Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Neutrophils play a central role in host defense, but they also play important effectors on acute and chronic inflammation. Neutrophil apoptosis is essential for the resolution of inflammation. Previous studies have shown that delayed apoptosis of neutrophils correlate with the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study aimed to investigate the effects of LY294002, the PI3K inhibitor, on neutrophil apoptosis in RA patients and collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice.
Methods: The peripheral blood from untreated RA patients (n=25) and healthy volunteers (HC) (n=15) were isolated the neutrophils by density gradient centrifugation and cultured with or without LY294002(LY) in vitro for 18 h. The rate of neutrophils apoptosis were analyzed by flow cytometry and the intracellular protein of PI3K-Akt pathway in neutrophils were measured by Western blot. CIA mice were treated with vehicle or LY294002, and then analyzed the effect of LY294002 on arthritis as well as the apoptosis rate of neutrophils from peripheral blood of CIA mice.
Results: The peripheral blood neutrophils apoptosis delayed in RA patients as compared with neutrophils from HC. LY294002 could significantly promote neutrophils apoptosis in peripheral blood from RA patients (Figure1 A). The expression of phosphorylation PI3K(p-PI3K), p-Akt were increased in RA patients and LY294002 inhibited the expression of p-Akt (Figure1 B). Moreover, LY294002 treatment delayed the onset, reduced the severity of arthritis in CIA mice (Figure2).The peripheral blood neutrophils apoptosis delayed in CIA mice as compared with the control group, and LY294002 treatment facilitated the neutrophil apoptosis (Figure3).
Conclusion: This data suggested that delayed apoptosis of neutrophils played an important role in the development of RA, therefore, inhibition of PI3K pathway to facilitate neutrophil apoptosis are possible approaches to reduce inflammatory arthritis which might open new doors to future clinical treatment of RA.
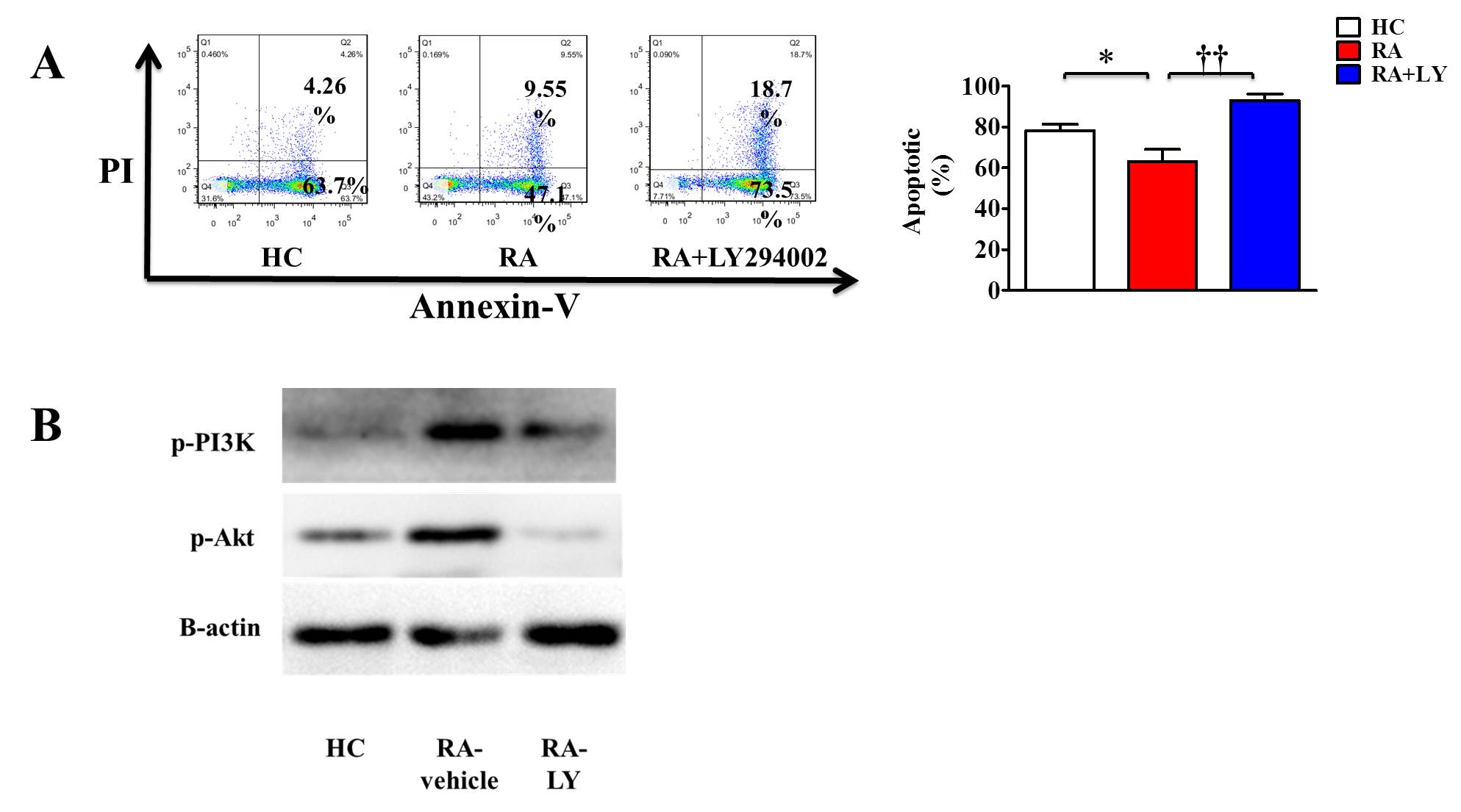 Figure1 (A) Apoptosis rate of neutrophils in peripheral blood of healthy controls(HC) or rheumatoid arthritis(RA) patients.(B) The expression of p-PI3K and p-Akt in HC and RA. *HC compare with RA **p<0.01 † LY294002(LY) treatment group compare with untreated group † † p<0.01
Figure1 (A) Apoptosis rate of neutrophils in peripheral blood of healthy controls(HC) or rheumatoid arthritis(RA) patients.(B) The expression of p-PI3K and p-Akt in HC and RA. *HC compare with RA **p<0.01 † LY294002(LY) treatment group compare with untreated group † † p<0.01
