Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2227–2264) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a frequent complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ranging from subclinical ILD to advanced fibrosis, and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Despite advancing immunosuppressive and antifibrotic therapies, many progress to end-stage respiratory failure and may require lung transplantation. The aim of this study was to compare clinical characteristics and lung transplant outcomes in patients with RA to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). In addition, a meta-analysis was performed to evaluate RA-ILD lung transplant outcomes in the literature.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed clinical data collected in patients with ILD diagnosed with RA and IPF who underwent bilateral lung transplant between January 1, 2014 and April 30, 2024 at the Vancouver General Hospital, and between January 1, 2012 and December 31, 2024 at the Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal. All RA patients satisfied their respective ACR classification criteria. Continuous variables were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test, categorical variables with Fisher’s Exact test, and survival using Kaplan-Meier analysis.For meta-analysis, we searched MEDLINE, Embase and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews from database inception to April 6, 2025. Participants were individuals with RA-ILD who underwent lung transplants. The outcomes studied were overall survival and morbidity following transplant. Bibliographies of selected articles were hand-searched for additional references. Data were extracted using a standardized extraction form. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Pooled post-transplant survival was combined for RA-ILD and IPF individually using a random effects model.
Results: In the retrospective analysis, we identified 27 RA and 64 IPF patients. RA patients were younger than IPF patients at ILD diagnosis (median age 57 vs 60.5, p=0.0028), more likely to be on pre-transplant immunosuppression (92.6% vs 6.2%, p< 0.001), and less likely to receive antifibrotics (22.2% vs 64.1%, p< 0.001). No difference was seen in one-year or cumulative survival. Post-transplant lung function, acute rejection, infection-related hospitalization, malignancy, and chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) were similar. IPF patients had more UIP patterns on explant pathology, whereas RA patients had more NSIP or mixed NSIP/UIP patterns.For our meta-analysis, four studies met inclusion criteria. At one year post-transplant, the pooled survival rate of RA-ILD patients was 72.1% (60.5-82.3% 95% CI, I2=45.8%), whereas in IPF patients, the pooled survival was 76.5% (74.6-78.2% 95% CI, I2=61.8%).
Conclusion: Post-transplant survival, lung function, and complication rates were comparable between RA and IPF patients at one year and at last follow-up, with the median follow up duration being 3.9 years and 3.6 years respectively. Our meta-analysis demonstrated improved short-term survival following lung transplantation compared to previously reported studies.
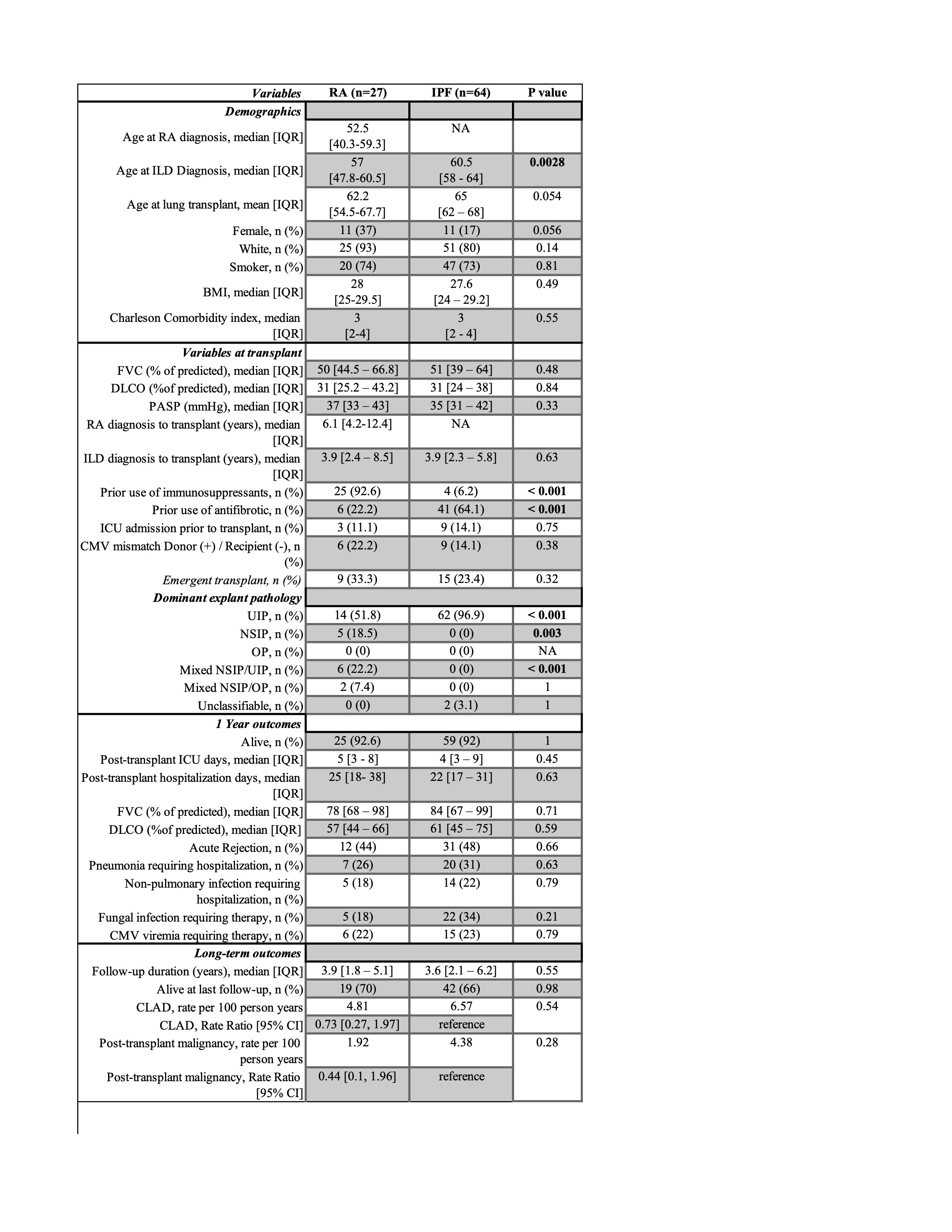 Table 1. Patient baseline characteristics, pre-transplant variables and post-transplant outcomes.
Table 1. Patient baseline characteristics, pre-transplant variables and post-transplant outcomes.
.jpg) Figure 1. Kaplan Meier survival curve Figure 1. Kaplan Meier survival curve
Figure 1. Kaplan Meier survival curve Figure 1. Kaplan Meier survival curve
.jpg) Figure 2: Meta-analysis forest plot of one-year post-transplant survival rate of RA-ILD patients and IPF patients.
Figure 2: Meta-analysis forest plot of one-year post-transplant survival rate of RA-ILD patients and IPF patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
AlHajeri S, Major M, S. Jalaledin D, Daviault B, Shah A, Yu A, Hoa S, Levy R, Wilson J, Poirier C, Choi J, Yee J, Landon-Cardinal O, Huang K, Kim H. Lung Transplant Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Compared to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Multicentric Retrospective Analysis and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lung-transplant-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-compared-to-idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis-a-multicentric-retrospective-analysis-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lung-transplant-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-compared-to-idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis-a-multicentric-retrospective-analysis-and-meta-analysis/
