Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Cognitive impairment (CI) is an increasingly prevalent neuropsychiatric manifestation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Although CI has been identified through patient-reported outcomes to significantly affect quality of life, targeted treatments remain limited as the pathogenesis of CI in SLE is complex and poorly understood. Our groups and others have demonstrated evidence of the validity of Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics (ANAM) in screening for CI in SLE, with superior patient acceptability compared to the American College of Rheumatology Neuropsychological Battery (ACR-NB) [gold-standard test]. Emerging data from our laboratory have revealed the serum analytes S100A8/A9 and MMP-9 to be associated with CI as identified on the ACR-NB. However, the relationship between these serum analytes, ANAM subtests and CI has not been elucidated. We therefore aimed to determine if serum analytes are associated with CI measure by ANAM.
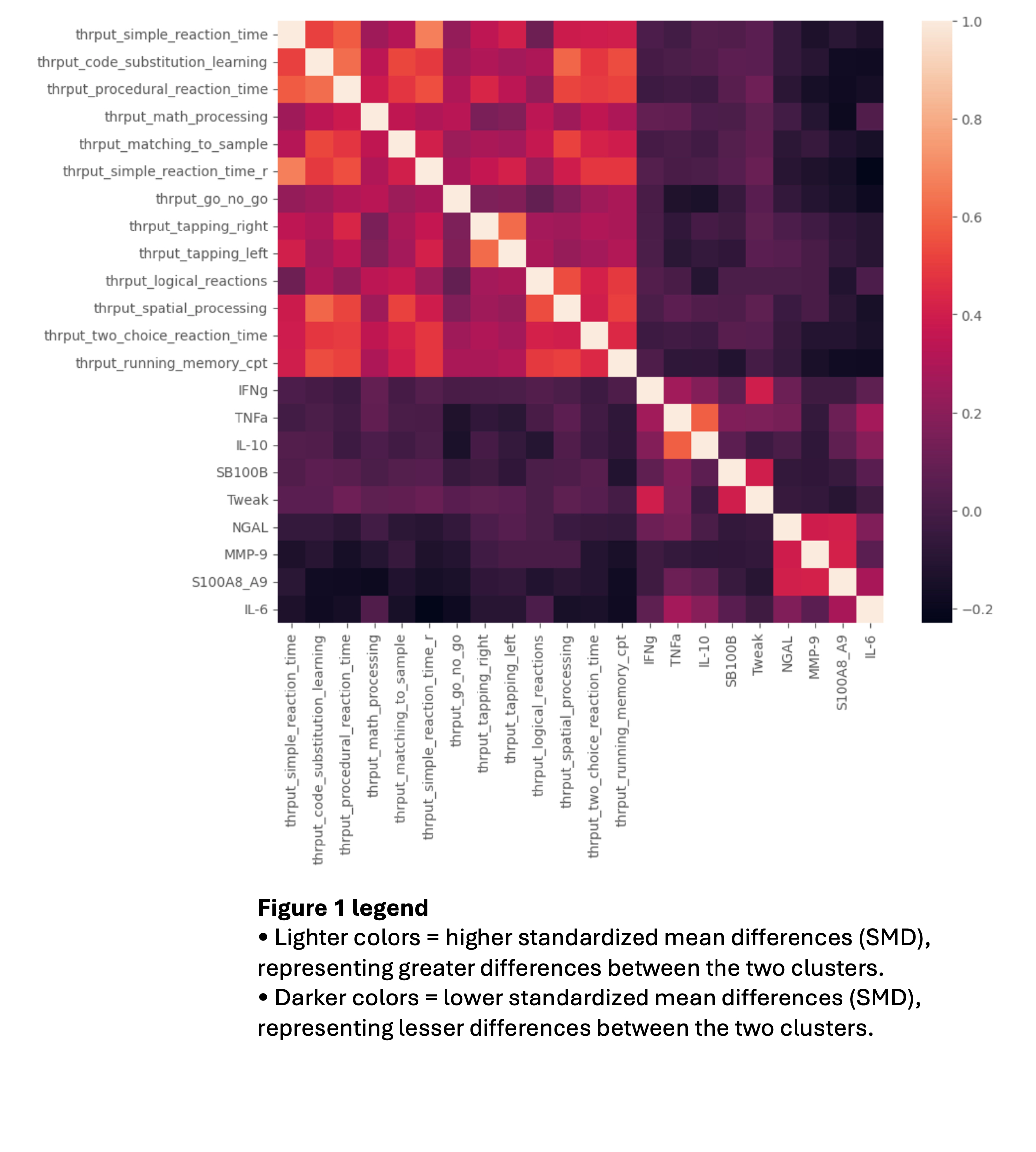
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis on the data of 327 adults between the ages of 18-65 who were followed longitudinally between January 2016 and October 2019 at a single SLE center. All participants