Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is adopted to evaluate the degree of disease activity and the inflammatory response in AS patients. ASDAS score < = 1.3 represents inactive disease status and achievement of T2T. SSDM is a mobile application for disease management.
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the patterns of T2T and related influential factors among AS patients after applying SSDM in the real world.
Methods: AS Patients were trained to master SSDM by healthcare professionals (HCPs) and to conduct ASDAS self-assessments. Patients were also required for repeating self-assessments after leaving the hospital. After entry by patients, data can be synchronized to the SSDM terminal of authorized rheumatologists. Based on these data, the patients can apply for consultation to their physicians and rheumatologists can provide medical advices to their patients.
Results: From Jan 2015 to Jan 2020, 17,870 AS patients enrolled in SSDM with the mean age of 34.62±10.98 years old and the median disease duration of 3.58 years. Among them, 1,127 AS patients from 150 hospitals were followed up for more than 6 months through SSDM. The results at baseline and in final follow up were summarized in Table 1.
The rate of T2T achievers were 27.95% (315/1,127) at baseline, and improved significantly to 41.08% (463/1,127) after 6 months follow up, p< 0.01. Among T2T achievers at baseline, 65.40% (206/315) maintained T2T, 34.60% (109/315) relapsed. Of patients who didn’t achieve T2T at baseline, only 31.65% (257/812) achieved T2T after 6 months follow up.
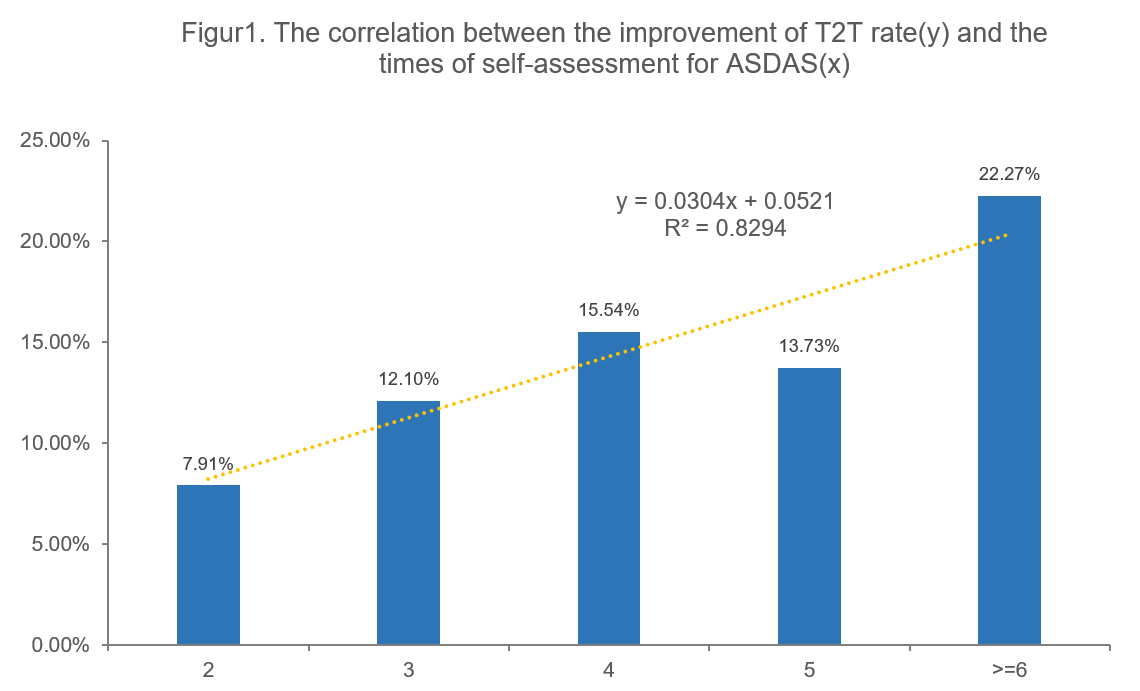
The impact of the online interaction between patients and physicians and the frequency of self-assessment for ASDAS on T2T has been analyzed. Compared with 544 patients who didn’t interact online with their physicians and self-assessed less than 3times, 104 patients with online interaction and monthly assessments achieved significant higher improvement rate of T2T (9.19% vs 23.08%, p< 0.01). The more frequent of the self-assessments being performed by patients, the higher improvement of T2T rate will be. The improvement of T2T rate(y) was positively correlated with times of self-assessment for ASDAS(x) independently. The regression equation as “y = 0.0304x + 0.0521”, r = 0.9107, p< 0.01 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Significant improvement was observed under applying SSDM through empowering AS patients. After proactive disease management via SSDM for more than 6 months, patients with ASDAS< =1.3 score at baseline had a significantly higher retention rate of inactive disease activity. The patients who performed more frequent self-assessments had lower probability of relapse and higher rate of T2T. Online interaction between patients and physicians contributed to promote the improvement rate of T2T. SSDM is a valuable tool for long term follow-up through empowering patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xue J, Wang H, Li H, Song H, Li Y, Shi X, Zhao H, Wei F, Wu B, Xiao H, Jia Y, Xiao F, Wu H. Pattern and Influential Factors in Promoting Treat-to-Target (T2T) for F Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) Patients with the App of Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM): A Cohort Study from China [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pattern-and-influential-factors-in-promoting-treat-to-target-t2t-for-f-ankylosing-spondylitis-as-patients-with-the-app-of-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm-a-cohort-study-from-china/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pattern-and-influential-factors-in-promoting-treat-to-target-t2t-for-f-ankylosing-spondylitis-as-patients-with-the-app-of-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm-a-cohort-study-from-china/