Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: T follicular helper cells (Tfh) constitute a distinct CD4+ helper T-cell subset, promoting B-cell maturation and activation. Circulating Tfh (cTfh) seem to play a critical role in auto-immune diseases. The aim of this study was to analyze cTfh cells involvement in active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), before and after three months of Adalimumab treatment.
Methods: Adalimumab treatment was introduced in biologics-naive RA patients. Disease activity score (DAS) was evaluated at baseline and 3 months later. At baseline, all RA patients have an active disease with a DAS > 3.2 and a corticosteroid treatment > 15 mg per day. All patients vaccinated less than 3 months before Adalimumab initiation were excluded. Three months after Adalimumab initiation, RA patients were classified in responders (R) or non-responders (NR) according to the DAS value (< or > 3.2). cTfh characterization was performed in healthy volunteer controls (HC), and in RA patients before and after 3 months of Adalimumab treatment. Fifteen-color panels of flow cytometry was used to define T helper cells, T regulatory cells, B cells, cTfh cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RA–CXCR5+), effector PD1+ cTfh subset (CD3+CD4+CD45RA–CXCR5+ PD1+), and cTfh1 subset (CD3+CD4+CD45RA–CXCR5+CXCR3+CXCR6–). cTfh related cytokine, interleukin 21 (IL21), was also quantified in RA plasma, at baseline and 3 months later.
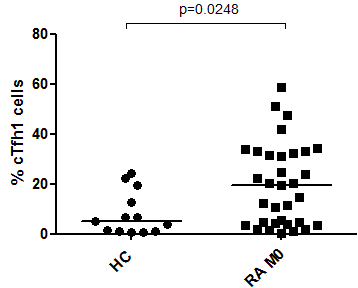
Results: The results concerned 33 RA patients and 13 HC. Mean age of patients was 58.6 years. Mean RA duration was 8.8 years. Mean DAS value was 4.28. Rheumatoid factors (RF) were positive in 72.7% patients. At baseline, frequency of cTfh1 cells (p=0.0248) (Figure 1), cTfh PD1+ (p=0.004) and IL21 plasma concentration (p=0.003) were higher in RA compared to HC. Moreover, a significant positive correlation was observed between the DAS value, and the percentage of cTfh PD1+ cells (r=0.3479; p=0.0472) (Figure 2) and IL21 plasma concentration (r=0.3755; p=0.0313). After 3 months of treatment, 20 RA patients (60.1%) achieved DAS response. Percentage of cTfh1 was significantly lower in responders than in non-responder patients (p=0.006) (Figure 3). Under treatment, IL21 plasma concentration decreased in all RA patients (p=0.0402).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that cTfh1 cells are involved in RA activation and in a clinical adequate response to adalimumab. Further analysis of these patients is necessary to understand the relationship between cTfh cells, the cTfh1/cTfh2 balance, B cells activation and antibodies production.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lucas C, Codo R, Albert J, Jean R, Rodriguez S, Amé-Thomas P, Perdriger A. Low Frequency of Circulating T Follicular Helper 1 Cells Is Associated to Adequate Response to Adalimumab Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-frequency-of-circulating-t-follicular-helper-1-cells-is-associated-to-adequate-response-to-adalimumab-therapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-frequency-of-circulating-t-follicular-helper-1-cells-is-associated-to-adequate-response-to-adalimumab-therapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/