Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In this study, we evaluated the safety and efficacy of an implantable, cervical vagus nerve stimulation device for treatment of RA.
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled study enrolled 242 patients at 41 sites in the U.S. with moderate to severe RA, inadequate response or intolerance to at least 1 prior biological DMARD (bDMARD) or targeted-synthetic DMARD (tsDMARD). All patients remained on stable background conventional DMARDs, and were washed off their b/tsDMARD prior to implant procedure. Randomization was 1:1 active (treatment) or non-active (control) stimulation. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving American College of Rheumatology 20% response (ACR20) at Week 12 from day of informed consent. Secondary endpoints included ACR20 from day of randomization, DAS28-CRP good/moderate EULAR and minimum clinically important difference (MCID) responses, and HAQ-DI response. Exploratory endpoints included ACR50/70, DAS28-CRP low disease activity (LDA) and remission, and proportion of erosion progressors ( >0.5 progression) as measured by RAMRIS. After Week 12, the study was open label, with one-way crossover of control to stimulation, with efficacy assessments repeated at Week 24. Patients were imputed as non-responder if rescued with steroids or b/tsDMARDs or if missing any data at Week 12.
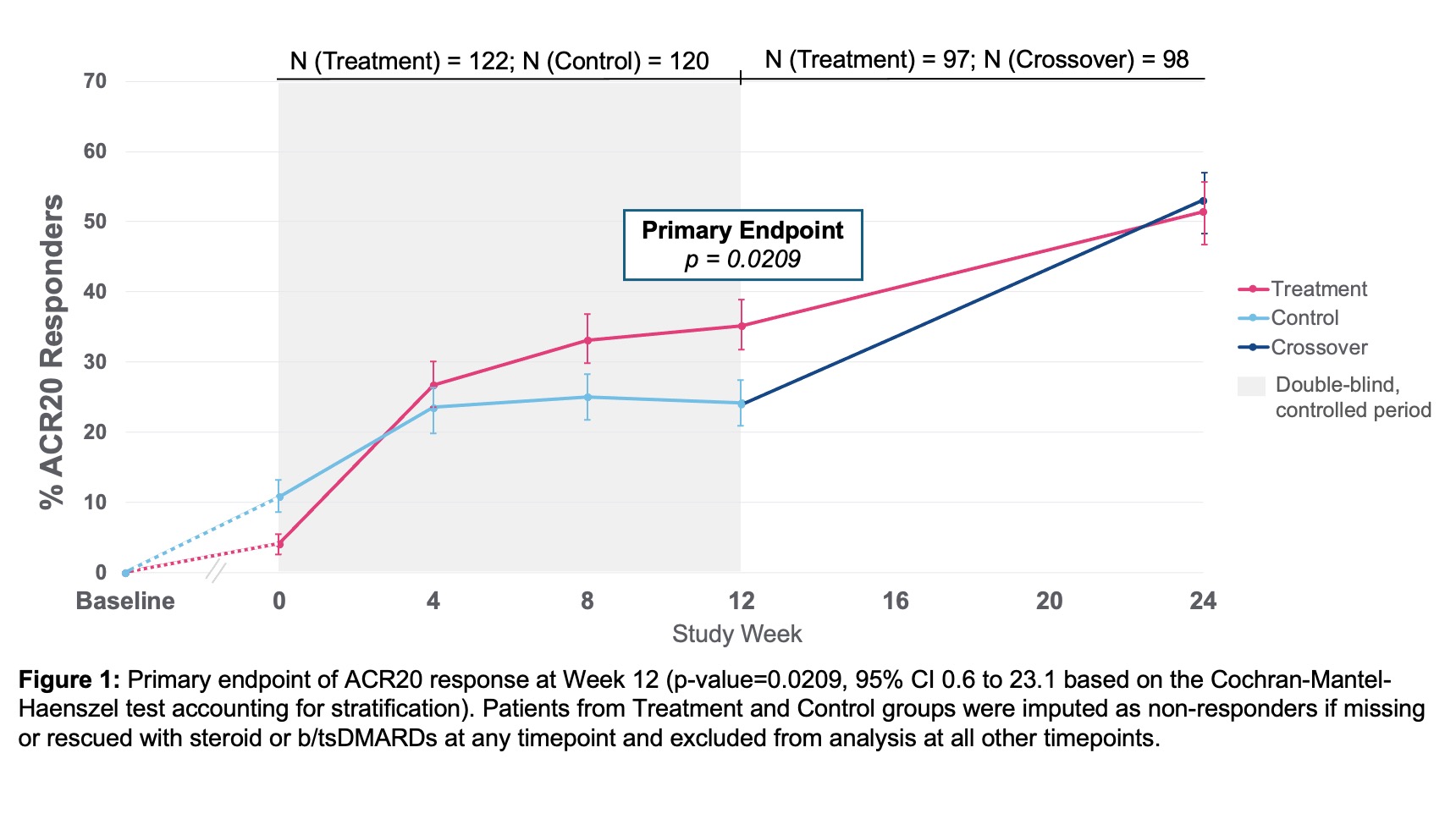
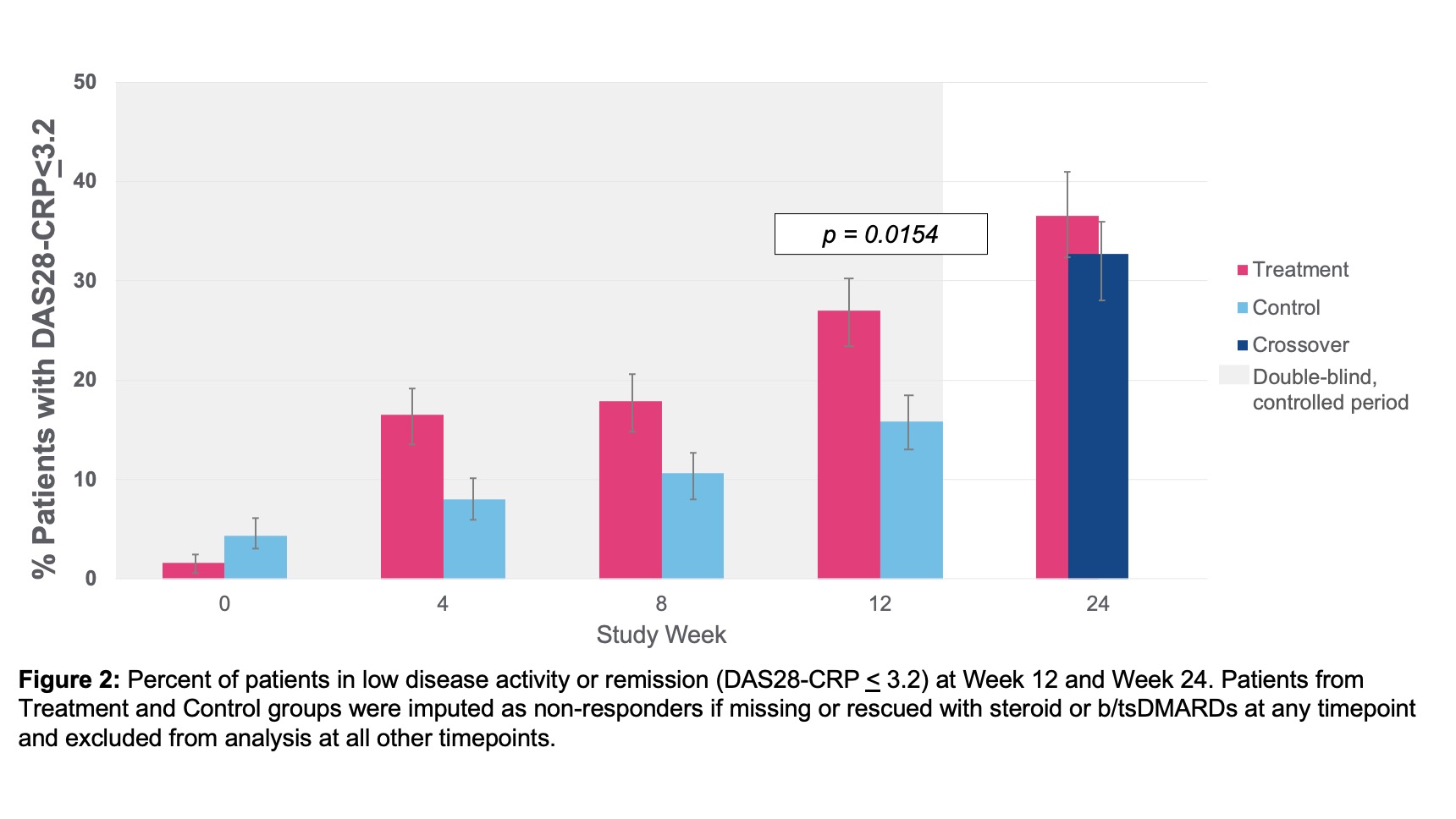
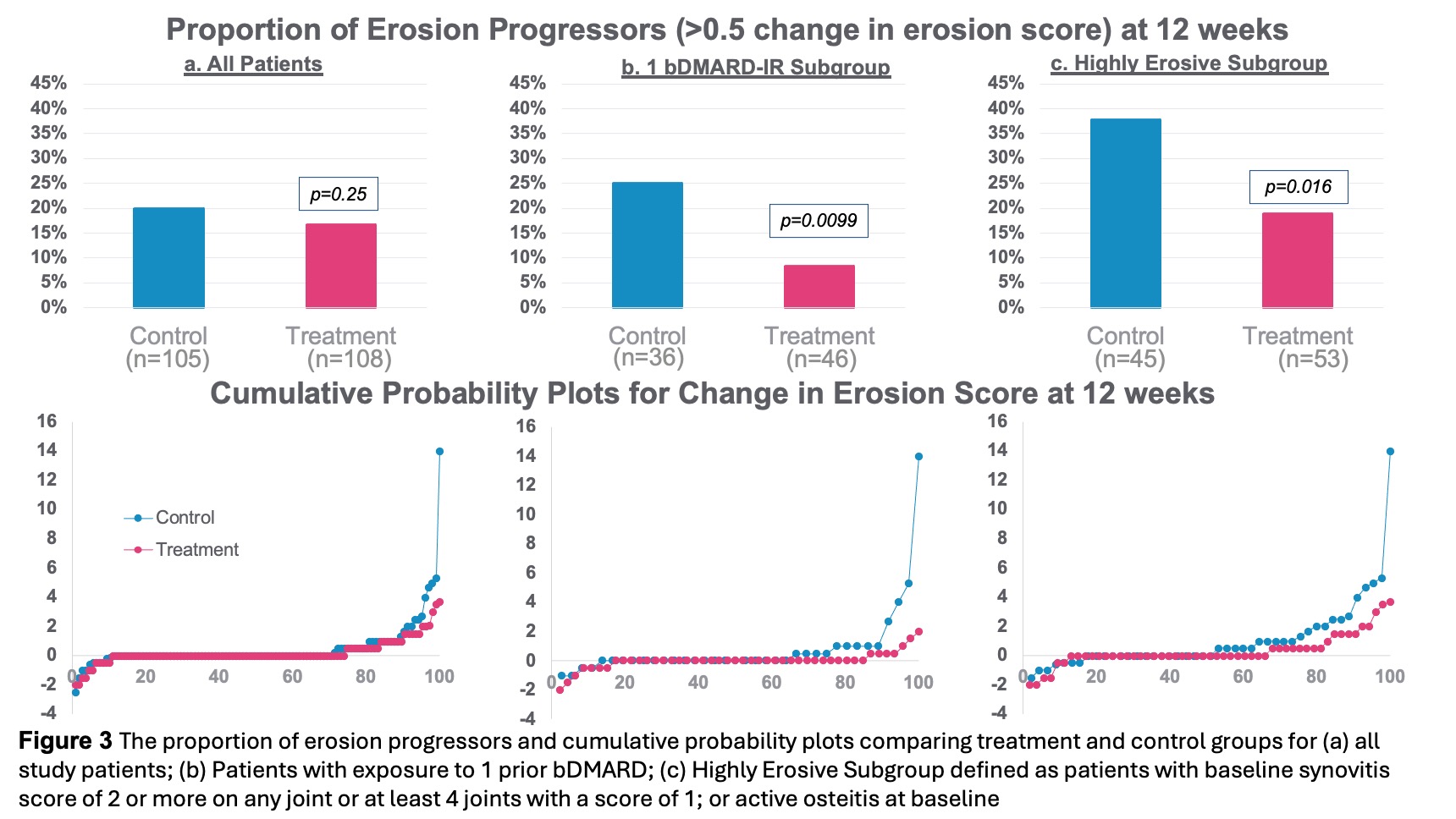
Results: Baseline demographics and characteristics were well-balanced with mean age 56 years, 86% female, RA duration 12 years, BMI 30, 15 tender joints, and 10 swollen joints (28 joint count). Number of prior b/tsDMARDs included 1 prior in 39%, 2 priors in 22%, and ≥3 priors in 39% of patients. 53% seropositive (RF and or anti-CCP) and mean hsCRP 8.2mg/L. ACR20 response at Week 12 showed a statistically significant difference between treatment 35.2% (43/122) vs. control 24.2% (29/120) (p-value=0.0209, 95% CI 0.6 to 23.1). ACR20 response improved further to 51.5% in treatment and 53.1% in control, after crossover, by