Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: B cells infiltrate the kidneys in lupus nephritis (LN) and likely contribute to the pathogenesis of kidney injury. The REGENCY trial (NCT04221477) showed that depletion of B cells with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, obinutuzumab, increased the proportion of clinical complete responses when added to standard therapy compared with standard therapy alone.
We postulated that obinutuzumab may deplete B cells in the kidney in addition to the periphery. Given the potential importance of deep, tissue B-cell depletion in LN, participants in the REGENCY trial were offered a post-Week 76 kidney biopsy to evaluate histologic changes over time. Here we present the results of kidney B-cell dynamics from participants with both biopsies.
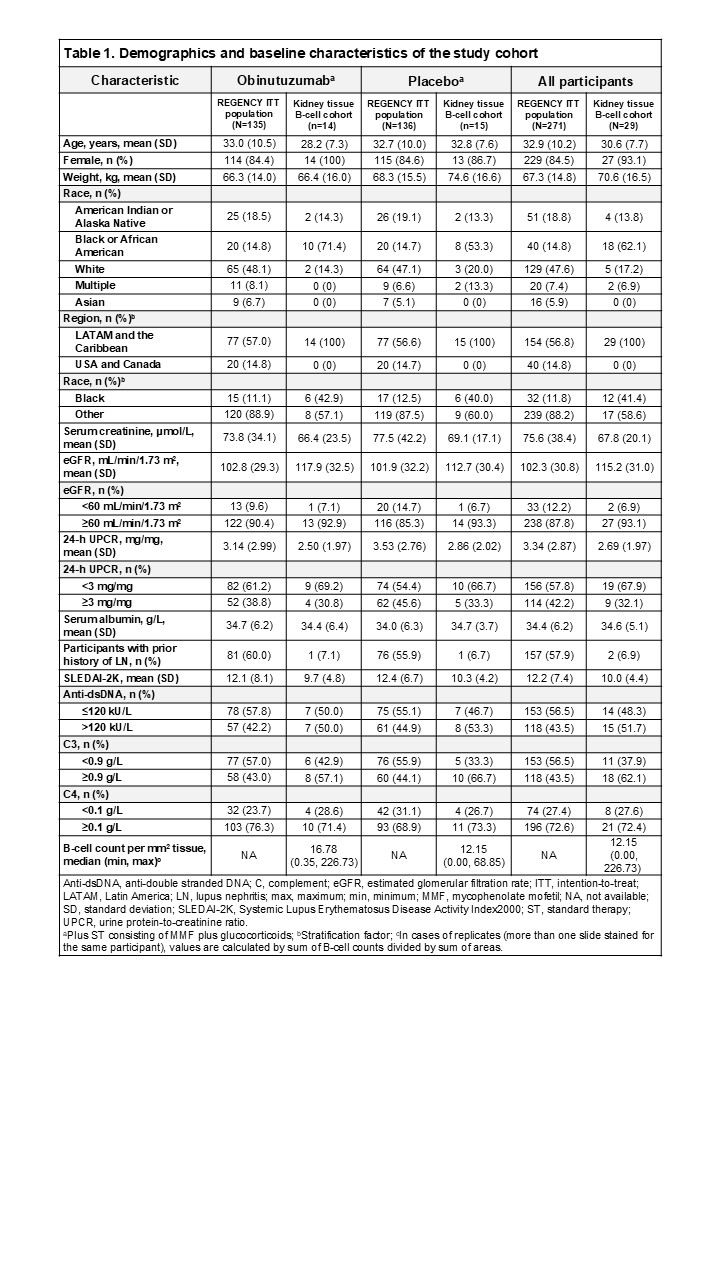
Methods: Blinded, central reads of baseline and post-Week76 (obtained between Week 76 and Week 80) biopsies were performed by nephropathologists at Arkana Laboratories using the 2018 ISN/RPS LN classification criteria. All participants met the American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus and had biopsy-proven proliferative LN. CD79a+/CD138- B cells were quantified on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections by immunofluorescence microscopy and digital whole-slide image analysis for participants with paired baseline and post-Week 76 biopsies with remaining material for tissue staining (Nf29 participants; 14 obinutuzumab plus standard therapy [OBI+ST] and 15 placebo plus standard therapy [PBO+ST]). Raw analysis data generation was performed blinded to treatment; data were unblinded for statistical evaluation. Treatment group comparison of absolute change from baseline at Week 76 in B-cell counts was assessed using ANCOVA model with baseline B-cell counts and stratification factor (Black vs Other) as independent variables.
Results: Baseline characteristics were generally balanced and consistent with the overall REGENCY population; however, the baseline level of tissue CD79a+/CD138- B cells was higher in the OBI+ST group compared with the PBO+ST group (Table 1). Spatial frequency of tissue CD79a+/CD138- B cells at baseline and Week 76 was similar in PBO+ST participants, whereas there was a highly significant decline of B-cell counts per mm2 at Week 76 vs baseline in OBI+ST participants, with measurements at or near zero (Figure 1). ANCOVA analysis showed that at Week 76, the adjusted mean change from baseline in B-cell counts was –28.5 (95% CI, –33.3 to –23.6) in OBI+ST and –11.9 (95% CI, –16.6 to –7.2) in PBO+ST, with a difference of –16.6 (95% CI, –23.4 to –9.7; P < 0.0001) between treatment groups.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that obinutuzumab potently depletes B cells in the kidneys of individuals with LN. These data represent the first demonstration of kidney tissue-level B-cell depletion by an anti-CD20 agent in any glomerular disease. Given the possible association of deep, tissue B-cell depletion and prolonged disease control in LN, the clearing of B cells from the kidneys by obinutuzumab may contribute to the improvement in kidney function and decline in LN flares observed in the obinutuzumab-treated patients during the REGENCY trial.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rovin B, Martins E, Austin C, Raghu H, Chan C, Chang P, Garg J, Alberton V, Santiago M, Aroca-Martínez G, Palazuelos F, Baczkowska T, Alfaro J, Ravelo-Hernández J, Furie R, Pinto L, Albiero E, Larsen C, Yoo B, Pulley J, Thorley A, Schindler T, Omachi T, Pendergraft III W, Malvar A. Obinutuzumab Leads to Deep B-Cell Depletion in the Kidney Parenchyma of Patients With Lupus Nephritis: An Exploratory Analysis of the REGENCY Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obinutuzumab-leads-to-deep-b-cell-depletion-in-the-kidney-parenchyma-of-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-an-exploratory-analysis-of-the-regency-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/obinutuzumab-leads-to-deep-b-cell-depletion-in-the-kidney-parenchyma-of-patients-with-lupus-nephritis-an-exploratory-analysis-of-the-regency-trial/

.jpg)