Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions
Session Time: 4:45PM-5:15PM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a complex heterogeneous autoimmune disease. Myositis-specific autoantibodies (MSAs), present in up to 80% of JDM patients, help define distinct phenotypes within JDM and may indicate distinct pathogeneses. To define biomarkers and better understand JDM pathogenesis, aptamer-based proteomic technology was used to mine the serum proteome in a well-characterized JDM cohort.
Methods: Sera from 41 JDM patients (prevalent cases on variable treatment) selected for higher disease activity (physician global activity or PGA median 4.0 (IQR 3.0-5.0)) with anti-p155/140 or TIF1 (n=21), NXP2 (n=10), and MDA5 (n=10) MSAs, were compared with 28 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HC). Broad proteomic analysis of 1306 targets using SOMAscan assay of slow off-rate modified aptamers (SomaLogic, CO) generated simultaneous quantitative serum levels. Individual MSA group vs. HC proteins with Mann-Whitney FDR-corrected p values of <0.05 with expression ratio of >1.3 were analyzed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis or IPA (Qiagen, CA).
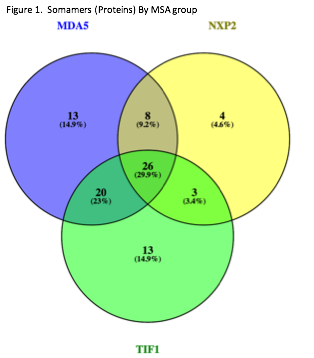
Results: 62, 41, and 67 proteins, met above criteria with overexpression (>1.3 ratio versus HC) with 13, 4, and 13 proteins specific to TIF1, NXP2, and MDA5 MSA groups respectively and 26 shared in all 3 groups and 31 shared in 2 groups (Figure 1). Top 10 proteins by MSA group are listed in Table 1. Within the top 20 dysregulated pathways by MSA group by IPA, Th1 and Th2 activation, acute phase response, IFN, and glucocorticoid receptor signaling were shared to all 3 MSA groups. Further analysis by MSA group is ongoing.
Conclusion: Preliminary broad quantitative proteomic analysis by MSA group compared to HC identified Th1/ Th2, acute phase response, IFN, and glucocorticosteroid receptor signaling shared in all MSA groups. Unique protiens were identified by MSA group, but further analysis by MSA group is pending. While in need of confirmation in other cohorts, these proteins identified through a high-throughput screen bring to light new pathways that may be important in JDM and potential MSA-group specific pathogenesis.
This research was supported by the Cure JM Foundation and the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, NIAMS, NIEHS, NHLBI, NIAID, and the CC.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim H, Biancotto A, Cheung F, O'Hanlon TP, Targoff IN, Huang Y, Miller F, Goldbach-Mansky R, Rider LG. Novel Serum Broad-Based Proteomic Discovery Analysis Identifies Proteins and Pathways Dysregulated in Juvenile Dermatomyositis (JDM) Myositis Autoantibody Groups [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-serum-broad-based-proteomic-discovery-analysis-identifies-proteins-and-pathways-dysregulated-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis-jdm-myositis-autoantibody-groups/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-serum-broad-based-proteomic-discovery-analysis-identifies-proteins-and-pathways-dysregulated-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis-jdm-myositis-autoantibody-groups/