Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-Drug antibodies (ADAb) are well studied and have an impact on response to treatment with monoclonal anti-TNF biologics. Rituximab treatment has an important immunogenic potential as it is a chimeric antibody. Most recent studies on biosimilars have identified low rates of ADAb among rituximab-treated patients without impact on treatment efficacy. The lack of sensitivity in the detection of ADAb might explain discrepancies between TNFi and rituximab. Methotrexate has been associated with less occurrence of ADAb when co-administered with adalimumab. CD73 and CD39 are ectoenzyme involved in the pathway of adenosine production, a known mechanism of action of methotrexate. The objective of this study was to characterize if CD39 and CD73 expression on B cells was a predictor of occurrence of ADAb in a population of RA patients treated with rituximab.
Methods: ABIRISK is an IMI-2 European consortium designed to identify predictors of ADAb among rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. Prospective assessment of ADAb was performed using sensitive technique based on Meso Scale diffusion. Response to rituximab was assessed at 6 months using delta DAS 28. Patient’s PBMCs at baseline were assessed for B cell lineage markers and CD73 and CD39 using flow cytometry.
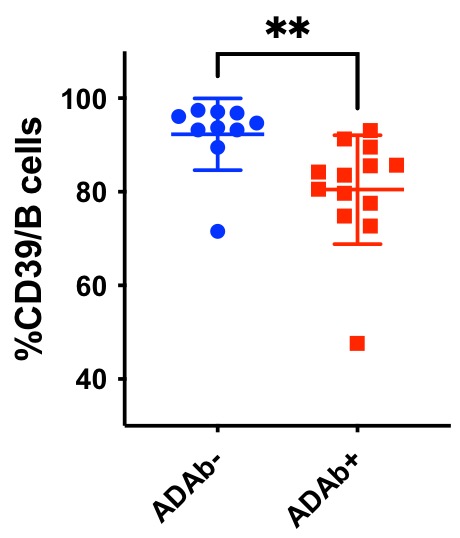
Results: Among the 23 analyzed RA patients treated with rituximab, 13 became ADAb+ and 10 remained ADAb negative. There was no difference in the proportion of patients with concomitant methotrexate in both groups with 77 % and 80% in ADAb+ and ADAb- respectively. B cells lineage markers did not vary between patients’ groups. Baseline levels of CD73 expression on B cells were similar among patients who later became ADAB+ or negative. At baseline lower levels of CD39 expression on B cells was significantly predictive of the future appearance of ADAb (see figure). There was a trend of correlation between pre-treatment CD39 expression levels and delta DAS 28 at 6 months indicating a potential diminished response to treatment in patients with lower CD39 expression (p= 0,059).
Conclusion: Pre-treatment lower CD39 expression levels on B cells is predictive of the future appearance of ADAb directed against rituximab in RA patients. CD 39 levels trended to negatively correlate with less treatment efficacy. Since the number of patients co-treated with methotrexate is not significantly different between ADAb+ and ADAb- patients, we might hypothesize that the level of CD39 accounts for the occurrence of ADAb. This suggests that the level of adenosine that might be modulated by methotrexate or by the level of CD39 expression may impact the occurrence of anti-rituximab antibodies in RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bitoun S, Ly B, Hässler S, Paoletti A, Gleizes A, Hacein-Bey S, Bröet P, Pallardy M, Mariette X. Low CD39 Expression on B Cells Predicts the Occurrence of Anti-Drug Antibodies in RA Patients Treated with Rituximab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-cd39-expression-on-b-cells-predicts-the-occurrence-of-anti-drug-antibodies-in-ra-patients-treated-with-rituximab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-cd39-expression-on-b-cells-predicts-the-occurrence-of-anti-drug-antibodies-in-ra-patients-treated-with-rituximab/