Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapies are constrained by the failure to deliver sufficient quantities of drug to the inflamed site, systemic side effects, and the inability for the patient to self-direct therapeutics in a site-targeted fashion. To address this, we have conjugated anti-inflammatory drugs to the light-responsive fluorophore Cy5, anchored to vitamin B12. These photocleavable drug-conjugates can be loaded into red blood cells (RBCs) and released only after laser light activation. In vitro studies have shown RBC-B12-Cy5-dexamethasone successfully induced nuclear migration of the glucocorticoid receptor after laser light photocleavage. We believe this system can be used in the treatment of RA, where externally and selectively applied laser to joints can trigger photocleavage of anti-inflammatories internally loaded into RBCs to the targeted site.
Methods: Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) was induced in 45 DBA1J mice. Arthritis was measured by a blinded observer with a clinical disease score index, and mice were randomized to 3 groups after symptom onset: RBC-B12-Cy5-dexamethasone (RBC-DEX), RBC-Cy5 (negative control), intraperitoneal dexamethasone (IP-DEX; positive control). Hypotonic solution was used to create a porous membrane in murine RBCs for drug uptake, followed by isotonic solution to close the pores and trap the phototherapeutic inside until photo-release. The RBC-DEX group received RBCs (90% hematocrit, 100μL) loaded with B12-Cy5-dexamethasone (approx. 0.0065 mg) intravenously. The RBC-Cy5 control group received RBCs internally loaded with only B12-Cy5. Intravenous injections were given one time at symptom onset for both RBC-DEX and RBC-Cy5. The IP-DEX group received 0.5mg/kg daily until a clinical score of 0 in the arthritic paw receiving laser. Laser (635 nm, 3 mW) was applied to one affected joint for 5 minutes immediately following i.v. or i.p. injection (based on group assignment) and each day until termination. There were no adverse reactions from laser application.
Results:
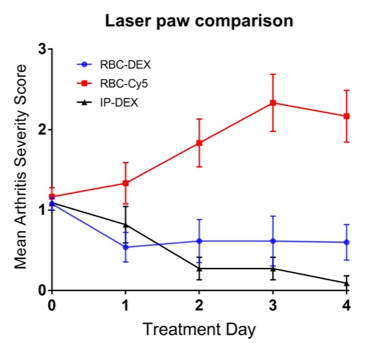
RBC-DEX and IP-DEX produce significant improvement in clinical arthritis compared to the control RBC-Cy5 (p=0.0007, p=0.0002 respectively), but do not significantly differ from each other (p=0.6) (Fig. 1). The RBC-DEX group received on average 80% less dexamethasone as compared to the IP-DEX treatment group, without significantly different results.
Conclusion: RBC-DEX is an effective CAIA treatment compared to negative control and is as effective as the positive drug control using a substantially lower dose of dexamethasone. This warrants further study into the parameters that are required for selective release of RBC-DEX in arthritis treatment.
Across 3 groups: p<0.0001*.
RBC-Cy5 vs. IP-DEX: p=0.0002*
RBC-DEX vs. IP-DEX: p=0.6
RBC-DEX vs. RBC-Cy5: p=0.0007*
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wickenheisser V, Rabjohns E, Zywot E, Orlova N, Marvin C, Ding S, Lawrence D, Tarrant T. Light Mediated Therapeutics in Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/light-mediated-therapeutics-in-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/light-mediated-therapeutics-in-arthritis/