Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Autoantibody profiles are associated with organ involvement and outcomes in patients with SSc. Anti-topoisomerase I antibody (ATA) positivity has been associated with a greater risk of developing SSc-ILD, while positivity for ACA or ARA has been associated with a lower risk. No prior studies have assessed the rate of progression of SSc-ILD in subgroups by ACA or ARA status in the context of a clinical trial. The purpose of this post-hoc analysis of the SENSCIS trial was to determine whether participants with ACA or ARA experience progression of SSc-ILD.
Methods: The SENSCIS trial enrolled participants with SSc with first non-Raynaud symptom in the prior ≤7 years and an extent of fibrotic ILD on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) ≥10%. Participants were randomized to receive nintedanib or placebo, stratified by ATA status. We analyzed the rate of decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) (mL/year) over 52 weeks in subgroups by ACA status and ARA status (based on central laboratory data) at baseline. Exploratory interaction p-values were calculated to assess potential heterogeneity in the effect of nintedanib versus placebo between the subgroups. We also analyzed the rate of decline in FVC (mL/year) over 52 weeks in participants who were negative for ATA, ACA and ARA.
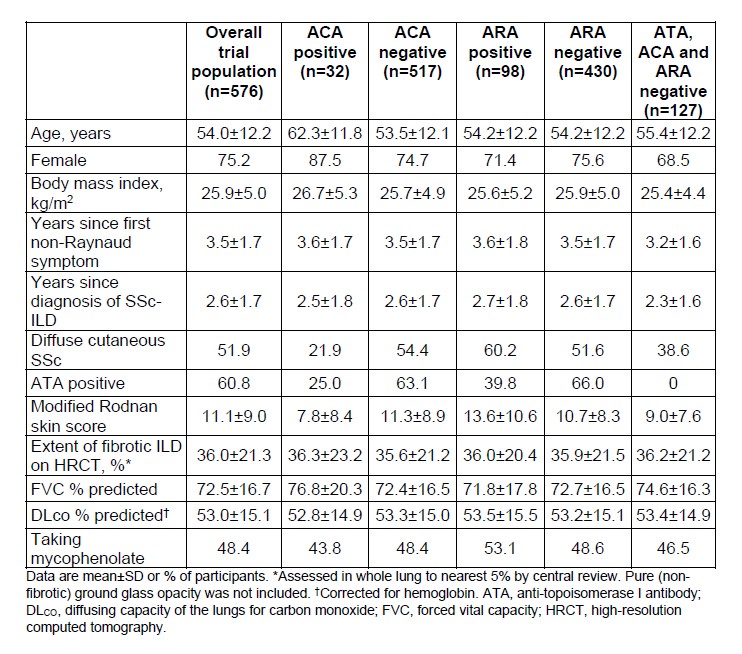
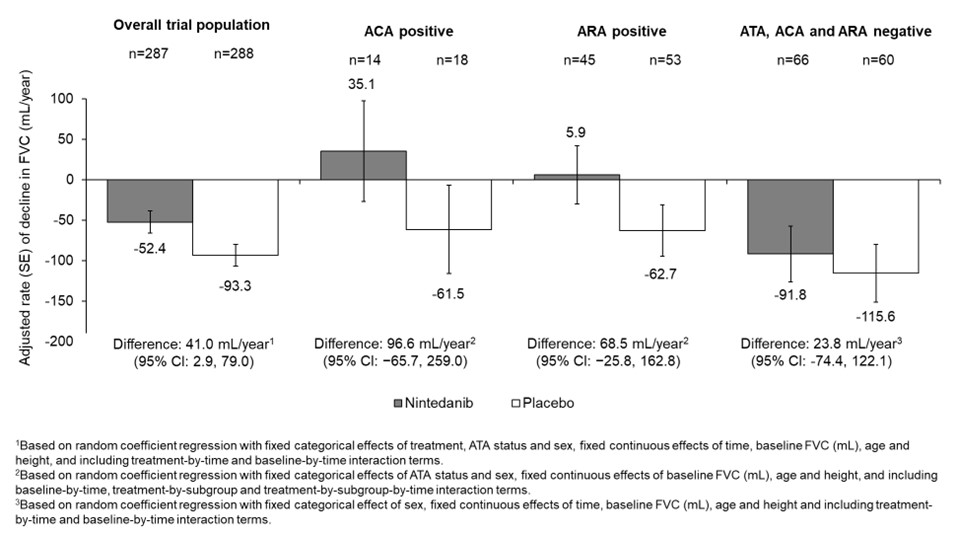
Results: Among 549 participants with available data, 5.8% were ACA positive. Compared with ACA negative participants, ACA positive participants were older, had a lower mean modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), and a lower proportion had diffuse cutaneous SSc (Table). Among 528 participants with available data, 18.6% were ARA positive. Compared with ARA negative participants, a greater proportion of ARA positive participants had diffuse cutaneous SSc (Table). In the placebo arm, the adjusted rate (SE) of decline in FVC (mL/year) over 52 weeks was numerically greater in participants who were ACA negative than positive (-94.8 [14.3] vs -61.5 [54.5]) and numerically greater in those who were ARA negative than positive (-99.1 [15.9] vs -62.7 [31.6]). The effect of nintedanib versus placebo on reducing the rate of FVC decline was numerically more pronounced in participants who were ACA positive than negative (difference 96.6 mL/year [95% CI −65.7, 259.0] vs 34.8 [-5.1, 74.6]) or ARA positive than negative (difference 68.5 mL/year [95% CI −25.8, 162.8] vs 26.9 [-16.8, 70.7]), but the interaction p-values ( >0.05) did not indicate heterogeneity in the effect of nintedanib between these subgroups. In the placebo arm, the rate of decline in FVC (mL/year) over 52 weeks, and the effect of nintedanib versus placebo in reducing the rate of FVC decline, were similar between the subset of patients who were negative for ATA, ACA and ARA and the overall trial population (Figure).
Conclusion: While the results of these post-hoc analyses should be interpreted with caution given the small number of participants who were ACA positive, the results suggest that patients who are ACA positive or ARA positive can experience SSc-ILD progression and should be monitored closely. The effect of nintedanib on slowing FVC decline was numerically more pronounced in participants with SSc-ILD who were ACA positive or ARA positive.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Volkmann E, Assassi S, Denton C, Simonovska R, Sambevski S, Bernstein E. Outcomes in Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD) Based on Serological Profiles: Focus on Anti-Centromere Antibody (ACA) and Anti-RNA Polymerase III (ARA) Antibodies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-based-on-serological-profiles-focus-on-anti-centromere-antibody-aca-and-anti-rna-polymerase-iii-ara-antibodies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/outcomes-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-based-on-serological-profiles-focus-on-anti-centromere-antibody-aca-and-anti-rna-polymerase-iii-ara-antibodies/