Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Human OA-affected cartilage does not show the cardinal signs of inflammation (redness and swelling with heat and pain—rubor et tumor cum calore et dolor) because of its unique architecture (avascular, aneural and alymphatic) of the cartilage. However, there is an upregulation of inflammatory mediators at the molecular and biochemical levels [1]. We examined if the human OA-affected cartilage [a] induced innate anti-inflammatory mediators like Lipoxin A4 [LXA4] to counter and promote inflammation resolution in OA, [b] if so, what was the range and mechanism of action of LXA4 at the genomics level in human OA-affected chondrocytes.
Methods: Primary human OA-affected cartilage or chondrocytes were examined for spontaneous release of LXA4 [in ex-vivo] condition using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and LXA4-specific ELISA. Furthermore, the effects of recombinant LXA4 [rLXA4] were validated in TNFα induced primary human neutrophils in vitro. The rLXA4 and then tested in spontaneous or IL-1β induced primary human OA-affected cartilage or human or bovine chondrocytes. Gene expression arrays and bioinformatic analysis examined the total genome. Inflammatory mediators were ELISA or RIA.
Results: LXA4 and 15-epi-LXA4 was spontaneously released [or augmented by IL-1β] in ex-vivo conditions in human OA-affected cartilage and chondrocytes. Exogenously added LXA4 (1nM) significantly [p ≤ 0.01] inhibited 77% TNFα-induced PGE2 production in human neutrophils. 1-100 nM of LXA4 significantly [p ≤ 0.01] inhibited IL-1β induced nitric oxide (NO), and PGE2, in human OA-affected cartilage, -chondrocytes or bovine chondrocytes. IL-1β and LXA4 exhibited an antagonistic pattern of gene expression in human chondrocytes. Specifically, LXA4 inhibited (basal and/or IL-1β-induced) gene expression of inflammatory mediators, their receptors and signaling apparatus [e.g., IL-8, CSF1, IL-1β, IL-1R1, IL-1R2, IL-6, IL-6STP1, TNFα, TNFRSF1A/B, ICAM1, SELE, CD44, ITGAV, CCL-20, -2 -3, CCL4L2, CXCR- 5, -7, MMP-1, -3, -13, -14, CD-46, -55, -59, LTC4, LTB4, LTA4, PTGS2 and PTGES]. Furthermore, LXA4 upregulated the expression of inhibitors of inflammation such as CR-1, TIMP-2 and -4, ARG-1, -2, IL-10, and IL-11. Unlike IL-1β, LXA4 induced lipoxygenases [ALOX5, ALOX5AP, ALOX15B], phospholipases [PLA2G1B, PLA2G7], and PGD synthase of the eicosanoid pathway. LXA4 significantly dampened the cycloxygenase pathway and related prostaglandins.
Conclusion: Human OA-affected cartilage spontaneously releases LXA4 and 15-epi-LXA4. rLXA4 inhibits gene expression of [basal and IL-1β-induced] inflammatory mediators. Furthermore, LXA4 induced lipid class switching by shifting the regulation of cyclooxygenases towards the leukotriene pathway discretely from IL-1β. LXA4 exhibits multiple targets and mechanisms during anti-inflammatory, pro-resolving, and tissue repairing activity in human cartilage and chondrocytes.
References:
- Attur et al. Osteoarthritis or osteoarthrosis: The definition of inflammation becomes a semantic issue in the genomic era of molecular medicine. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, (2002) 10, 1–4.