fulfilled the 2019 EULAR/ACR SLE classification criteria. Cognitive function was measured using ANAM throughput scores, and serum levels of 9 analytes (IL-10, IL-6, IFN-γ, TNF-α, TWEAK, S100B, S100A8/A9, NGAL and MMP-9) were measured using ELISA. The K-means clustering algorithm was used to cluster the patient data, and the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used to characterize the clusters (Figure 1). The silhouette coefficient (s) was calculated for a range of 2 to 15 clusters to determine the optimal number of clusters.
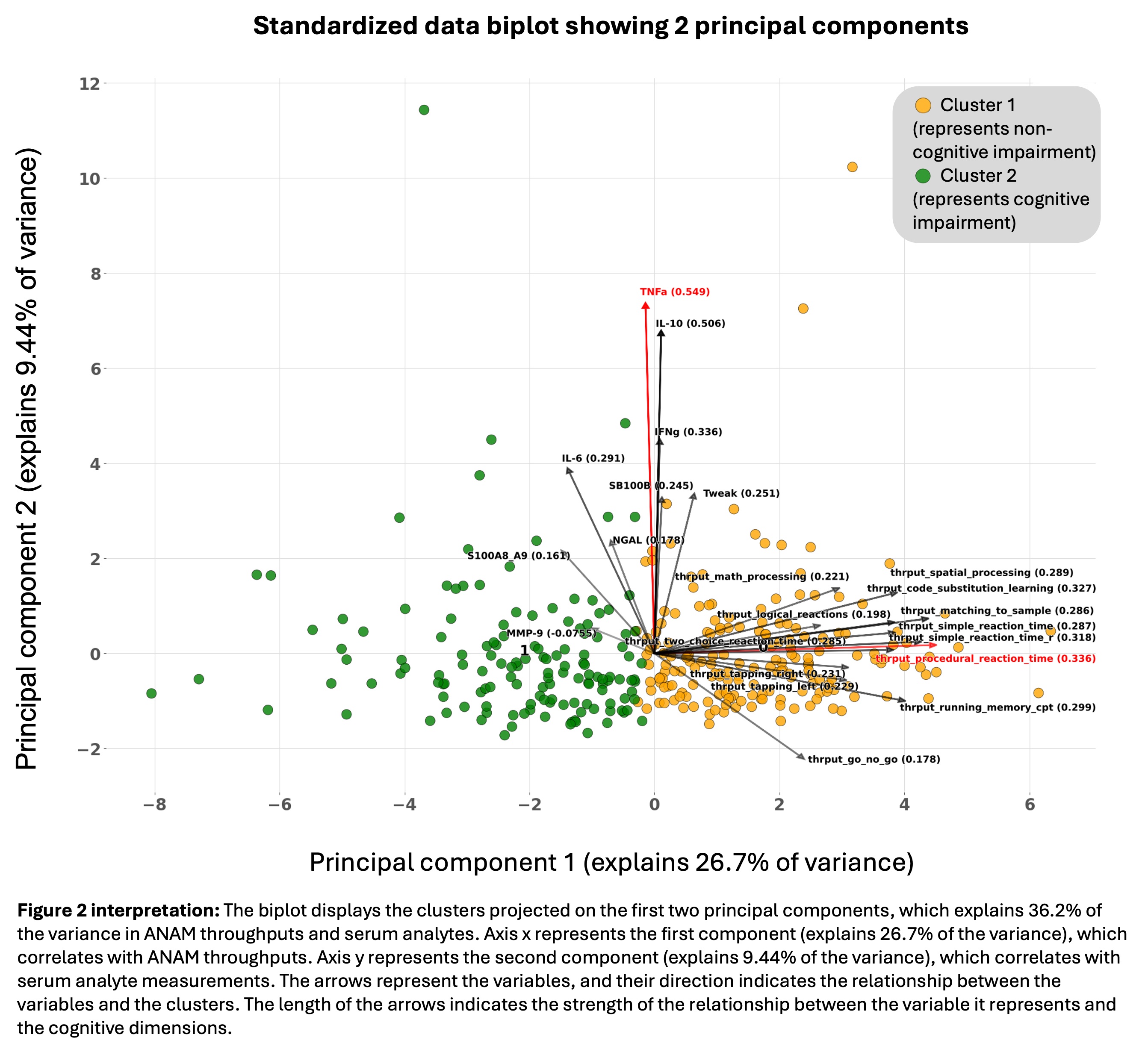
Results: PCA identified two principal components explaining 36.2% of the variance in ANAM throughputs and serum analytes. The first component (26.7% of the variance) was correlated with ANAM throughputs, with the strongest contribution from procedural reaction time. The second component (9.44% of the variance) was correlated with serum analyte measurements.
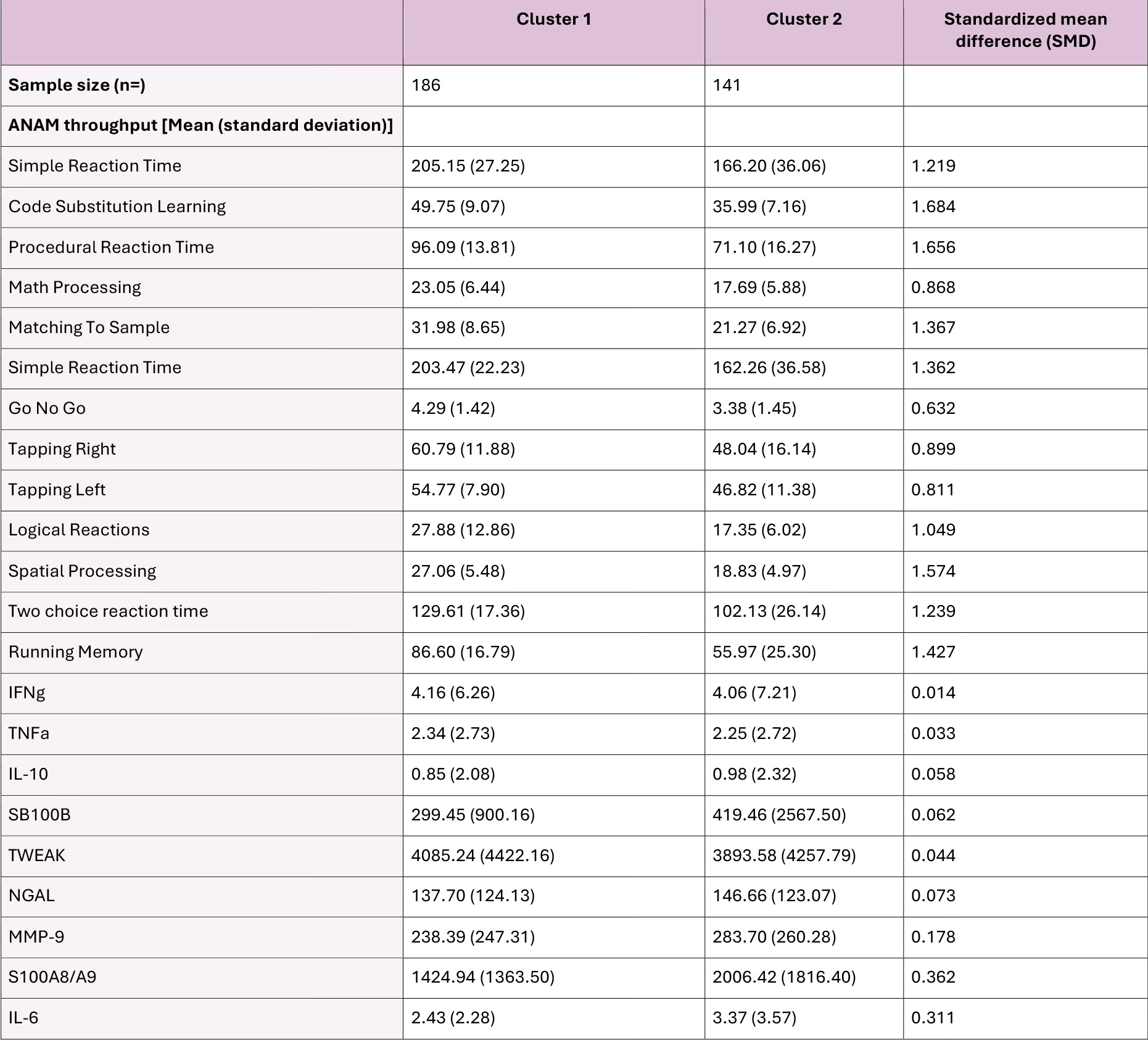
The highest silhouette value was found for 2 (s=0.177) and 3 (s=0.176) clusters. Only 4% of patients were classified in the 3 cluster model, so a 2 cluster model was selected. Cluster 1 had low throughput scores representing CI, and Cluster 2 had higher throughput scores representing no CI. A significant