Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are heterogeneous immature myeloid cells with suppressive functions. It is known that MDSCs are expanded in inflammatory sites after migrating from bone marrow (BM) or spleen. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized as polyarthritis. Although previous reports indicate that MDSCs are increased in BM and spleen of arthritis model mice, detailed analysis of MDSCs in inflammatory joints is very limited.
The purpose of this study is to characterize the MDSCs in the joints of autoimmune arthritis.
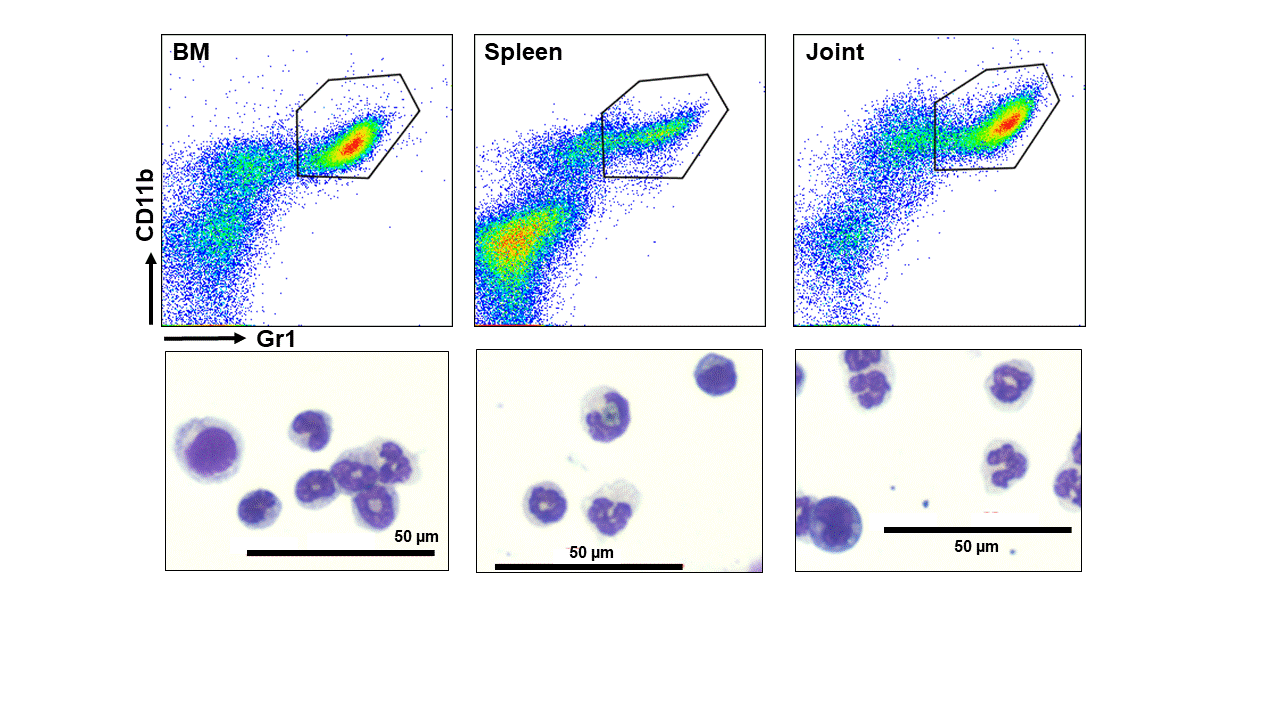
Methods: We isolated CD11b+Gr1+ cells as MDSCs from joints (Jo-MDSCs), bone marrow (BM-MDSCs) and spleen (Sp-MDSCs) of arthritis-induced SKG mice, and investigated differential expressed genes (DEGs) among MDSCs from three tissues by microarray analysis. Based on the results, we analyzed the suppressive function and the osteoclast differentiation ability of MDSCs from each organ.
