Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1553–1591) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is highly prevalent in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and a leading cause of mortality. Recent studies have identified clinical risk factors for new onset of ILD at both 1-year and long-term follow-up (1,2), still not optimally identifying patients at high risk. Pulmonary vascular volume (PVV%) quantified on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is associated with both presence and severity of SSc-ILD (3). In this study, we investigate the potential of radiomics in identifying patients with risk of developing ILD.
Methods: We included patients from a single SSc referral centre, with no ILD on baseline HRCT and at least one clinical and HRCT follow-up. Images 1) were assessed by experienced thoracic radiologist for presence/absence of ILD at all timepoints, 2) underwent lung texture analysis (LTA, Imbio), quantifying PVV, normal lung, lung pathologies (hyperlucency, ground-glass, reticular, honeycombing), as percentage of the lung volume, both for whole lungs and for upper, middle, lower zones.Univariable and multivariable prediction models were developed to identify radiomics risk factors for ILD onset, using Cox regression and generalizes estimating equation (GEE) analysis for ILD onset ever and at 1-year, the latter allowing for multiple observations of the same patient. Both models were adjusted for the established clinical risk factors (1,2).
Results: Among 248 SSc patients with no ILD at baseline HRCT, new onset of ILD occurred in 54 (22%) cases over a median follow-up of 39 (24-72) months. Patients developing ILD were more frequently males, with diffuse skin involvement, anti-topoisomerase I antibodies and shorter disease duration (Table I, left panel). Additionally, patients with new onset ILD over the study period presented higher values of PVV across all lung zones at baseline HRCT (Table II). In multivariable Cox regression analysis, new ILD onset was independently predicted by PVV% from the whole lung [HR 1.054 (1.030-1.078)], as well as from each individual zone. When integrating the PVV% of each single zone with the clinic risk factors in the multivariable analysis, we observed the significant, independent impact of the lower zone PVV% [HR 1.217 (1.113–1.332)], in addition to the known risk associated with clinical features [HR 3.281 (2.145–5.021)] (Fig IA).Focusing on 1-year ILD onset, we analysed 279 follow-up visits from 193 patients and observed 22 (11.4%) new onset ILD (Table I, right panel). On univariable GEE, we confirmed the association of PVV from the whole lung on ILD onset, with particular focus on the middle and upper zones, alongside the clinical risk factors. When tested in a multivariable model adjusted for clinical risk factors, PVV% of the upper zone remained significantly associated with ILD onset [OR 4.127 (1.016–16.761)] (Fig IB).