difference was observed in mean serum S100A8/A9 (SMD=0.362), MMP-9 (SMD=0.178) and IL-6 (SMD=0.311) between the 2 clusters, reflected by the correlation between these analytes and the first principal component (Table 1). Serum levels of S100A8/A9, MMP-9, IL-6 had a strongly negative correlation between the Go No Go and Running Memory throughputs (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In patients with SLE, elevated serum S100A8/A9, MMP-9, and IL-6 are associated with low ANAM throughput scores, representing CI. These findings coincide with our recent study showing elevated S100A8/A9 and MMP-9 in patients with CI identified by the ACR-NB. Further studies are needed to uncover mechanistic relationships between these serum analytes and CI in SLE, and whether these analytes may represent valuable therapeutic targets to explore.
Disclosures: E. Neary: None; C. Munoz-Grajales: None; J. Wither: AstraZeneca, 1, 2, Pfizer, 5; J. Diaz Martinez: None; M. Barraclough: None; K. Bingham: None; R. Kretzmann: None; M. Tartaglia: None; L. Ruttan: None; M. Choi: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, 6, Amgen, 2, 6, AstraZeneca, 2, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 6, Celgene, 2, 6, Celltrion, 2, Eli Lilly, 2, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, Janssen, 2, 6, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, 2, Merck/MSD, 2, MitogenDx, 8, Organon, 2, Pfizer, 2, 6, Roche, 2, Werfen, 2; S. Appenzeller: None; S. Marzouk: None; D. Bonilla: None; P. Katz: None; D. Beaton: None; R. Green: None; L. Whittall Garcia: None; D. Gladman: AbbVie, 2, 5, Amgen, 2, 5, AstraZeneca, 2, BMS, 2, Celgene, 2, 5, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, Galapagos, 2, 5, Gilead, 2, 5, Janssen, 2, 5, Novartis, 2, 5, Pfizer, 2, 5, UCB, 2, 5; Z. Touma: None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Neary E, Munoz-Grajales C, Wither J, Diaz Martinez J, Barraclough M, Bingham K, Kretzmann R, Tartaglia M, Ruttan L, Choi M, Appenzeller S, Marzouk S, Bonilla D, Katz P, Beaton D, Green R, Whittall Garcia L, Gladman D, Touma Z. Novel Analytes Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Serum S100A8/A9, MMP-9 and IL-6 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-analytes-associated-with-cognitive-impairment-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-serum-s100a8-a9-mmp-9-and-il-6/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/novel-analytes-associated-with-cognitive-impairment-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-serum-s100a8-a9-mmp-9-and-il-6/