Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2177–2194) Sjögren’s Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lung cysts are a frequent finding in patients with SS, with previous data indicating a prevalence of approximately 30% on chest CT scans. In SS, it is postulated that, among others, its genesis may be due to bronchiolar obstruction by the lymphoid tissue. Retrospective and small-sample data showed that the disease was not associated with radiological progression, suggesting an innocuous disease. However, prospective data are scarce.
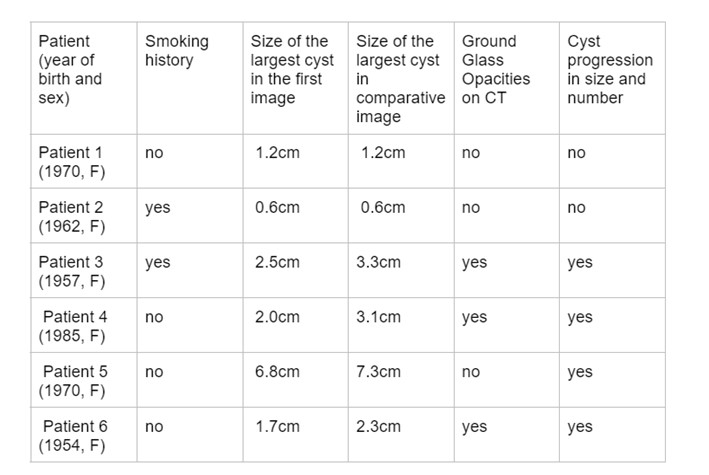
Methods: Between 2015 and 2019, patients classified as having primary SS (pSS) according to the 2002 American-European Consensus or the 2016 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and respiratory asymptomatics were systematically evaluated using high-resolution chest CT. Cysts were defined as an air space delimited by a thin (< 2 mm) layer of thin layer.Other findings were classified according to the standard descriptive guidelines. Patients with findings of pulmonary cysts on examination were subsequently evaluated with a new CT scan within at least 1 year, using the same CT machine, and analyzed by the same thoracic radiologist. The cysts were characterized comparatively by their largest diameters and numerically. Patients who increased in size by at least 0.5 cm and the total number of cysts were considered to have radiological progression.
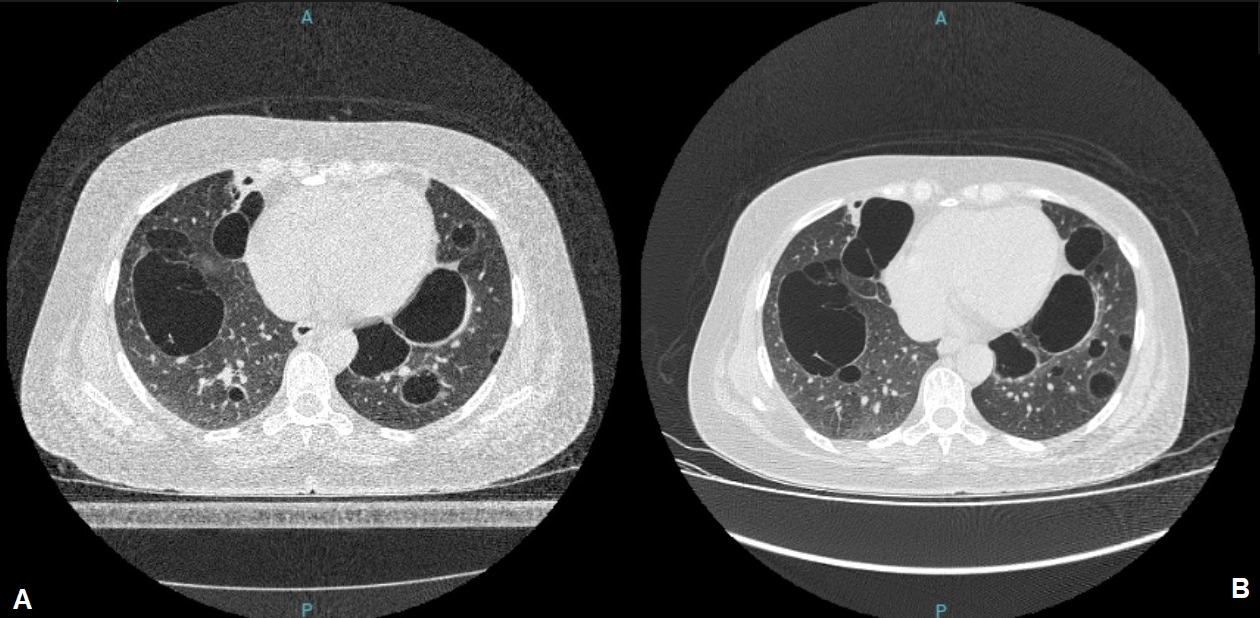
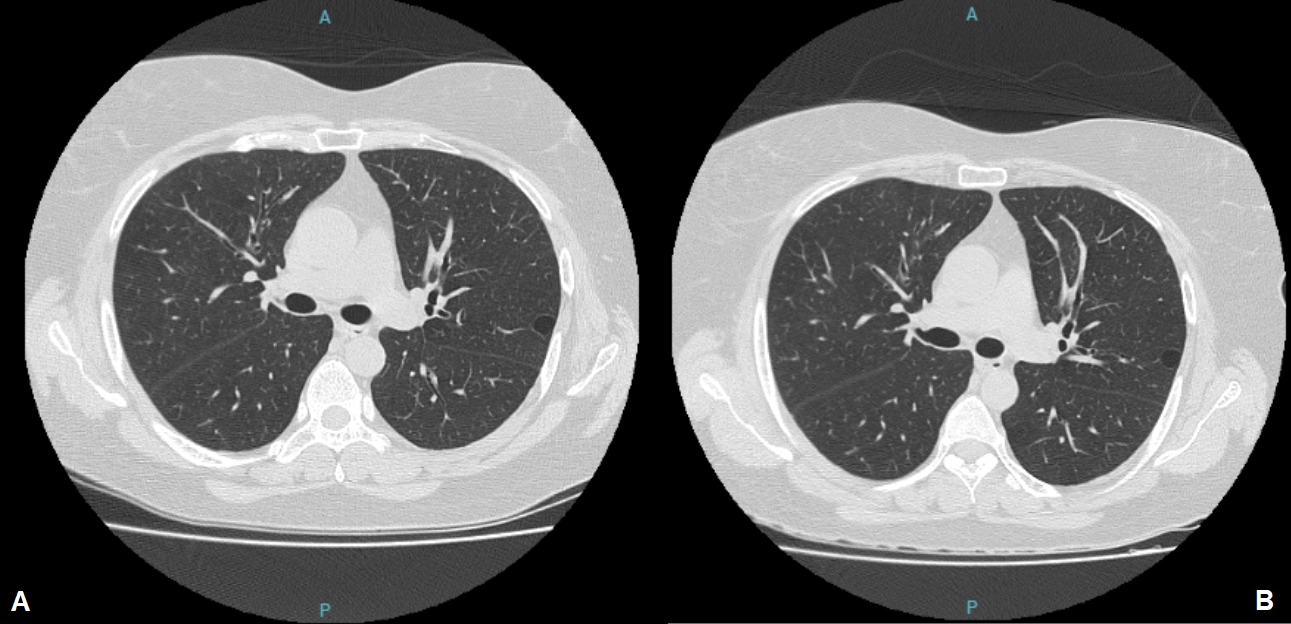
