Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster IV: COVID-19 (1589–1613)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Prior to COVID-19, few studies examined how patients with a chronic illness, such as systemic sclerosis (SSc), react to a pandemic. This study examined if fears of COVID are affecting health care for scleroderma patients, their mental and physical functioning, and if patients with SSc engage in COVID-19 risky behavior.
Methods: Participants were 60 people with SSc who had not had COVID-19 and had not yet been vaccinated for COVID. Participants had a mean age of 58 years (SD = 11.5) and were primarily female (92%) and white (87%). The ACR-Eular criteria for diagnosis of systemic sclerosis was met for 87% of participants and was unknown for the rest.
Participants completed an online survey after learning about it from a scleroderma organization newsletter or at their visit with a rheumatologist specializing in scleroderma. Data were collected August 2020 through March 2021. Participants completed measures assessing exercise, risk behaviors, vaccination intent, health-related appointments attendance, and PROMIS measures of anxiety, depression, fatigue, sleep disturbance, and physical function.
Results: Eighteen percent of the sample reported exercising less during the pandemic. For COVID-19 risk behaviors, 37% ate indoors at a restaurant, 28% went to an indoor gathering (e.g., wedding), and 58% went to a hair/nail salon. In terms of COVID-19 vaccination intent, 32% would be vaccinated as soon as eligible, 27% intended to wait, 12% might get vaccinated, 16% did not plan to get vaccinated, 8% were letting their physician decide, and 5% were not sure.
