Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Hand osteoarthritis (HOA) is a highly prevalent disease, associated with important disability and socio-economic burden. Erosive HOA, almost exclusively found in women, induces more disability, but the pathophysiology is poorly known. Susceptibility genes identified to date only explain a minor proportion of the risk. We have hypothesized that epigenetic processes could play a role and we focused on micro-RNAs, which are small noncoding RNAs interfering with messenger RNAs, leading to their repression or destruction, as potential regulators involved in the pathophysiology of HOA.
Methods: We have assessed HOA status according to ACR criteria for HOA in 1189 post-menopausal women (the QUALYOR Study). We have studied the micro-RNA signature in two steps. First, in the screening phase, we have measured in blood samples the 768 most-described micro-RNAs using Taqman Low Density Array cards (TLDA) after RNA extraction, micro-RNAs reverse transcription and pre-amplification, in 3 different groups: 10 patients with erosive HOA (at least 3 erosive joints), 10 patients with symptomatic HOA without erosions and 10 controls without HOA matched for age and BMI. We have pairwise compared each micro-RNA expression level between HOA groups using Wilcoxon test. The p-values were corrected for false discovery rate (FDR) with the Benjamini-Hochberg method and were considered significant for values < 0.05. In a second step, we will proceed to the validation of micro-RNAs identified at screening phase in larger samples (60 patients with erosive HOA and 60 patients without HOA).
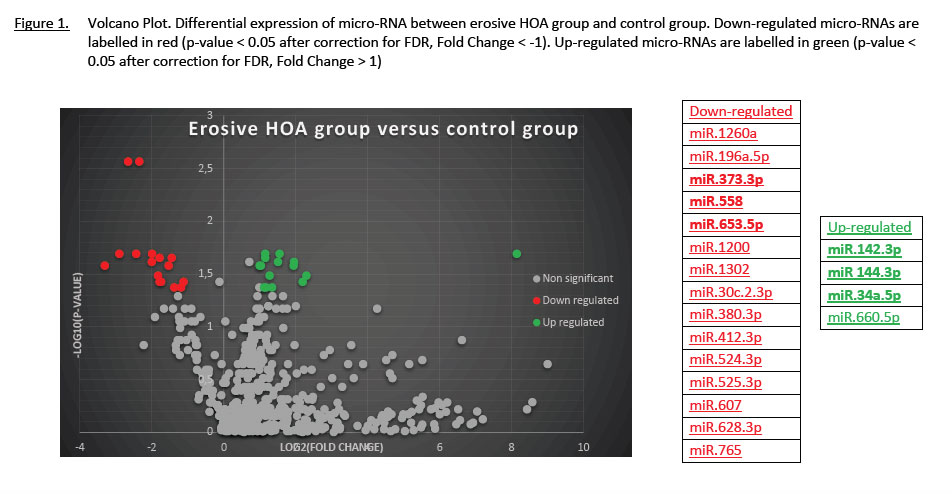
Results: We have first compared micro-RNAs expression levels between the erosive HOA group and controls. After exclusion of micro-RNAs weakly expressed and those that do not segregate clearly between groups, we have identified 12 down-regulated micro-RNAs and 4 up-regulated micro-RNAs. Among these, 4 down regulated (miR 373-3p, miR 558, miR 607 and miR 653-5p) and 3 up-regulated micro-RNAs (miR 142-3p, miR 144-3p and miR 34a-5p) were previously described in chondrocytes homeostasis or osteoarthritis. We have then compared micro-RNAs expression level between erosive HOA and non-erosive HOA but did not find any significant difference, possibly suggesting that even if these two HOA phenotypes are clinically different, some of the pathophysiological mechanisms might be shared.
Conclusion: We have identified for the first time in HOA a micro-RNA signature associated to the disease, that will be validated in the second step of the study. This micro-RNA signature could become a biomarker of interest and could help better understanding the pathophysiology.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Auroux M, Millet M, Merle B, Fontanges E, Duvert F, Gineyts E, Rousseau J, Borel O, Mercier A, LESPESSAILLES E, Chapurlat R. New Biomarkers in Hand Osteoarthritis: The Micro-RNA Signature [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/new-biomarkers-in-hand-osteoarthritis-the-micro-rna-signature/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/new-biomarkers-in-hand-osteoarthritis-the-micro-rna-signature/