Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 29, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical III (2651–2656)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:45AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Digital ulcers (DUs) affect approximately 50% of SSc patients, causing significant pain and disability. Current management involves both systemic and local therapies. However, the burden in terms of pain and quality of life due to refractory DUs remains heavy. Indeed, over 67% of SSc patients experience >5 DUs in their disease course, reflecting the high burden of this disease domain. While selexipag, an oral selective IP prostacyclin receptor agonist, is approved for the treatment of SSc-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), its potential in healing DUs is largely unexplored. We aimed at evaluating the long-term efficacy of selexipag compared to iloprost in treating SSc-DUs.
Methods: This retrospective multicentre study included 96 SSc patients with refractory DUs, 32 treated with selexipag (median dose of 1600mg/day- IQR1100mg) and 64 with intravenous iloprost (0.5–2ng/kg/min), matched for gender, disease subset, and age at diagnosis (Table 1). Both groups were concomitantly treated with conventional vascular therapies (i.e. calcium channel blockers, endothelin receptor antagonists and phosphodiesterase 5- inhibitors). DUs number, ischemic pain and Raynaud phenomenon (RP) severity were assessed at baseline, 6,12, and 24 months. Pain and RP were evaluated using Likert Pain Scale (LPS) and Raynaud Condition Score (RCS), respectively. Additionally, DUs recurrence and new onset were recorded. Healing rates were estimated using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Results: DUs healing rate was significantly higher in selexipag-treated patients in comparison with iloprost-treated ones (87% vs 28%) at 96 weeks, with the formers achieving faster healing (75% vs 18% by week 40) (p< 0.001) (Figure1). DUs number, RCS and LPS scores showed significant improvement in selexipag-treated group compared to iloprost (p< 0.001 for all) throughout the 24-month follow-up (Figure 2 A-B-C). Repeated measures analysis demonstrated significant changes over time for all three outcomes. The difference in treatment effect was supported by Mann-Whitney U analyses, showing comparable baseline measures (DUs: p=0.901; RCS: p=0.561; LPS: p=0.708) significant differences emerged by 6 months (DUs: p=0.001; RCS: p< 0.001; LPS: p< 0.001) and were maintained through 12 and 24 months (all p< 0.001). Additionally, selexipag-treated patients experienced significantly lower relapse rates (5% vs 45% at 24 months, p< 0.001) (Figure2D). Consistently, DUs formation remained lower with selexipag (5% vs 40% at 24 months, p< 0.001)(Figure 2E).
