Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: T peripheral helper (Tph) cells promote B cell maturation and the generation of antibodies in the inflamed joints of adults with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and children withanti-nuclear antibody(ANA) positive oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (oligo JIA). We recently identified a population of T cells in the synovial fluid (SF) of patients with oligo JIA that express both regulatory T (Treg) cell (FOXP3, CTLA4, GITR) and B cell-helper T cell factors (PD1, ICOS, CXCL13), which we term T peripheral regulatory (Tpr cells). We sought to determine if Tpr cells are a suppressive T cell population that may have the capacity to restrain Tph cell-B cell interactions in peripheral tissues.
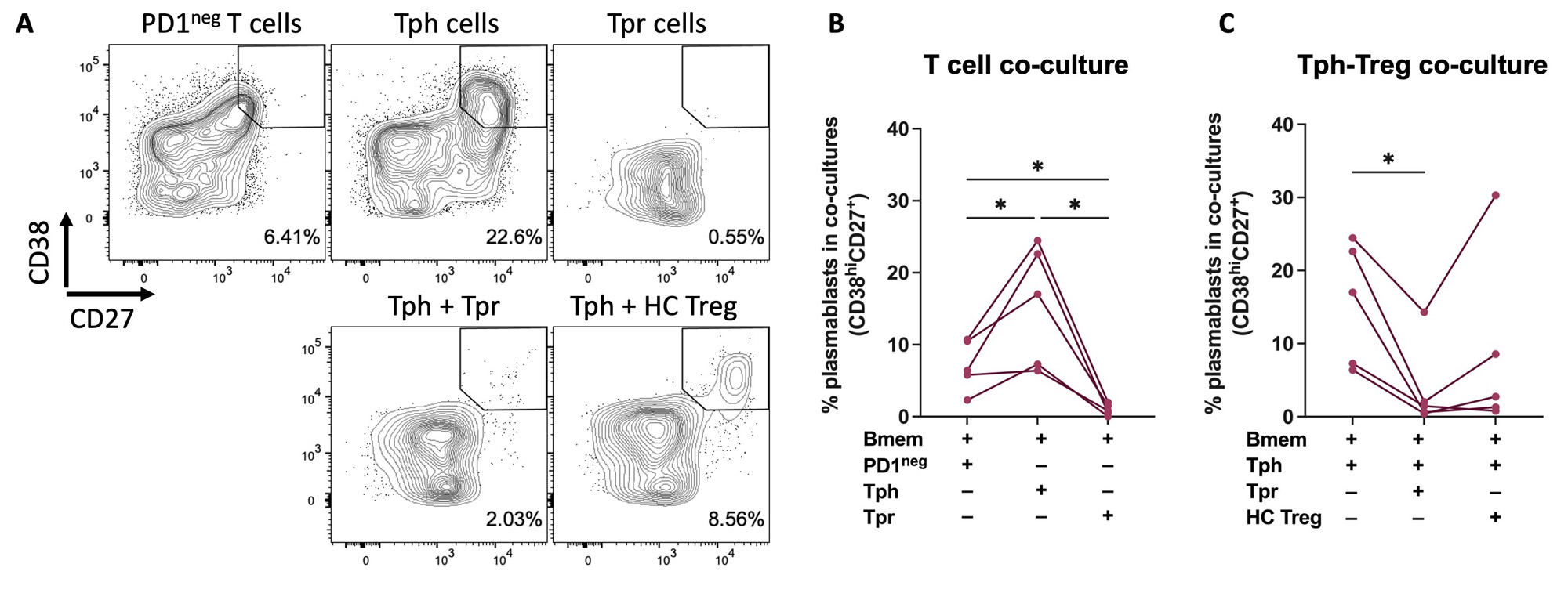
Methods: Children with oligo or the closely related seronegative polyarticular JIA (ILAR criteria) provided SF samples. Healthy adults provided peripheral blood (PB) samples. PB mononuclear cells (MCs) and SFMCs were isolated by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation. Cells were stained for surface markers and then fixed and permeabilized for FOXP3 staining. Flow cytometry was used to measure FOXP3 expression in various T cell populations. For T cell-B cell co-cultures, memory B cells (Bmem; CD19+CD27+IgD–) were sorted from leukocollars obtained from controls. Bmem were co-cultured with various effector T cell populations from ANA+JIA patients at a ratio of 10:1 for 5 days in the presence of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). These T cell-B cell co-cultures were also performed with the addition of PB Treg cells from controls (CD4+CD25+CD127lo) or autologous Tpr cells from SF (CD4+ CD25+CD127loPD1intCXCR5–) at a ratio of 1:1. After 5 days of incubation, cells were harvested and stained to determine the frequency of plasmablasts (CD19+CD27+CD38hi) in the co-cultures. Study subjects with co-cultures of Tph cells and Bmem cells with less than 10% of cells in the lymphocyte gate and/or without visible lymphocyte proliferation in the FSC/SSC gate were excluded. GraphPad Prism was used for statistical analysis.