As can be seen in Table 1, 29% of respondents had health care appointments in-person, 32% had only telemedicine appointments, 24% had a combination of appointments, and 10% cancelled appointments due to COVID concerns. As can be seen in Table 2, of the respondents for whom pulmonary function tests were relevant, 40% cancelled or postponed these due to COVID concerns. Similarly, among respondents who normally had physical or occupational therapy, 46-50% of them cancelled due to COVID concerns. Patients cancelled 24% of dental appointments due to COVID concerns.
We compared respondents who cancelled one or more appointments due to COVID-19 concerns (N = 28) versus those who did not (N = 32). Participants who cancelled reported higher anxiety, t(58) = 2.46, p =.02, sleep disturbance, t(56) = 3.31, p = .002, and worse physical functioning, t(56) = 2.00, p = .05.
Many participants reported moderate or severe anxiety (36%), depression (22%), fatigue (32%), sleep disturbance (28%), and physical dysfunction (40%, see Table 3).
Conclusion: The results that a majority of participants were willing to get vaccinated for COVID-19 are encouraging. Less encouraging, almost one in five participants exercised less during the pandemic and half of them did not exercise to begin with. Additionally, almost half of participants cancelled one or more health appointments due to their COVID fears. This subgroup reported significantly higher anxiety, sleep disturbance, and worse physical functioning. Future research should examine the extent to which changes in health-related behavior during the pandemic have implications for disease progression in patients with SSc.
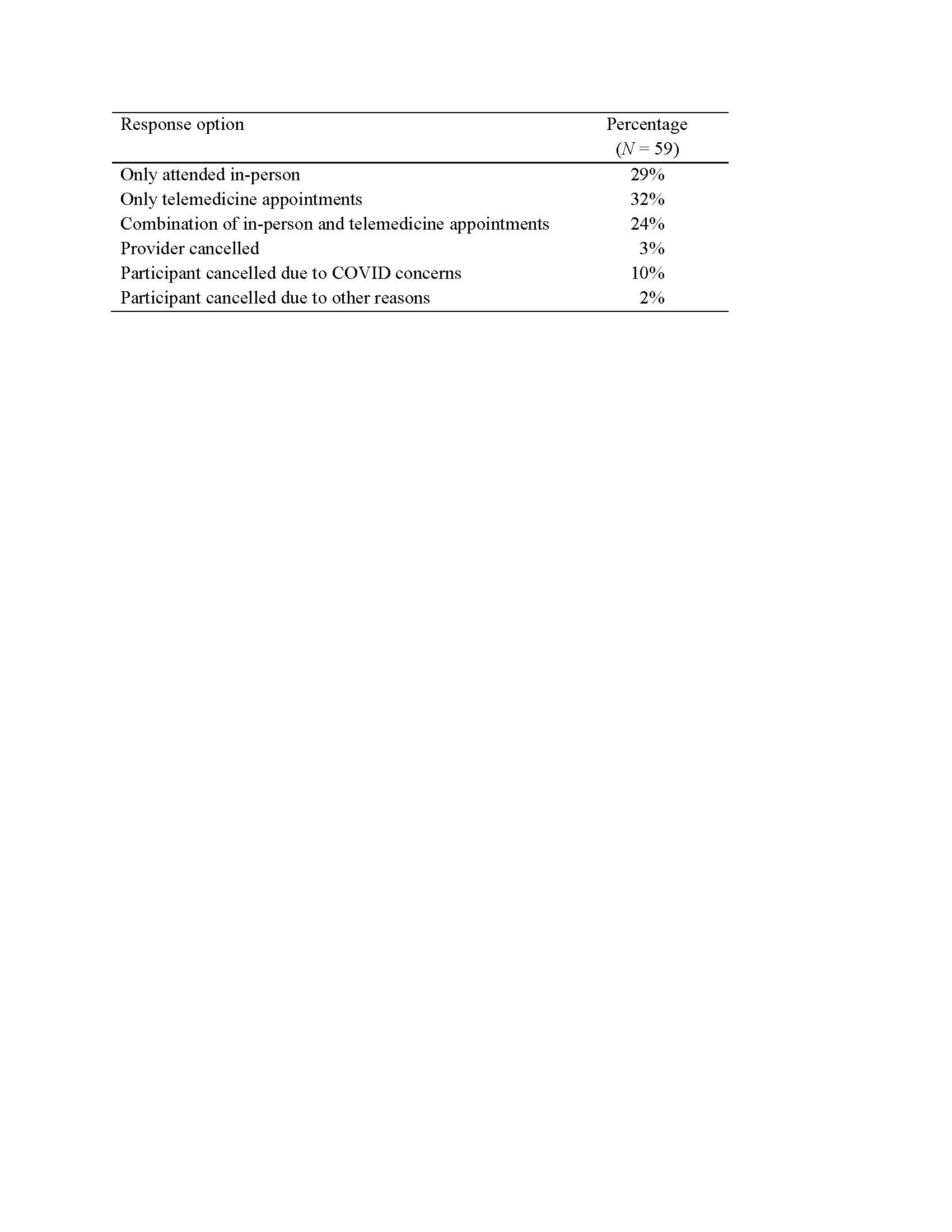 Percentage of Respondents who Attended or Cancelled an Appointment with a Health Care Professional Since the Beginning of the COVID_19 Pandemic in the U.S.
Percentage of Respondents who Attended or Cancelled an Appointment with a Health Care Professional Since the Beginning of the COVID_19 Pandemic in the U.S.
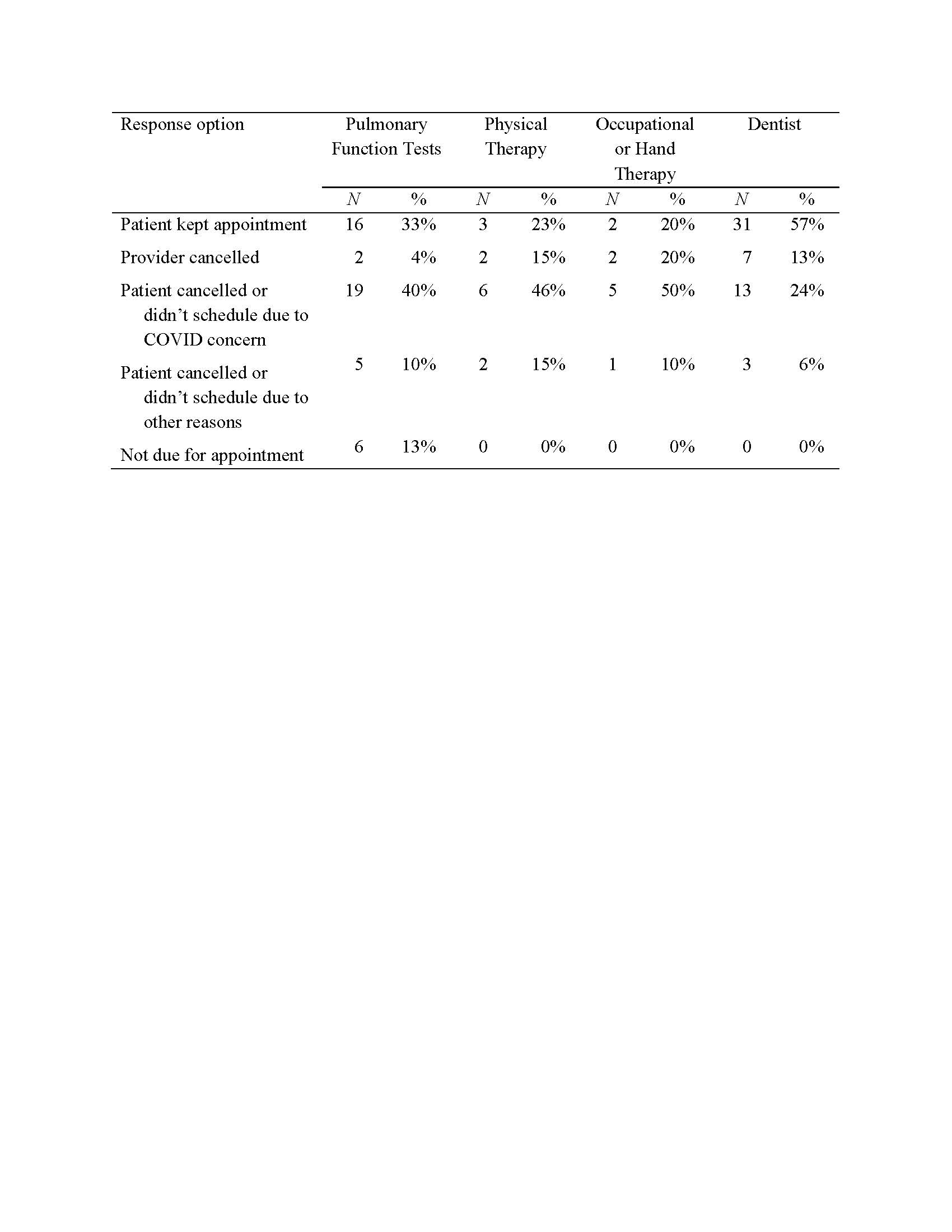 Frequency and Percentage of Respondents who Attended or Cancelled a Health-Related Appointment Since the Beginning of the COVID Pandemic in the U.S.
