Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Osteoarthritis & Joint Biology – Basic Science (0940–0943)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:15AM-9:30AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterized by increased cartilage thinning, bone remodeling, and inflammation. Post-traumatic OA, which develops after acute direct trauma to the joints, accounts for approximately 12% of all OA cases.1 Current therapeutic options focus on alleviating symptoms and pain rather than disease modification. Lorecivivint (LOR; SM04690), an intra-articular (IA), small-molecule CLK/DYRK inhibitor that modulates the Wnt pathway, has been shown in animal studies to induce chondrogenesis, protect cartilage, and reduce inflammation and, thereby, improve joint health.2 A single IA LOR injection was evaluated in a rat model of knee instability to determine its protective and regenerative effects when injected at different timepoints after induction of post-traumatic OA.
Methods: Knee instability/post-traumatic OA was surgically induced in rats by combining anterior cruciate ligament transection with partial medial meniscus transection (ACLT+pMMx). LOR (0.3 µg) or vehicle was injected into the IA space of the damaged knee at 2, 3, or 4 weeks after induction of OA. OA-induced (n=10/group) or sham-operated (surgery without ACLT+pMMx; n=5/group) rats were sacrificed at the injection timepoint (baseline) or 12 weeks after LOR/vehicle injection (study conclusion). Histological grades were evaluated using the summed OARSI scores (stage and grade of cartilage damage)3 of the anterior and posterior medial femoral condyle (MFC) and medial tibial plateau (MTP). Weight distribution analysis was performed using an incapacitance meter at several timepoints. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
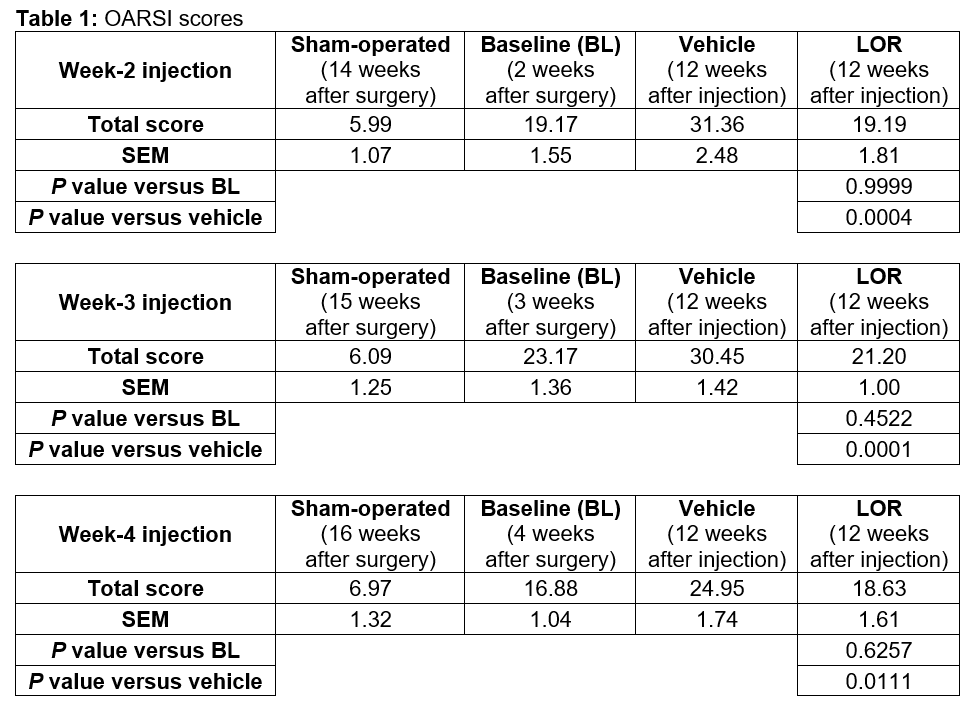
Results: ACLT+pMMx surgeries led to increased OARSI scores in rats by 2 weeks compared with sham surgeries. LOR treatment at Weeks 2, 3, and 4 led to significant decreases (P< 0.05) in total OARSI scores (Table 1) at the end of the study compared with vehicle treatment. Rats treated with LOR for 12 weeks and rats at injection baseline had similar OARSI scores, suggesting that LOR treatment arrested the progression of cartilage damage. Significant improvements (P< 0.05) were also observed in the weight distribution of LOR-treated rats in the 3- and 4-week groups at 6 and 12 weeks after their respective IA injections compared with vehicle-treated rats.
Conclusion: LOR exhibited cartilage-protective effects and slowed disease progression in the ACLT+pMMx model in vivo and, therefore, has potential as a structure-modifying treatment for OA.
References:
- Englund M, et al. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009.
- Collins JE, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019.
- Pazin DE, et al. Dev Dyn. 2012.
- Deshmukh V, et al. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2019.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Seo T, Deshmukh V, Yazici Y. Lorecivivint (SM04690), an Intra-articular, Small-Molecule CLK/DYRK Inhibitor That Modulates the Wnt Pathway, Provided Cartilage-Protective Effects in an Animal Model of Post-traumatic OA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lorecivivint-sm04690-an-intra-articular-small-molecule-clk-dyrk-inhibitor-that-modulates-the-wnt-pathway-provided-cartilage-protective-effects-in-an-animal-model-of-post-traumatic-oa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lorecivivint-sm04690-an-intra-articular-small-molecule-clk-dyrk-inhibitor-that-modulates-the-wnt-pathway-provided-cartilage-protective-effects-in-an-animal-model-of-post-traumatic-oa/