Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sarcoidosis is a disease occurring in the form of non-caseating granulomas, with unclear etiology and multi-system manifestations. Pulmonary involvement in sarcoidosis is a cardinal manifestation and has a risk of progression to pulmonary fibrosis in about 5% of patients with increased mortality. This study has been conducted to review variable lung manifestations, treatment choices and outcomes at our health center.
Methods: A cohort of forty-eight patients evaluated by Rheumatology for pulmonary sarcoidosis over three years (January 2021 through January 2024) was selected for manual chart review at LSU-Health Shreveport. Data was collected and a retrospective analysis was performed regarding imaging findings, diagnosis and treatment approaches for pulmonary sarcoidosis. It was checked whether diagnosis had been supported with biopsy or whether it was determined based on clinical, and imaging findings. Computed tomography (CT) scan findings of chest were reviewed to evaluate improved, stable, or worsened outcomes. Statistical analysis through T-tests and Chi square tests was performed for quantitative and categorical values, respectively.
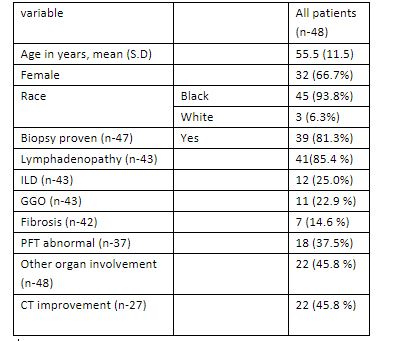
Results: The mean age of all patients (n=48) was 55.5 years (SD=11.5). Among all patients, 66.7% were female. Most patients were Black (93.8%). Approximately 81.3% of patients had biopsy-proven sarcoidosis. Lymphadenopathy was present in 85.4% of patients overall, with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and ground glass opacities (GGOs) present in 23.9% of patients overall. Fibrosis was present in 14.6% of patients overall, and abnormal PFT results were found in 37.5% of patients.
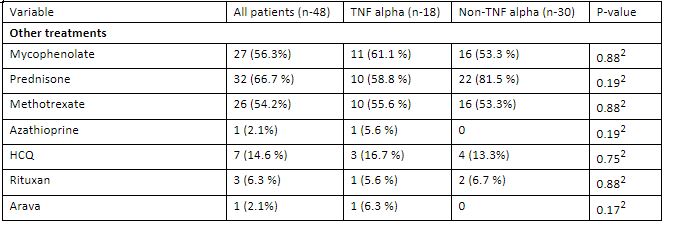
Other organ involvement was observed in 45.8% of patients overall. CT improvement was observed in 45.8% of patients overall, with similar percentages in both the TNF alpha (44.4%) and non-TNF alpha (46.7%) groups. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups (p=0.632).
Various treatments were administered, including Mycophenolate, Prednisone, Methotrexate, Azathioprine, HCQ (Hydroxychloroquine), Rituxan, and Arava. The proportions of patients receiving these treatments were generally comparable between the TNF alpha and non-TNF alpha groups, with no statistically significant differences observed for most treatments.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this retrospective study offers insights into pulmonary sarcoidosis management at our center, highlighting common manifestations like lymphadenopathy, interstitial lung disease, and ground glass opacities. Extrapulmonary organ involvement was prevalent, underscoring the systemic nature of the disease.
Limitations include the small sample size and potential benefits of incorporating detailed measures like serial PFT findings to enhance outcomes. Treatment typically begins with glucocorticoids, followed by csDMARDs, and anti-TNFs for refractory cases or to reduce glucocorticoid use. Mycophenolate, Prednisone, and Methotrexate were commonly prescribed, often with TNF-alpha inhibitors, yet treatment outcomes, including CT scan improvements, did not significantly differ between TNF alpha inhibitors and other therapy groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Qamar A, Agrawal U, Sachdeva K, Hassan Z, Zamora A, Nida S, Umer S, Hayat S, Muzaffar K. Overview of Lung Manifestations in Sarcoidosis and Various Treatment Approaches at a University Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/overview-of-lung-manifestations-in-sarcoidosis-and-various-treatment-approaches-at-a-university-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/overview-of-lung-manifestations-in-sarcoidosis-and-various-treatment-approaches-at-a-university-center/