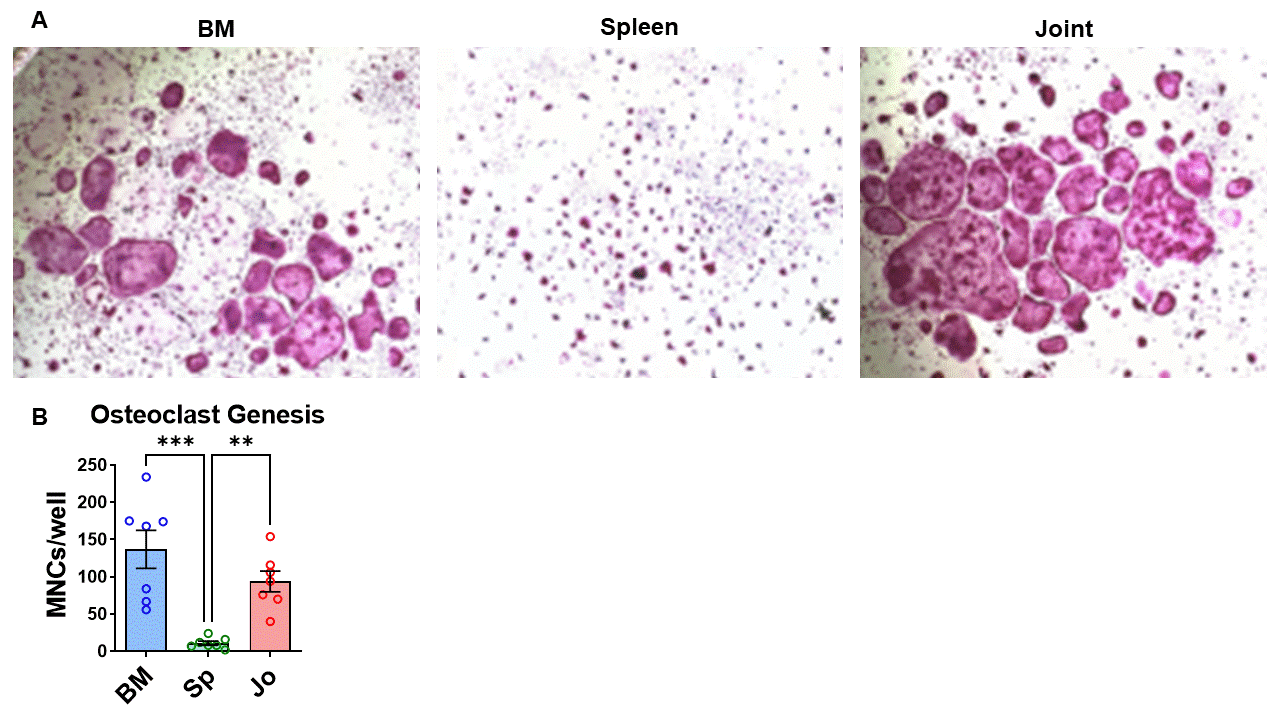
Results: We detected CD11b+Gr1+ cells as MDSCs in joints of SKG arthritic mice by flowcytometric analysis and morphological inspection. Microarray analysis revealed that Jo-MDSCs had differential characteristics compared with BM-MDSCs or Sp-MDSCs. Microarray and qPCR analysis showed that Jo-MDSCs highly expressed immunosuppressive DEGs (Pdl1, Arg1, Egr2 and Egr3). In vitro, Jo-MDSCs suppressed CD4+ T cell proliferation with significance compared to control (% proliferated cells: 44±4 % and 70±3 % for Jo-MDSCs and control, respectively; p< 0.01). Microarray analysis also revealed that Jo-MDCSs highly expressed NF-κB non-canonical pathway DEGs (Nfkb2 and Relb), which is relevant to osteoclast differentiation. In vitro, Jo-MDSCs differentiated into osteoclasts but not Sp-MDSCs (Count of multiple nuclei cells/well: 94±14 and 11±3 for Jo-MDSCs and Sp-MDSCs, respectively; p< 0.01).
Conclusion: Jo-MDSCs are immunosuppressive while potentially differentiate into osteoclasts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fujikawa Y, Sendo S, Nagamoto T, Yamamoto Y, Okano T, Nishimura K, Ueda Y, Saegusa J. MDSCs in Inflammatory Joints of SKG Mice Suppress T Cells and Differentiate into Osteoclasts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mdscs-in-inflammatory-joints-of-skg-mice-suppress-t-cells-and-differentiate-into-osteoclasts/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mdscs-in-inflammatory-joints-of-skg-mice-suppress-t-cells-and-differentiate-into-osteoclasts/