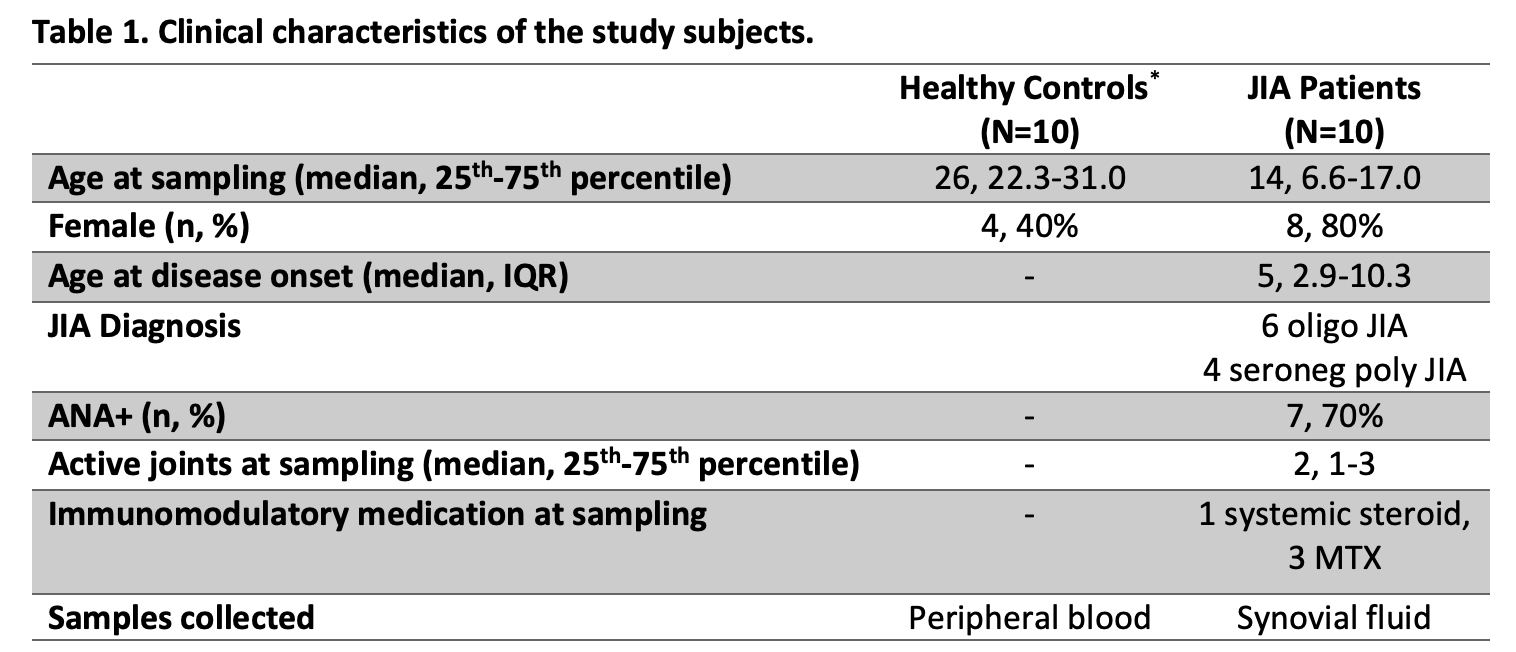
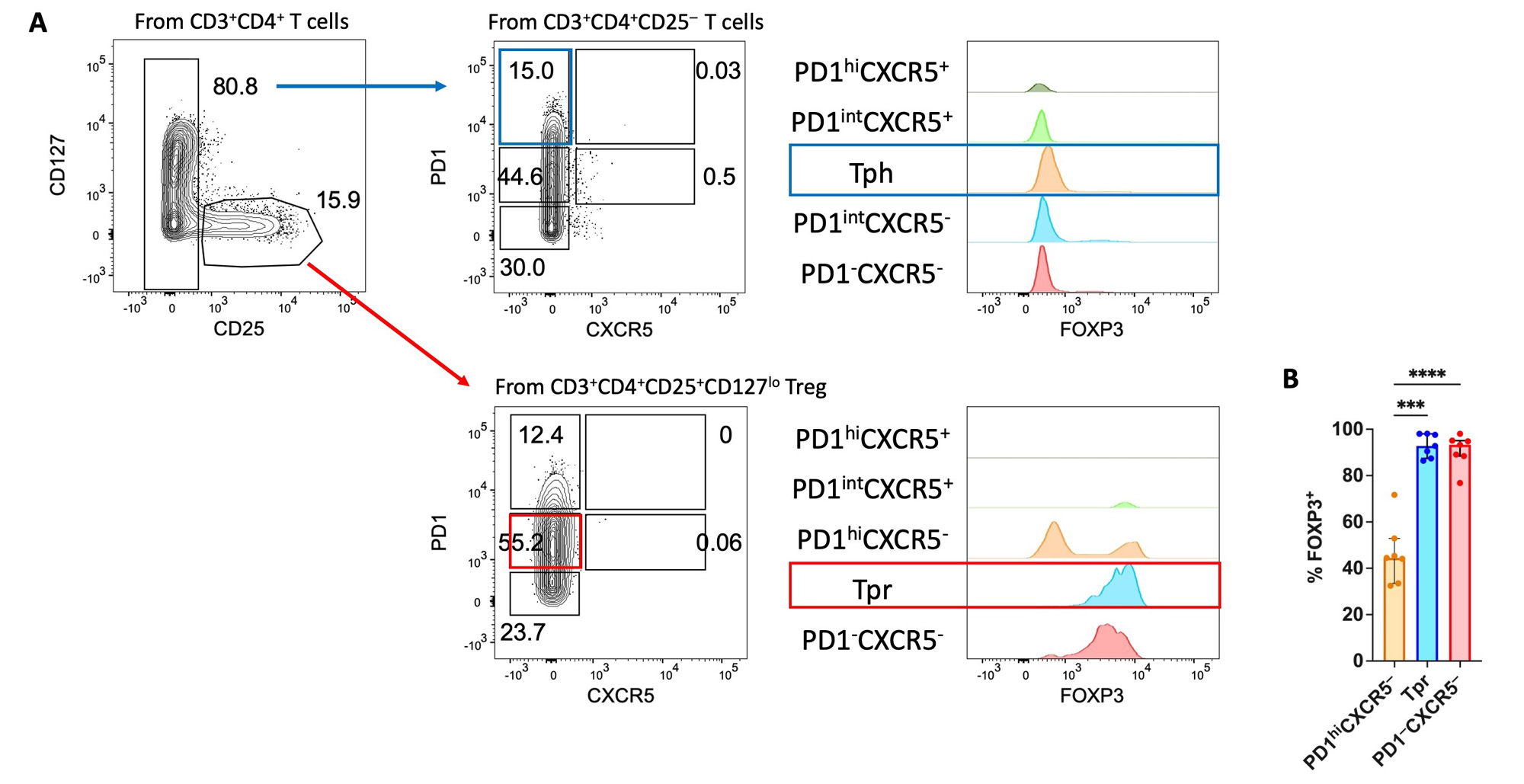
Results: 10 JIA and 10 healthy controls were studied (Table 1). FOXP3, the Treg lineage defining transcription factor, was measured in PD1+ T cells from JIA SF by flow cytometry (Figure 1). FOXP3 levels were highest in CD4+CD25+CD127lo Treg cells with intermediate PD1 (PD1int) expression. Thus, we identified cell surface markers to isolate viable Tpr cells (CD4+CD25+CD127loPD1intCXCR5–) for functional assays. To evaluate T cell-B cell interactions, we used our co-culture system to study SF samples from 5 ANA+ JIA patients (Figure 2). As expected, co-culture of Bmem with Tph cells (CD4+CD25–PD1hiCXCR5–) from JIA SF induced the production of plasmablasts. In contrast, co-culture of Bmem with Tpr cells resulted in essentially no plasmablast differentiation. Once Tpr cells were added to co-cultures of Tph and Bmem cells, they significantly reduced the frequency of plasmablasts while bulk Treg cells from control blood did not.
