Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologicals – bring a hope of recovery or amelioration to people suffering from RA, but only half of the patients respond to such treatment. Therefore, finding reliable biomarkers predicting response is very valuable. Previously we demonstrated that central nervous system (CNS) response to nociceptive stimuli, measured by fMRI of the brain, decreases already after 24 hours and that a higher pre-treatment BOLD signal volume seems to predict clinical response to treatment with certolizumab-pegol (CZP). 1,2 Therefore we hypothesized that the CNS response upon compression of a painful joint could predict subsequent anti-TNF treatment response.
To follow the longitudinal effect of CZP treatment on brain activity in RA patients stratified byhigh and low brain activation volumes measured by BOLD fMRI at baseline and to compare their brain activity during 24 weeks of treatment to that of placebo in DMARD-refractory RA patients.
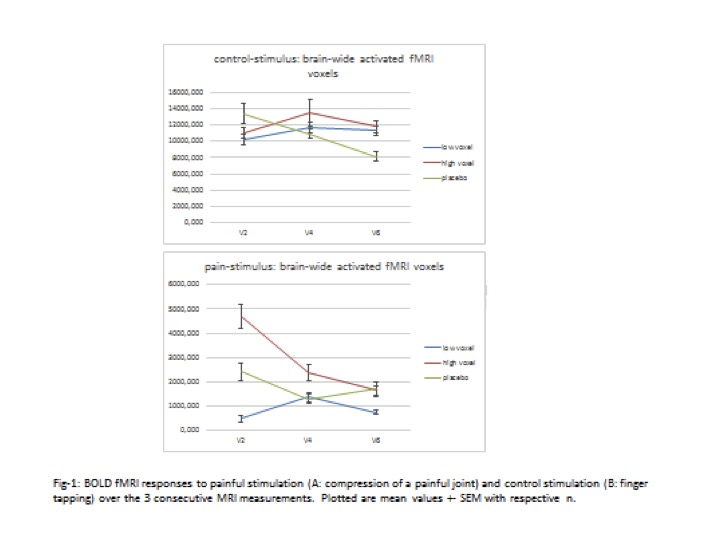
Methods: Adult RA patients fulfilling the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria with a DAS28 >3.2 under stable DMARD treatment for at least 3 months were eligible. Patients underwent the first fMRI at screening for stratification. Whole brain BOLD-signal-voxel-count of 700 classifying between low and high and patients were randomized to CZP or placebo (2:1 ratio) resulting in 3 study arms (CZP low voxel count (CZP-L), CZP high voxel count (CZP-H), and placebo). The second fMRI was performed after 12 and the third fMRI – after 24 weeks. In parallel control stimulation we measured brain activation during non-painful finger tapping.
Results: 156 patients, inadequate responders to csDMARD signed the informed consent. In the finger tapping control paradigm, fMRI showed no significant changes in the number of brain-wide activated voxels in CZP-L and CZP-H arms, but, surprisingly, there was a significant decrease (p=0.043) in the placebo arm in fMRI-3 compared to the pre-treatment fMRI-1 value. By painful stimulation in CZP-L fMRI showed significant increase in the number of brain-wide activated voxels (p=0.043) in fMRI-2 as compared to fMRI-1 with no further significant changes. Most importantly, in CZP-H the number of activated voxels was significantly reduced (p=0.037) in fMRI-2 and continued to decrease further in fMRI-3 ( p=0.007).
Conclusion: As revealed by our study high pre-treatment fMRI BOLD brain activity in response to pain seems to serve as a (long-term) positive predictor of patient’s response to CZP treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rech J, Schenker H, Tascilar K, Hagen M, Valor Mendez L, Schoenau V, Sergeeva M, Prade J, Sulvakumar M, Konert L, Kleyer A, Simon D, Strobelt S, Behrens F, Baerwald C, Finzel S, Voll R, Hueber A, Feist E, Roesch J, da Silva J, Doerfler A, Damjanov N, Hess A, Schett G. Longitudinal Change in the Central Nervous System Pain Response After Treatment with Certolizumab or Placebo. a Post-hoc Analysis from the Pre-CEPRA Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-change-in-the-central-nervous-system-pain-response-after-treatment-with-certolizumab-or-placebo-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-the-pre-cepra-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-change-in-the-central-nervous-system-pain-response-after-treatment-with-certolizumab-or-placebo-a-post-hoc-analysis-from-the-pre-cepra-trial/