Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) patients may have widely divergent scores for pain severity vs X-ray joint damage, indicating that elevated OA pain 0-10 visual numeric scale (VNS) scores may result from several mechanisms, including nociceptive – based on structural damage, nociplastic – based on central sensitization, and comorbidities – including fibromyalgia (FM) and/or depression (DEP). FM and DEP are feasibly-collected on 2 validated indices within a multidimensional health assessment questionnaire (MDHAQ), FAST3F (fibromyalgia assessment screening tool), which agrees ~90% with reference 2011 FM revised criteria and does not include a pain VNS, and MDS2 (MDHAQ depression screen 2), which agrees ~80% with reference PHQ-9 and HADS-D depression scales. We estimated the prevalence of FM and/or DEP in unselected routine care patients with a primary ICD10 diagnosis of OA at two academic clinical settings.
Methods: The MDHAQ is a 2-page patient self-report questionnaire designed for routine care, given to all patients at all visits at the 2 rheumatology settings studied, completed by most patients in fewer than 10 minutes. The MDHAQ includes a 0-10 pain VNS, 0-10 fatigue VNS, 0-3.3 depression query, self-report 0-54 patient painful joint count, 60-symptom checklist including depression, medical history queries, and FAST3F and MDS2 indices. FAST3F is positive (POS) for FM if 2/3 of: fatigue VNS ≥6/10, self-report painful joint count ≥16/54, and/or symptom checklist ≥16/60. MDS2 is POS for depression if 0-3.3 depression query is ≥2.2 OR depression is checked on the symptom checklist. Data were analyzed for the proportion of patients who screened POS or negative (NEG) for FAST3F and/or MDS2 using descriptive statistics and chi square tests.
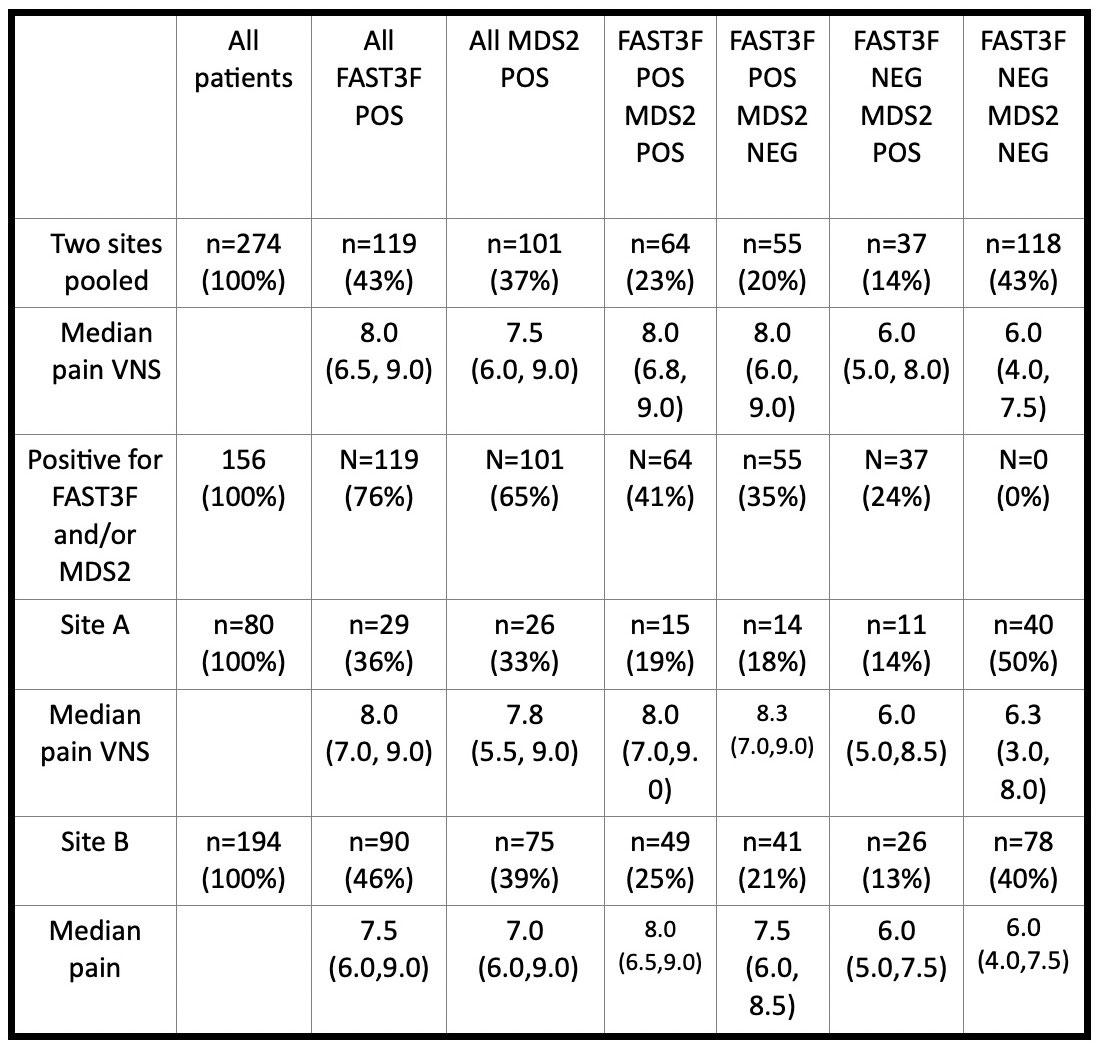
Results: The study included 274 patients with a primary ICD-10 diagnosis of OA, 80 from Site A and 194 from Site B (Table); the patients were typical of OA in age and sex. Among these patients, 43% screened POS for FM by FAST3F, 36% from Site A and 46% from Site B, and 37% screened POS for depression by MDS2, 33% from Site A and 39% from Site B (Table) (chi-square< 2, p >0.15). Overall, 57% screened POS for either FAST3F or MDS2, 14% POS only for MDS2, 20% POS only for FAST3F, and 23% POS for both FAST3F and MDS2, while 43% screened NEG for both indices (Table). Among 156 patients who were FAST3F and/or MDS2 POS, 37 (24%) screened POS only for depression, 55 (35%) POS for only for FM, and 64 (41%) POS for both FM and depression (Table). Median pain score was 6.0 in patients NEG for FAST3F and MDS2 screening, 6.0 in those POS only for MDS2, 8.0 for those POS only for FAST3F, and 8.0 for those POS for both indices, with similar results in the 2 settings (Table).
Conclusion: More than half of patients with OA screen positive for FM and/or depression according to FAST3F and/or MDS2 within an MDHAQ. Median pain VNS is 2/10 units higher in patients with POS screen for FM on FAST3F, but not with POS screen for depression on MDS2. The complexity of pain among OA patients may help to explain a limited response to conventional analgesic therapies in clinical trials and routine care, and of some patients to surgical interventions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pincus T, Gibson K, Schmukler J, Li T, Block J. More Than Half of Patients with Osteoarthritis Have Positive Screening for Fibromyalgia And/or Depression, Feasibly Assessed in Routine Care on Indices Within a Single MDHAQ (multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/more-than-half-of-patients-with-osteoarthritis-have-positive-screening-for-fibromyalgia-and-or-depression-feasibly-assessed-in-routine-care-on-indices-within-a-single-mdhaq-multidimensional-health-a/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/more-than-half-of-patients-with-osteoarthritis-have-positive-screening-for-fibromyalgia-and-or-depression-feasibly-assessed-in-routine-care-on-indices-within-a-single-mdhaq-multidimensional-health-a/