Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s disease (SjD) is a chronic, progressive autoimmune disease characterized by aberrant B lymphocyte activity, elevated IgG production, and the presence of IgG autoantibodies (AAbs). Elevated levels of pathogenic IgG AAbs, particularly anti-Ro, are associated with more severe SjD. Nipocalimab is a fully human neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) blocking monoclonal antibody that reduces circulating IgG levels by selectively blocking IgG recycling. In the phase 2, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind DAHLIAS study (NCT04968912), nipocalimab 15 mg/kg demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in efficacy compared to placebo, with no new safety concerns. This analysis characterized the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of nipocalimab in participants with SjD from DAHLIAS.
Methods: Adults with moderately-to-severely active SjD who were seropositive for anti-Ro AAbs were randomized 1:1:1 to receive intravenous nipocalimab 5 or 15 mg/kg or placebo every 2 weeks through Week 22, with protocol-permitted background standard of care. Blood samples were collected from participants to measure concentrations of serum nipocalimab and the FcRn-dependent IgG, including total IgG and IgG AAbs (ie, anti-Ro52, anti-Ro60, and anti-La/SSB), through Week 30. Data were summarized using descriptive statistics. Population PK/PD modeling based on observed data and available nipocalimab clinical study data was performed to predict IgG lowering.
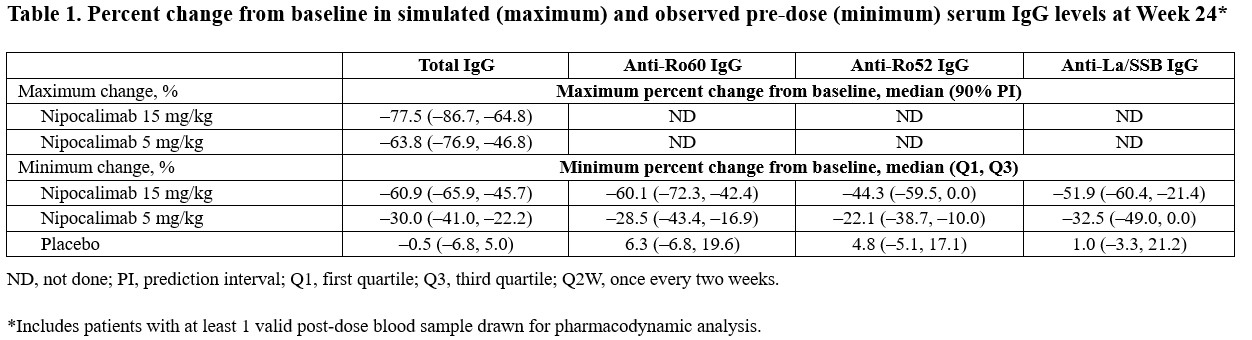
Results: The analysis set consisted of 163 participants. Baseline concentrations of disease-associated biomarkers were similar across groups. Median, post-dose (~45 min after nipocalimab administration) serum nipocalimab concentrations for the nipocalimab 5 and 15 mg/kg groups ranged from 111.5 to 116.5 µg/mL and from 336.5 to 367.0 µg/mL, respectively across Weeks 0 to 12. Both nipocalimab doses led to substantial, observed pre-dose changes (ie, minimum reductions) from baseline in total IgG and AAb levels from Week 2 through Week 24 (final efficacy visit), when the median total IgG change from baseline was –30.0%, –60.9%, and –0.5% for the nipocalimab 5 mg/kg, 15 mg/kg, and placebo groups, respectively (Table 1). PK/PD simulations indicated a median maximum IgG reduction of 77.5% at the IgG nadir along with observed pre-dose (minimum) IgG reductions of 61% with nipocalimab 15 mg/kg. By Week 30 (8 weeks after last administration), all treatment groups returned to near-baseline levels of IgG, anti-Ro60, anti-Ro52, and anti-La.
Conclusion: Nipocalimab administration was associated with substantial, median maximum reductions of approximately 77.5% in total IgG, with persistent, substantial minimum reductions in total IgG and AAbs (including anti-Ro60, anti-Ro52, and anti-La antibodies) at the nipocalimab nadir before each dose. There was clear separation between each nipocalimab dose and placebo that was apparent as early as Week 2 and resolved within 6 weeks after the end of treatment, suggesting that the impact of FcRn inhibition on IgG levels is reversible upon discontinuing nipocalimab. These data show potent engagement of nipocalimab with FcRn, clearly demonstrating the mechanism of action of nipocalimab in SjD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liva S, Zheng f, Leu J, Sivils K, Ma K, Li H, Leonardo S, Lo K, Idokogi J, Campbell K, Hubbard J. Observed and Simulated Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nipocalimab, a Fully Human FcRn Blocking Monoclonal Antibody, in Adults with Sjögren’s Disease: Results from a Phase 2, Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-blind Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/observed-and-simulated-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-nipocalimab-a-fully-human-fcrn-blocking-monoclonal-antibody-in-adults-with-sjogrens-disease-results-from-a-phase-2-multicen/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/observed-and-simulated-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-nipocalimab-a-fully-human-fcrn-blocking-monoclonal-antibody-in-adults-with-sjogrens-disease-results-from-a-phase-2-multicen/