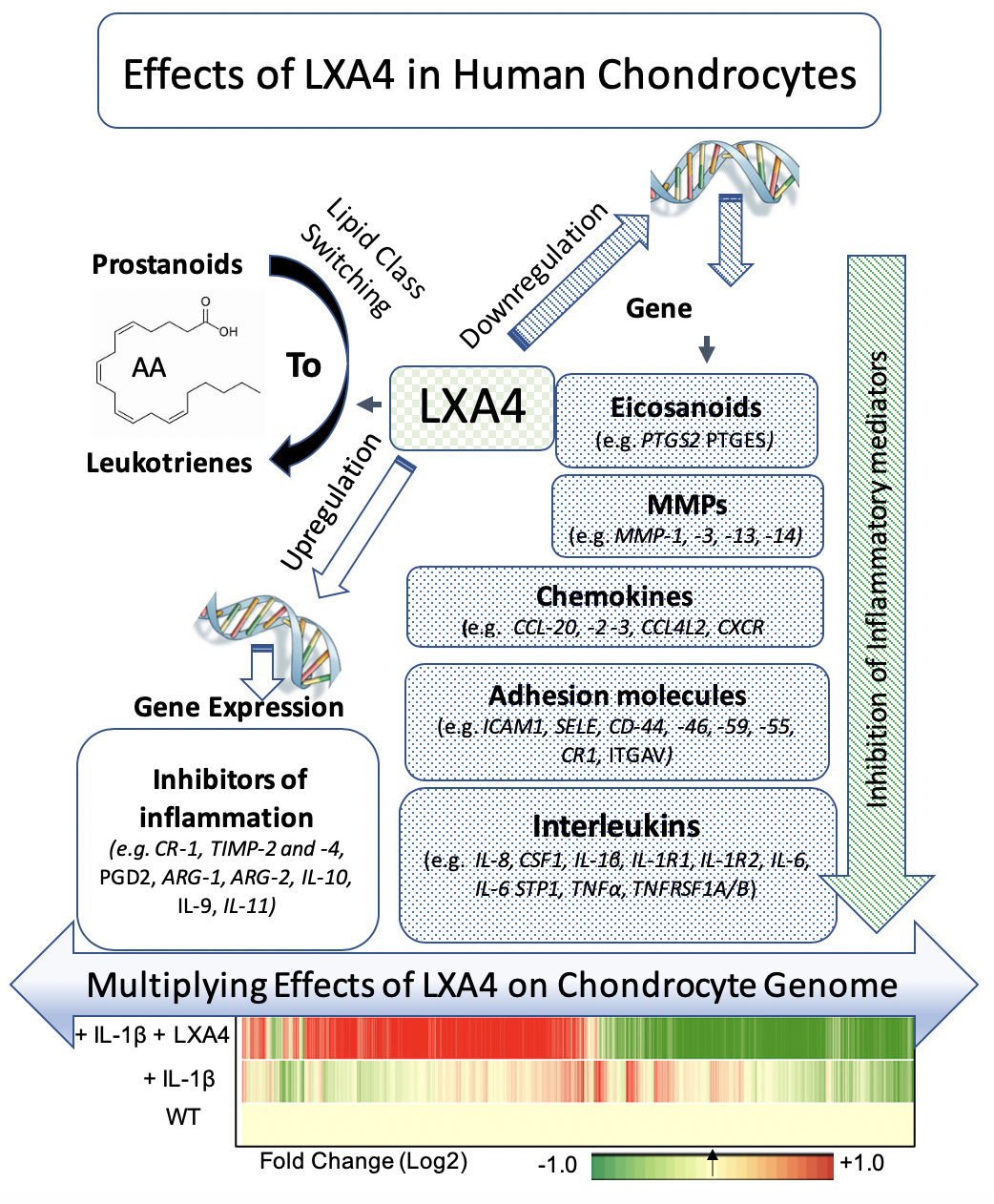 The effects Lipoxin A4 in human chondrocytes in inducing lipid class switching from prostanoids to leukotrienes, downregulation of multiple inflammatory mediators, and upregulation of several inhibitors of inflammation. The effect of Lipoxin A4 on genomic expression in IL-1B-stimulated chondrocytes is depicted on a log2 fold change heat map exhibiting their antagonistic pattern of gene expression.
The effects Lipoxin A4 in human chondrocytes in inducing lipid class switching from prostanoids to leukotrienes, downregulation of multiple inflammatory mediators, and upregulation of several inhibitors of inflammation. The effect of Lipoxin A4 on genomic expression in IL-1B-stimulated chondrocytes is depicted on a log2 fold change heat map exhibiting their antagonistic pattern of gene expression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dave M, Islam A, Parekh A, Patel J, Chawla A, Amin A. Lipoxin A4 Induces Lipid Class Switching and Inflammation Resolution at the Genomic Level in Human Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lipoxin-a4-induces-lipid-class-switching-and-inflammation-resolution-at-the-genomic-level-in-human-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lipoxin-a4-induces-lipid-class-switching-and-inflammation-resolution-at-the-genomic-level-in-human-osteoarthritis/