Conclusion: We identified a novel Treg population present in inflamed joints that expresses B cell-help factors and restrains Tph cell-B cell interactions. Further work is needed to define the effector functions of Tpr cells and determine their role in regulating inflammation in tissues.
JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; oligo, oligoarticular; seroneg, seronegative; poly, polyarticular; ANA, anti-nuclear antibody; MTX, methotrexate; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; IRB, institutional review board.
A) Representative dot plots showing flow cytometry gating strategy and Tph/Tpr cells from JIA SF. Histogram overlay showing % of maximum FOXP3 expression in each T cell subset. B) Summary data showing % FOXP3+ cells in each T cell subset, gated on CD4+CD25+CD127lo cells (n=7). SF Tph: CD4+CD25-PD1hiCXCR5-; SF Tpr: CD4+CD25+CD127loPD1intCXCR5-. Statistical analysis: paired, one-way ANOVA. ***, P≤0.001; ****, P≤0.0001.
JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; SF, synovial fluid.
A) Representative flow cytometry dot plots showing % plasmablast (CD38hiCD27+) of alive CD19+ B cells after co-culture of the indicated population(s) of T cells with Bmem cells from the peripheral blood (PB) of a healthy donor. B) Summary data showing % plasmablast in co-culture conditions of Bmem cells with the indicated single population of T cells and C) co-culture conditions of Bmem cells plus Tph cells with autologous Tpr cells or bulk Treg from PB of a healthy donor. SF from 5 ANA+ JIA patients. JIA SF Tph: CD4+CD25-PD1hiCXCR5-; JIA SF Tpr: CD4+CD25+CD127loPD1intCXCR5-; HC Treg (PB): CD4+CD25+CD127lo. Statistical analysis: paired, one-way ANOVA. *, P≤0.05.
SF, synovial fluid; ANA, anti-nuclear antibody; JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; HC, healthy control.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lam K, Julé A, Harris C, Taylor M, Hahn M, Ohlms L, Lee P, Chang M, Chatila T, Nigrovic P, Henderson L. PD1-Expressing Regulatory T Cells Found in Inflamed Joints Suppress Tph Cell-B Cell Interactions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pd1-expressing-regulatory-t-cells-found-in-inflamed-joints-suppress-tph-cell-b-cell-interactions/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pd1-expressing-regulatory-t-cells-found-in-inflamed-joints-suppress-tph-cell-b-cell-interactions/