Week 24 (Figure 1). ACR20 response at Week 12 for patients with 1 prior bDMARD exposure (prespecified analysis) was treatment 44.2% (23/52) and control 19.0% (8/42) (p-value=0.0054, 95% CI 7.1 to 43.3). All secondary and exploratory endpoints trended in favor of the treatment group. DAS28-CRP LDA/remission at Week 12 showed a statistically significant difference between treatment and control groups and improved further through Week 24 (Figure 2). The proportion of erosion progressors was lower in the treatment vs. control group (Figure 3). Overall, the safety profile was acceptable. Related serious adverse event (SAE)-rate was low (1.7%) by ITT. AE with highest frequency related to treatment was mild/moderate hoarseness/vocal cord dysfunction. Stimulation therapy specifically was well-tolerated. There were no deaths in the study. At Week 24, 81% of patients were on stimulation therapy alone and free of added b/tsDMARD.
Conclusion: Neuroimmune modulation using an implantable device to stimulate the vagus nerve is well-tolerated and effective among adults with active RA disease and inadequate response or intolerance to at least one b/tsDMARD. (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04539964)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tesser J, June J, Wickersham P, Box J, Valenzuela G, Crowley A, Kumar N, Gaylis N, Lam G, Ridley D, Pinto-Patarroyo G, Chernoff D. Neuroimmune Modulation in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response or Intolerance to Biological or Targeted Synthetic DMARDs: Results at 12 and 24 Weeks from a Randomized, Sham-Controlled, Double-Blind Pivotal Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neuroimmune-modulation-in-adults-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-or-intolerance-to-biological-or-targeted-synthetic-dmards-results-at-12-and-24-weeks-from-a-randomized-sham-control/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/neuroimmune-modulation-in-adults-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-or-intolerance-to-biological-or-targeted-synthetic-dmards-results-at-12-and-24-weeks-from-a-randomized-sham-control/