Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Basic Science Poster (0046–0068)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Oxylipins are bioactive lipids derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that modulate inflammation. Oxylipins derived from n-6 PUFA precursors, such as arachidonic acid (AA), linoleic acid (LA), and dihomo-γlinolinic acid (DGLA), are known for their proinflammatory effects. Oxylipins, derived from the n-3 PUFA precursors such as decosahexanoic acid (DHA), eicosapentanoic acid (EPA), and α-linoleic acid (ALA), have inflammation resolving properties. Several studies have suggested that these mediators in plasma might be biomarkers of synovial pathology. The goal of this study is to evaluate the expression of oxylipins in synovial biopsies obtained from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and correlate oxylipin levels between synovial tissue and plasma.
Methods: Thirteen patients with established RA and 11 patients with established PsA with active disease in at least one knee or one wrist were recruited, and synovial tissue (ST) was collected by either arthroscopy or ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy. 9 patients with RA and 8 patients with PsA had blood collected at the time of the procedure. Oxylipins in plasma and ST were determined by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS) and were classified into groups according to their precursor: AA, LA, ALA, DHA, EPA and DGLA. The levels of oxylipins are expressed in pmoles/ml. Data were analyzed using SPSS v27.0 Results were considered significant if the 2-sided P value was less than 0.05.
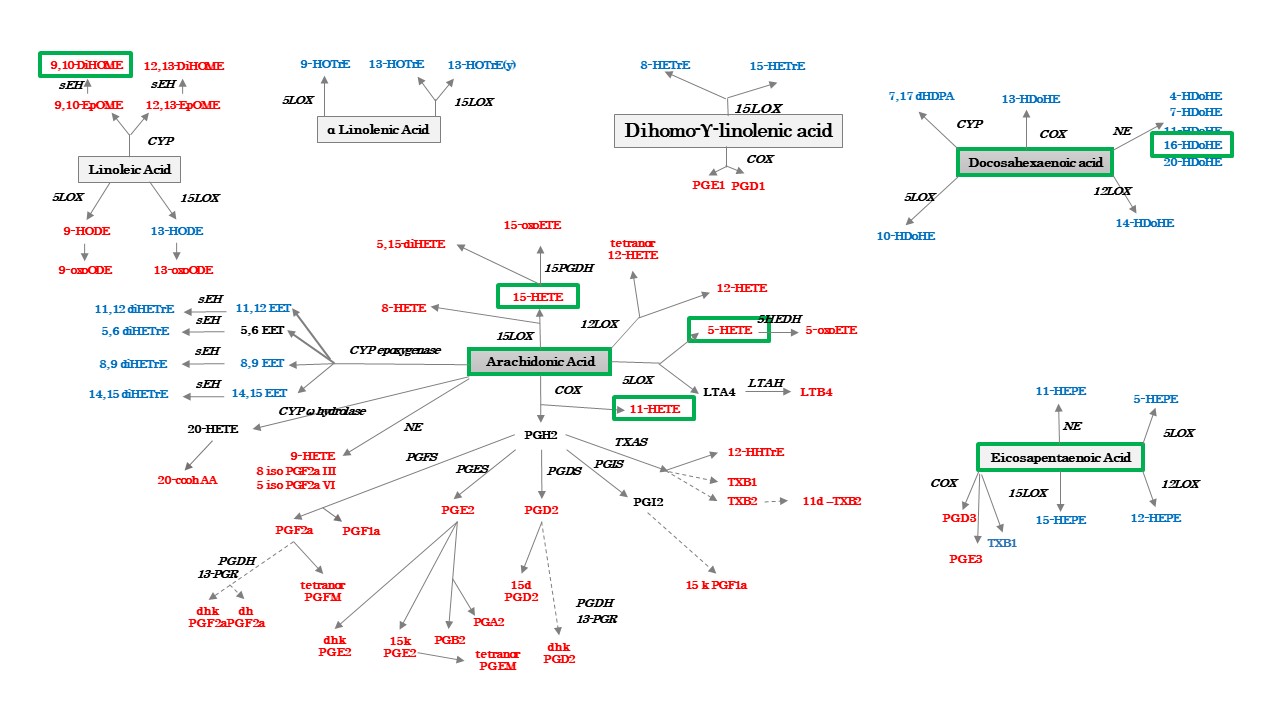
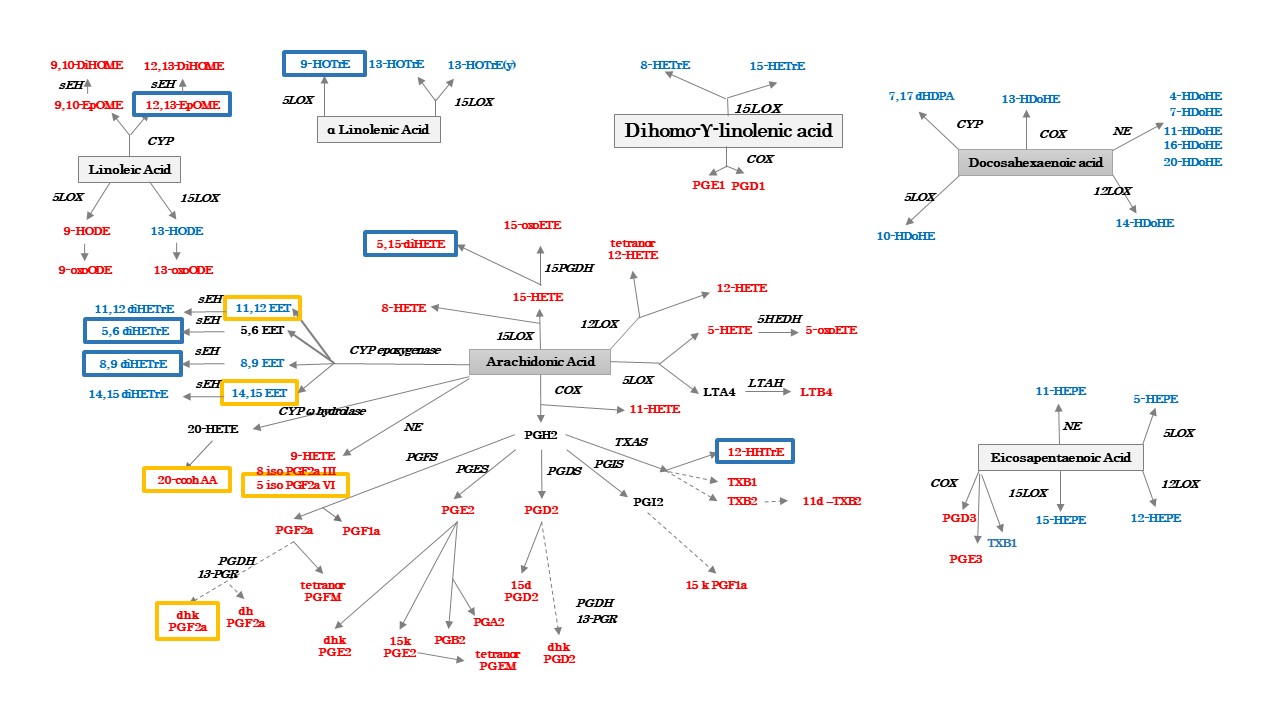