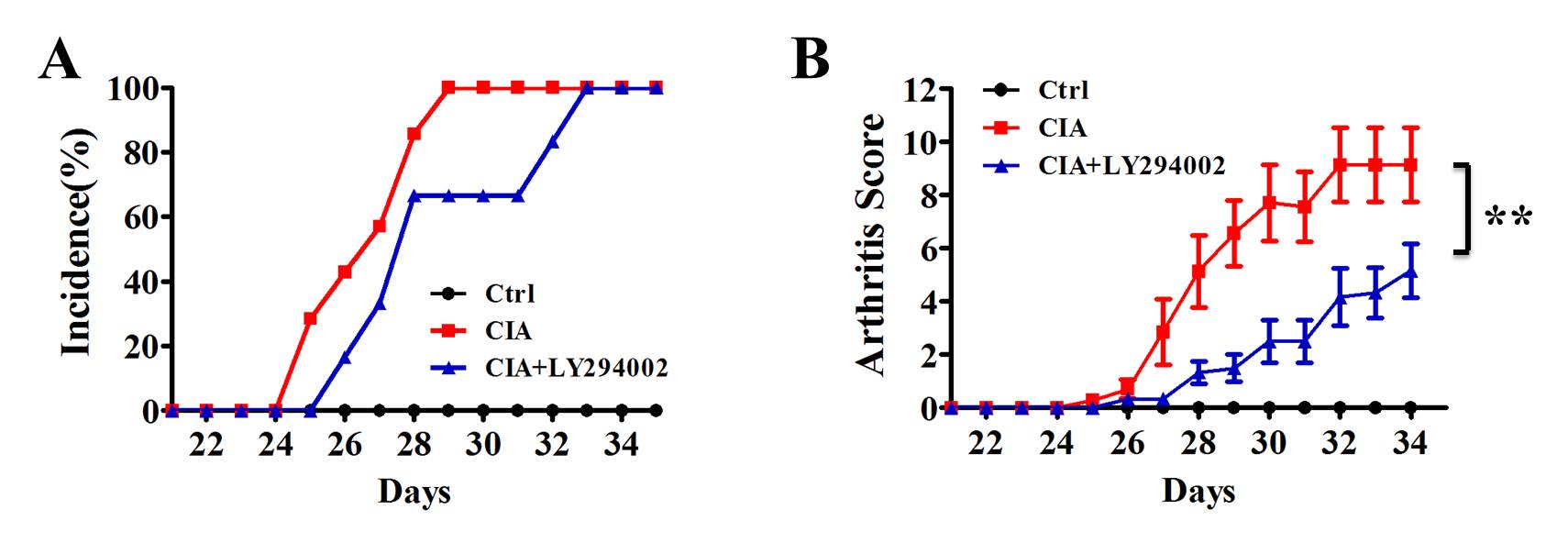 Figure2 LY294002 treatment delayed the onset(A), reduced the severity (B)of arthritis in CIA mice.*CIA+LY294002 compare with CIA **p<0.01
Figure2 LY294002 treatment delayed the onset(A), reduced the severity (B)of arthritis in CIA mice.*CIA+LY294002 compare with CIA **p<0.01
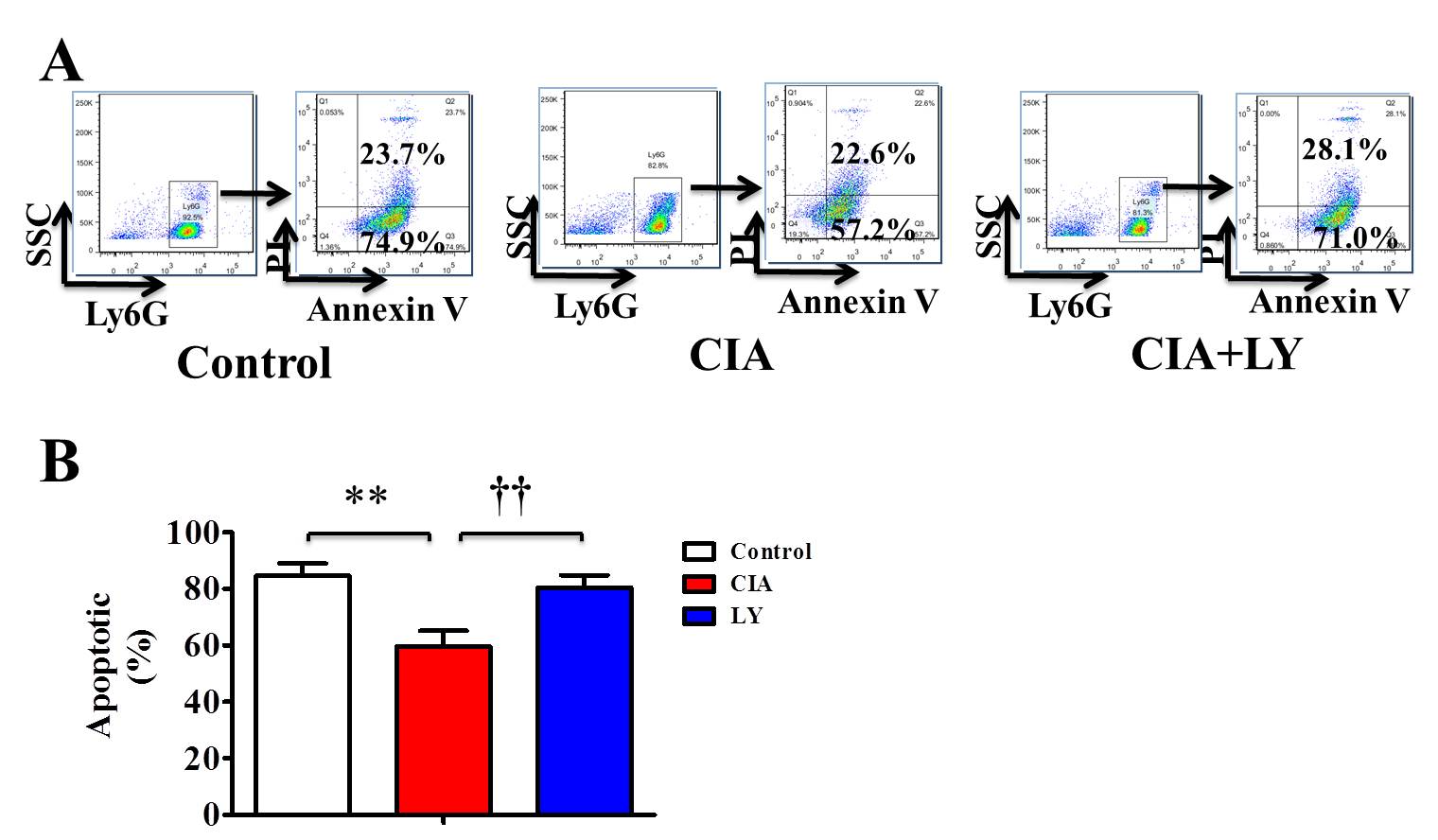 Figure3 Apoptosis rate of neutrophils in peripheral blood of Collagen-Induced Arthritis(CIA) mice. *Control compare with CIA **p<0.01 † LY294002(LY) treatment group compare with untreated group † † p<0.01
Figure3 Apoptosis rate of neutrophils in peripheral blood of Collagen-Induced Arthritis(CIA) mice. *Control compare with CIA **p<0.01 † LY294002(LY) treatment group compare with untreated group † † p<0.01
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huang X, Li T, Chen S, Huang Z, Chen J. LY294002 Improves the Collagen-induced Arthritis by Inducing Neutrophil Apoptosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ly294002-improves-the-collagen-induced-arthritis-by-inducing-neutrophil-apoptosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ly294002-improves-the-collagen-induced-arthritis-by-inducing-neutrophil-apoptosis/