Conclusion: Our study shows that SSc patients treated with selexipag have a better sustained outcome of DUs compared to those treated with intravenous iloprost over 24 months. Furthermore, oral administration and good tolerability profile make selexipag a promising alternative option to standard therapy for SSc-related DUs, overcoming challenges such as difficult venous access, high hospitalization costs, and lost work productivity associated with IV administration. Prospective studies are needed to confirm a wider use of selexipag other than PAH.
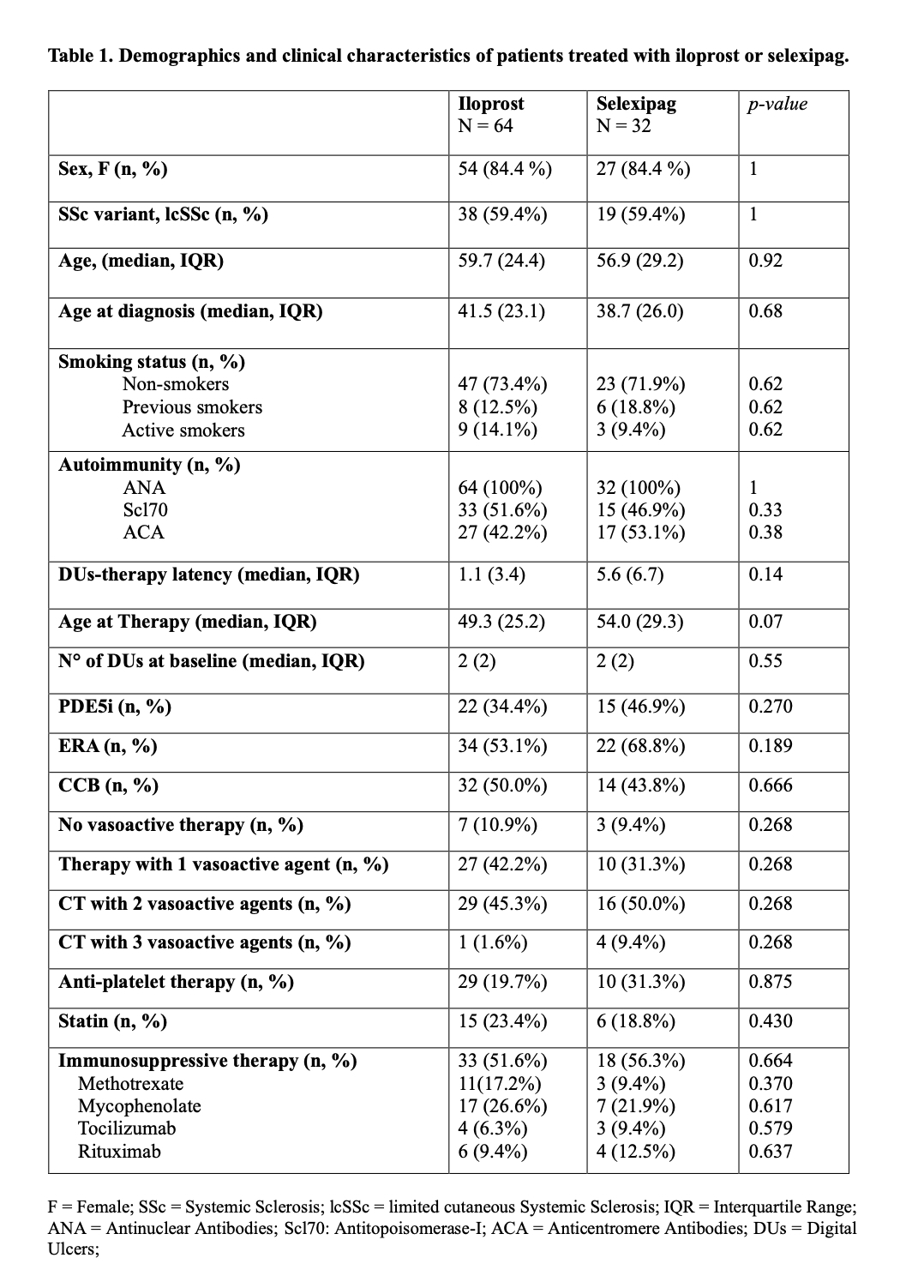 Demographics and clinical characteristics of patients treated with iloprost or selexipag.
Demographics and clinical characteristics of patients treated with iloprost or selexipag.
.jpg) Kaplan-Meier analysis showing cumulative healing rates of DUs in SSc patients treated with selexipag versus iloprost over 96 weeks of
Kaplan-Meier analysis showing cumulative healing rates of DUs in SSc patients treated with selexipag versus iloprost over 96 weeks of
follow-up.
.jpg) Clinical outcomes comparing Iloprost (blue) versus Selexipag (red) therapies in scleroderma patients over 24 months. Panels show: (A) Digital ulcer reduction, (B) Pain scale improvement, (C) Raynaud condition score decrease, (D) Relapse rates, and (E) New ulcer rates. Error bars represent standard deviation; asterisks indicate statistical significance.
Clinical outcomes comparing Iloprost (blue) versus Selexipag (red) therapies in scleroderma patients over 24 months. Panels show: (A) Digital ulcer reduction, (B) Pain scale improvement, (C) Raynaud condition score decrease, (D) Relapse rates, and (E) New ulcer rates. Error bars represent standard deviation; asterisks indicate statistical significance.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Iannone C, Di Battista M, Pellico M, Magi i, Minniti A, Armentaro G, Cavalli S, Sette M, Giudice L, Bochicchio C, Della Rossa A, Tavoni A, Cacciapaglia F, Stano S, Orlandi M, Giuggioli D, Mosca M, Caporali R, Del pAPA N. Long-term effect of selexipag in systemic sclerosis-associated digital ulcers: a case control, multicentre, observational study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-effect-of-selexipag-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-digital-ulcers-a-case-control-multicentre-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/long-term-effect-of-selexipag-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-digital-ulcers-a-case-control-multicentre-observational-study/