Results: We included a total of 24 ST and 17 plasma samples. A total of seventy-five oxylipins where identified in ST but only 39 were identified in plasma (Figure 1). While most of the proinflammatory AA-derived oxylipins were detected in both synovial tissue and plasma, several of the anti-inflammatory EPA- DHA- and LA-derived oxylipins were only detected in ST (Figure 1). Only levels of 11-HETE, 5-HETE, 15-HETE, 9,10-DiHOME and 16-HDoHE had a statistically significant positive correlation between plasma and ST (Figure 2). In addition, while several oxylipins were different in ST between RA and PsA patients (Figure 3) only the levels of 9-HOTrE and 5,15-diHETE were different between both diseases in plasma.
Conclusion: Lipidomic profiling detected almost twice the number of oxylipin species in synovial tissue as compared with plasma. More importantly, levels of only a few oxylipins correlated between plasma and synovial tissue. This work suggests that lipidomic profiling in synovial tissue can more accurately identify biomarkers than in plasma. Further studies with early, non-treated arthritis patients are needed to determine whether lipidomic profiling of synovial tissue can identify new therapeutic targets in inflammatory arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Singh A, Murillo Saich J, Coras R, Ramirez J, Chang E, Celis R, Armando A, Quehenberger O, Kavanaugh A, Cañete J, Guma M. Lipidomic Profiling Identifies Different Expression of Oxylipins Between Synovial Tissue and Plasma of Patients with Rheumatoid and Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lipidomic-profiling-identifies-different-expression-of-oxylipins-between-synovial-tissue-and-plasma-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-and-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lipidomic-profiling-identifies-different-expression-of-oxylipins-between-synovial-tissue-and-plasma-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-and-psoriatic-arthritis/