Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:15AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is often characterized by bone loss and fragility fractures and is a frequent comorbidity. The NLRP3 inflammasome, a key mediator of inflammation, drives inflammatory processes that fundamentally accompany the pathogenesis of RA. However, the role of NLRP3 inflammasome in RA fracture healing remains unclear.
Methods: For in vivo analyses, we established tibial fractures in two murine RA models: TNF-transgenic (TNFTg) mice and collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). To address the contribution of NLRP3 inflammasome to fracture repair in RA, we generated TNFTg;NLRP3KO mice by deleting the NLRP3 gene in TNFTg mice. The effects of TNFα overexpression on osteogenic differentiation were assessed using mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPCs) with or without MCC950, a potent and specific inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome. The role of MCC950 in RA fracture repair was investigated using CIA mice.
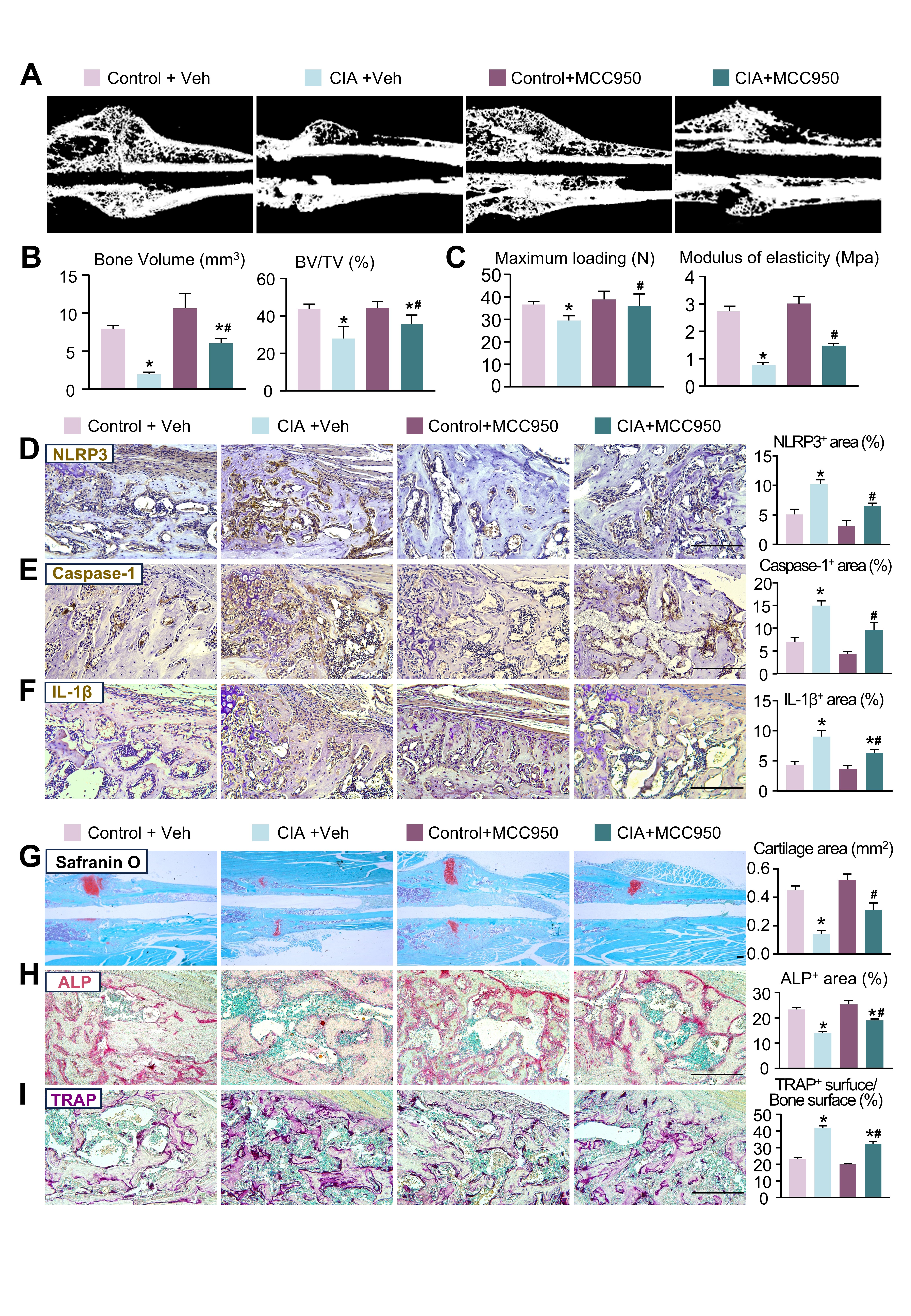
Results: TNFTg mice exhibited delayed fracture healing, characterized by decreased callus bone volume and reduced bone mechanical strength. The NLRP3 inflammasome was excessively activated in TNFTg mice, leading to elevated expression of NLRP3, IL-1β, and Caspase-1. Moreover, NLRP3 deficiency in TNFTg mice significantly mitigated the delayed fracture healing (Fig. 1). Mechanistically, TNFα overexpression suppressed osteogenic differentiation of MPCs through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. This process involves RhoA/Rac1-dependent NF-κB signaling that triggers inflammasome assembly, ultimately leading to IL-1β secretion. Notably, MCC950 administration significantly attenuated these pathological effects. Lastly, in vivo MCC950 treatment rescued the delayed fracture healing by reducing NLRP3 inflammasome activation and promoting bone formation in CIA mice (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: This study provides novel insights into the mechanisms underlying delayed fracture healing in RA and highlights the potential therapeutic benefits of targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome (Fig. 3).
 NLRP3 deficiency improves delayed fracture healing in TNFTg RA mice
NLRP3 deficiency improves delayed fracture healing in TNFTg RA mice
.jpg) MCC950 treatment alleviated the delayed fracture healing in CIA mice
MCC950 treatment alleviated the delayed fracture healing in CIA mice
.jpg) Schematic representation of the NLRP3 inflammasome delaying fracture healing in RA mice through RhoA/Rac1‒IL-1β-mediated osteoblast differentiation
Schematic representation of the NLRP3 inflammasome delaying fracture healing in RA mice through RhoA/Rac1‒IL-1β-mediated osteoblast differentiation
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sun W, Wang H. NLRP3 Inflammasome Impairs Fracture Repair in Rheumatoid Arthritis through RhoA/Rac1-IL1β Axis-Mediated Suppression of Osteoblast Differentiation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nlrp3-inflammasome-impairs-fracture-repair-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-through-rhoa-rac1-il1%ce%b2-axis-mediated-suppression-of-osteoblast-differentiation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/nlrp3-inflammasome-impairs-fracture-repair-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-through-rhoa-rac1-il1%ce%b2-axis-mediated-suppression-of-osteoblast-differentiation/