Conclusion: PVV% from HRCT scans of SSc patients without ILD can predict new onset of ILD at both 1-year and long-term follow-up, supporting the use of radiomics in clinical risk phenotyping.References1. Petelytska, L., et al., Arthritis Rheumatol, 20232. Hoa S, et al., Arthritis Rheumatol. 20253. Occhipinti M, et al., PLoS One. 2019
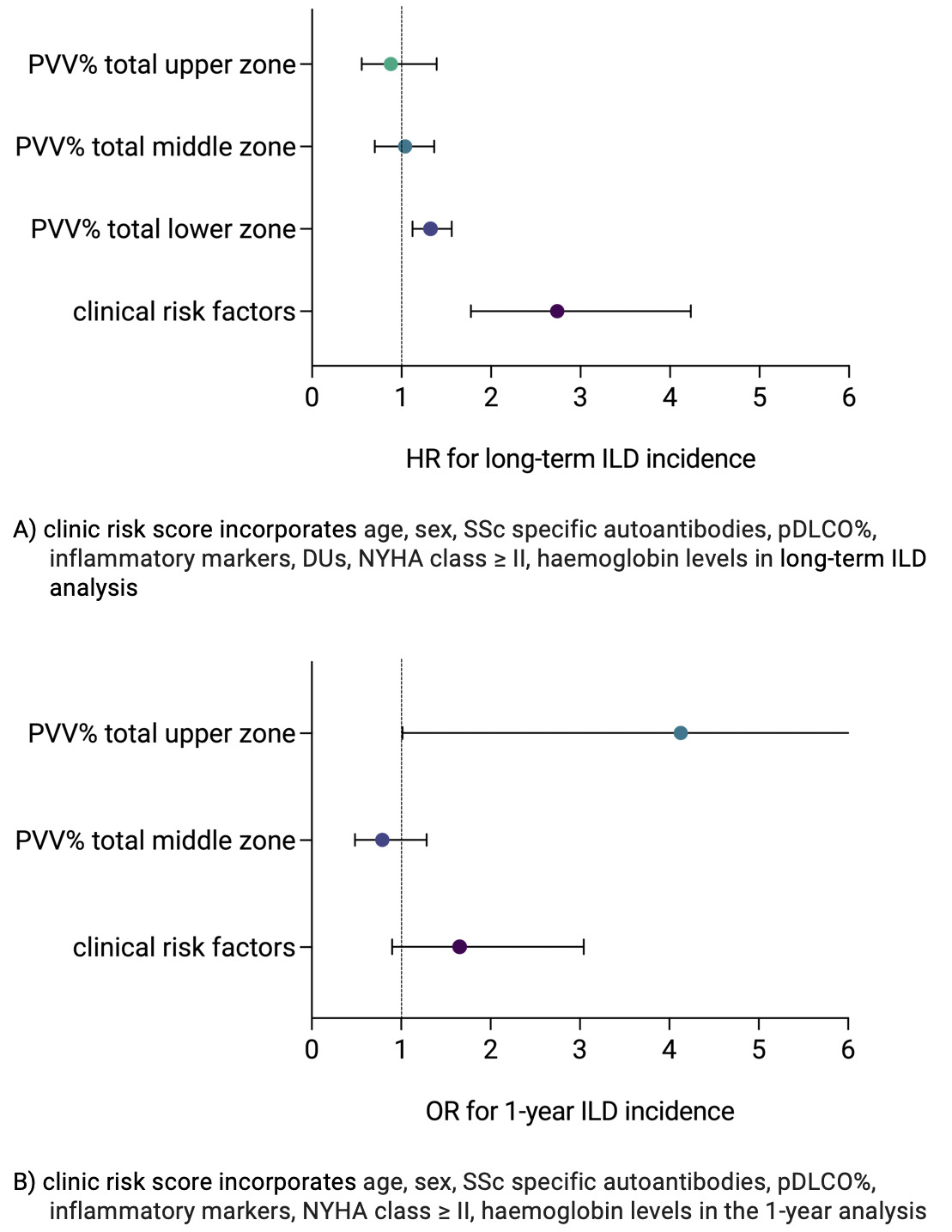 Table I. Clinical characteristics and functional features of SSc patients with and without ILD onset ever and ILD onset 1-year
Table I. Clinical characteristics and functional features of SSc patients with and without ILD onset ever and ILD onset 1-year
ACA: anti-centromere antibodies ATA: anti-topoisomerase I antibodies; ARA: anti-RNA polymerase III antibodies; antiPm/Scl: anti-PM-scleroderma-antibodies; dcSSc: diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis; NVC: nailfold videocapillaroscopy; NYHA: New York Hearth Association; pFVC%: predicted forced vital capacity; pDLCO/SB%: predicted diffusion of the lung for carbon monoxide on single breath; 6MWT: 6 minutes walking test; SD: standard deviation.
Increased inflammatory markers defined as ESR or/and CRP above normal limit
.jpg) Table II. Distribution of parenchymal and vascular radiomics parameters among SSc patients with and without ILD-onset ever.
Table II. Distribution of parenchymal and vascular radiomics parameters among SSc patients with and without ILD-onset ever.
Data are presented as percentage of lung volume (total or upper/middle/lower zone).
PVV: pulmonary vascular volume
.jpg) Fig I: Forrest plot showing predictive radiomics and clinical risk factors for long-term ILD incidence (A) and 1-year ILD incidence (B)
Fig I: Forrest plot showing predictive radiomics and clinical risk factors for long-term ILD incidence (A) and 1-year ILD incidence (B)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Iacovantuono M, landini N, Jungblut l, Sauer G, Dobrota R, Muraru S, Elhai M, Mihai C, Becker M, Chimenti M, Frauenfelder T, Hoffmann-Vold A, Distler O, Bruni C. Lung vasculature quantification on computed tomography predicts new onset of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lung-vasculature-quantification-on-computed-tomography-predicts-new-onset-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lung-vasculature-quantification-on-computed-tomography-predicts-new-onset-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis/