Results: Thirty-five patients with pSS without respiratory symptoms were evaluated using high-resolution chest CT. Of these, 11 (31.4%) had at least one lung cyst, and in six, a prospective evaluation was performed (the remaining patients were not evaluated because of difficulties caused by the Covid-19 pandemic). Among them, four patients showed an increase in both the size and quantity of the cysts, especially those with cysts larger than 2 cm in diameter and with ground-glass opacities on CT. Two patients who had fewer than five cysts each, all smaller than 1.3 cm, had no radiological evolution. In figure 1, we summarize the main radiological characteristics of the evaluated patients, and in figures 2 and 3, we illustrate two patients with lung cysts but with different evolutions.
Conclusion: We found a high prevalence (31.4%) of lung cysts in asymptomatic respiratory patients with pSS who underwent chest CT scans, with most showing radiological progression. In our small sample, patients with cysts > 2 cm or those with ground-glass opacity showed radiological progression. Our findings do not support the hypothesis that lung cysts in patients with pSS do not progress, and point to the need for further larger studies to better evaluate this common lung manifestation of pSS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sewa Marques R, Zacarin M, Bellini P, Dudienas D Pereira R, Guinami Scabora A, Sachetto Z, Bertolo M, PUGLIESI A. Lung Cysts in Primary SS: New Findings on an Allegedly Innocuous Iiagnosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lung-cysts-in-primary-ss-new-findings-on-an-allegedly-innocuous-iiagnosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lung-cysts-in-primary-ss-new-findings-on-an-allegedly-innocuous-iiagnosis/