocyte Subsets in Arthritis in the Elderly [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-t-and-b-lymphocyte-subsets-in-arthritis-in-the-elderly/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/peripheral-blood-t-and-b-lymphocyte-subsets-in-arthritis-in-the-elderly/