Frequency and Percentage of Respondents who Attended or Cancelled a Health-Related Appointment Since the Beginning of the COVID Pandemic in the U.S.
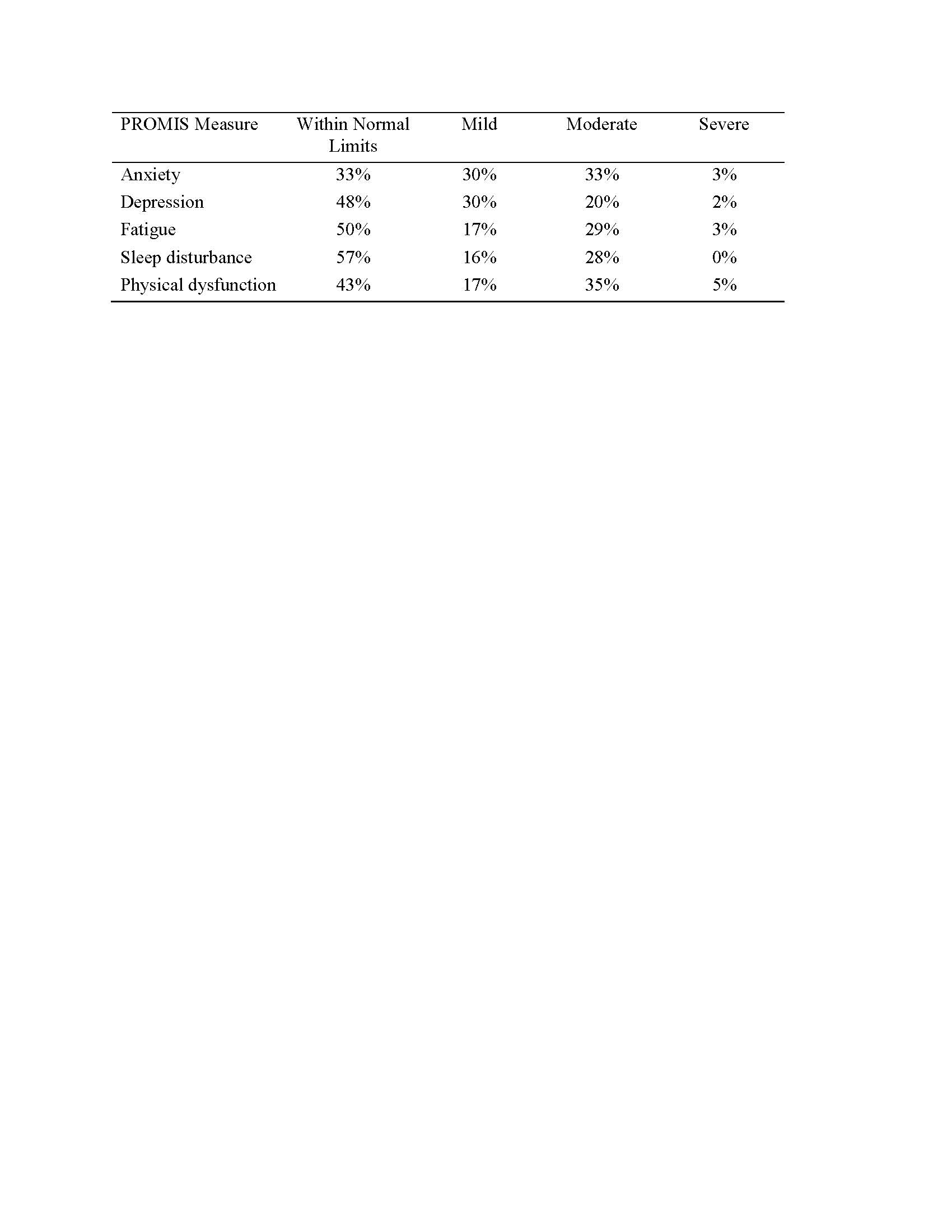 Percentage of Scores Within Each Category of Severity on PROMIS Measures
Percentage of Scores Within Each Category of Severity on PROMIS Measures
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dorr N, Fennell P, Shapiro L. Pandemic and Patients: Examining Health-Related Behaviors of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis During the COVID-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pandemic-and-patients-examining-health-related-behaviors-of-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pandemic-and-patients-examining-health-related-behaviors-of-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/
