Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Recent data suggest that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pain may be noninflammatory and inflammatory, and improvement in pain scores and other patient-reported outcomes (PROs) may be seen in patients who do not respond to treatment based on disease activity measures that evaluate inflammation. This study evaluated changes in pain scores and other PROs in patients with RA who did or did not achieve ≥ 20% improvement in swollen joint count (SJC) in tocilizumab (TCZ) clinical trials.
Methods: Data from patients with active RA who received intravenous TCZ 8 mg/kg + methotrexate (MTX) or placebo (PBO) + MTX in 3 Phase III studies (OPTION [NCT00106548], TOWARD [NCT00106574] and LITHE [NCT00109408]) were included. Changes in pain (visual analog scale [VAS], 0-100 mm), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI, 0-3), 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36) physical component score (PCS) and mental component score (MCS; 0-50) and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) score (0-52) from baseline to Week 24 were evaluated. Results were compared between patients receiving TCZ + MTX and those receiving PBO + MTX in both patients who achieved ≥ 20% improvement in SJC (responders) and those who did not (nonresponders). The changes from baseline were analyzed using a mixed model with repeated measures, including the following covariates and interactions: treatment, visit, baseline of endpoint, region, baseline DAS28 and interactions of visit with treatment and baseline of endpoint.
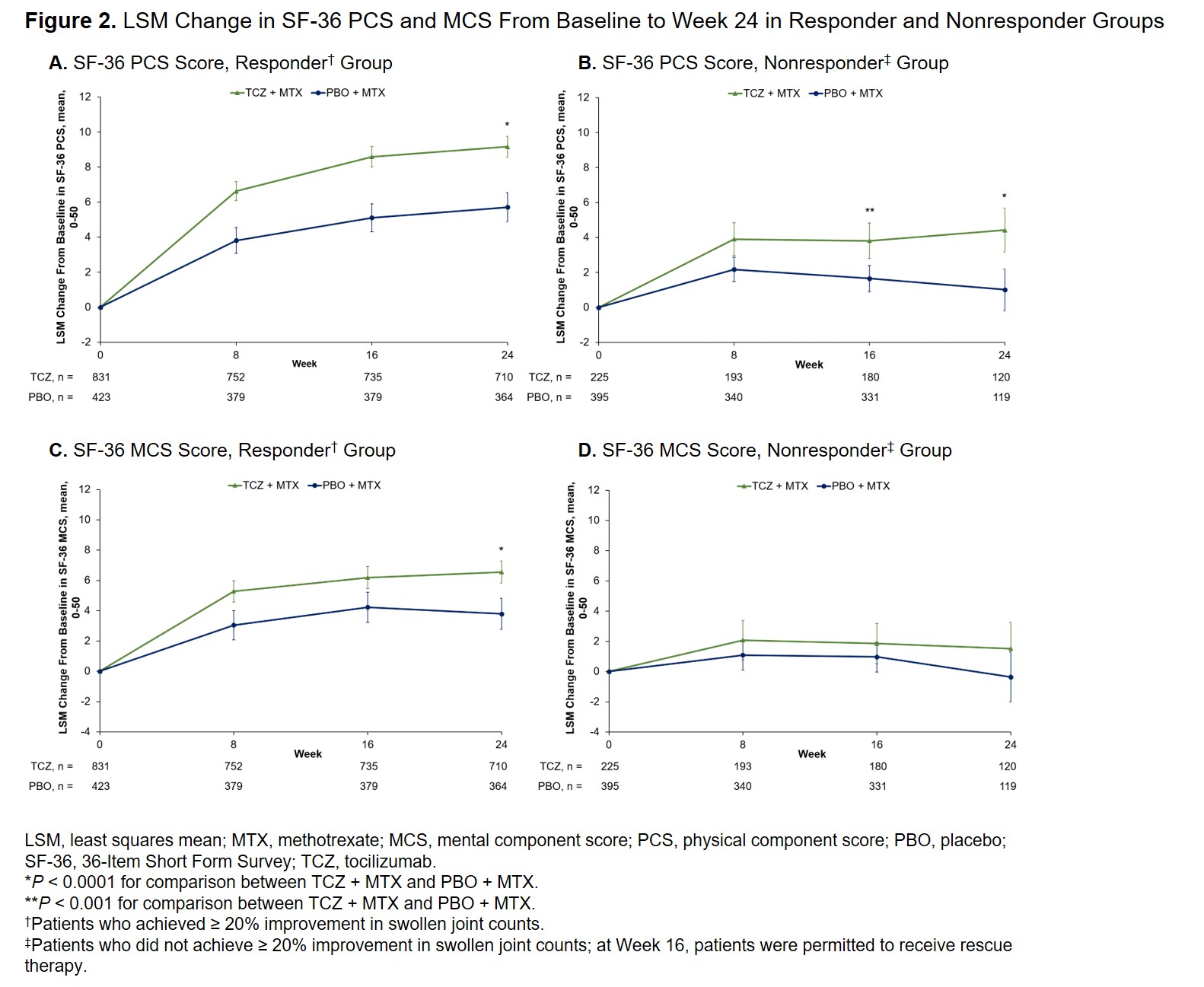
Results: Data from 1254 responders (TCZ + MTX, n = 831; PBO + MTX, n = 423) and 620 nonresponders (TCZ + MTX, n = 225; PBO + MTX, n = 395) were included. Patients receiving TCZ + MTX had significantly greater improvement in pain and HAQ-DI than PBO + MTX in the responder group (–27.19 vs –16.77 and –0.55 vs –0.34, respectively; P < 0.0001 for both) and nonresponder group (–9.59 vs 2.53 and –0.20 vs 0.01; P < 0.0001 for both) at Week 24 (Figure 1). Similar results were seen at Week 16 in the nonresponder group (–11.06 vs –2.38 and –0.23 vs –0.04; P < 0.0001 for both). At Week 24 in the responder group, patients receiving TCZ + MTX had significantly greater improvements compared with PBO + MTX in SF-36 PCS and MCS (9.16 vs 5.71 and 6.55 vs 3.79, respectively; P < 0.0001 for both) (Figure 2) and FACIT-F (8.39 vs 5.11; P < 0.0001). In the nonresponder group, patients receiving TCZ + MTX had significantly greater improvements compared with PBO + MTX in SF-36 PCS at Week 16 (3.81 vs 1.65; P = 0.0006) and Week 24 (4.42 vs 1.01; P < 0.0001) (Figure 2) and FACIT-F at Week 16 (3.82 vs 1.32; P = 0.0039) and Week 24 (3.90 vs 1.40; P = 0.0111).
Conclusion: Patients with RA who received TCZ + MTX had significantly greater improvements in pain and other PROs than those who received PBO + MTX regardless of whether they achieved ≥ 20% improvement in SJC. Clinical outcome at Week 24 correlated well with PROs, with a relatively larger improvement in PROs in the responder group than in the nonresponder group; relative to PBO + MTX, these improvements appear numerically similar in the responder and nonresponder groups. The consistent effect of TCZ on PROs in responder and nonresponder groups warrants further study on TCZ’s impact on pain sources independent of that caused by joint inflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sebba A, Han J, Mohan S. Pain and Other Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Did or Did Not Achieve Treatment Response Based on Improvement in Swollen Joints in Tocilizumab Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-and-other-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-did-or-did-not-achieve-treatment-response-based-on-improvement-in-swollen-joints-in-tocilizumab-clinical-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-and-other-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-who-did-or-did-not-achieve-treatment-response-based-on-improvement-in-swollen-joints-in-tocilizumab-clinical-trials/