Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Cardiopulmonary Aspects
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Despite the known excess mortality of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD), its association with certain lifestyle factors such as obesity and future prediction have not yet been determined. We aimed to investigate the association between novel lifestyle factors on risk of incident RA-ILD, to define the threshold at which smoking increases risk of RA-ILD, and to calculate the degree to which known clinical risk factors predict RA-ILD.
Methods: This nested case-control study was performed within a prospective RA registry. All participants had RA confirmed by a rheumatologist using ACR/EULAR criteria. Three radiologists/pulmonologists determined incident RA-ILD status based on research review of clinically-obtained chest computed tomography (CT) scans. Controls had RA and no patient/physician report or billing codes for ILD. Index date was the first CT with RA-ILD or matched date. We matched each incident RA-ILD case to three controls on age, sex, RA duration, rheumatoid factor positivity, and time from exposure assessment to index date. Exposures were assessed at the earliest study visit prior to RA-ILD and included education, body mass index (BMI), smoking pack-years, anti-CCP positivity, race, hand bone erosions, rheumatoid nodules, CRP, DAS28-CRP, functional status (multi-dimensional HAQ [MDHAQ]), disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug use, and glucocorticoid use. Conditional logistic regression models for each exposure determined odds ratios (OR) for RA-ILD, adjusting for matching factors, anti-CCP, race, education, BMI, and smoking pack-years. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROC) were calculated based on lifestyle and clinical exposures.
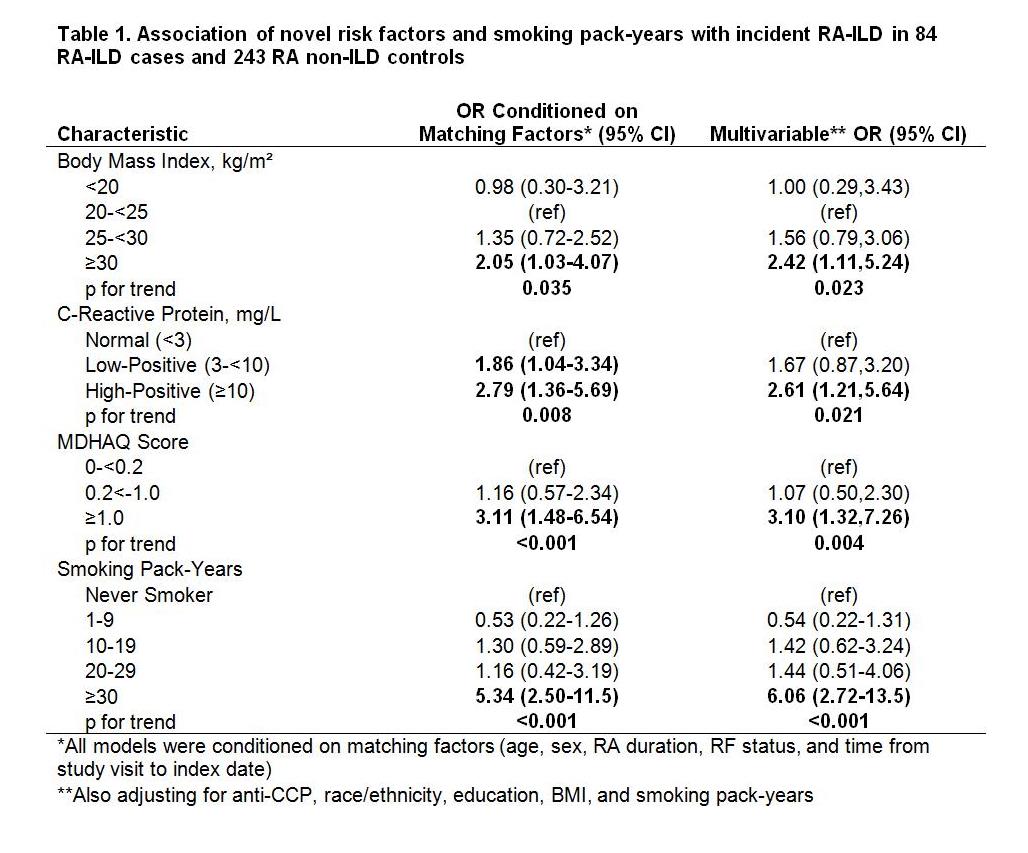
Results: We identified 84 confirmed incident RA-ILD cases and 243 matched controls. RA-ILD cases had a mean age of 67 (standard deviation 10), and 77% were female. Mean time from exposure assessment to RA-ILD onset was 1.5 years. After adjustment, obesity, high-positive CRP (≥10 mg/L), and poor functional status (MDHAQ ≥1) were each associated with increased risk of RA-ILD (Table 1). Smoking pack-year history greater than 30 was associated with a six-fold increased risk of RA-ILD compared to nonsmokers; less than 30 pack-years were not associated with RA-IOLD risk. Together, lifestyle and clinical risk factors for RA-ILD had an AUROC of 0.79 (95% CI 0.73-0.85) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This study identified obesity, high-positive CRP, poor functional status, and a smoking threshold of 30 pack-years as novel predictors of RA-ILD. The overall ability to predict RA-ILD based on lifestyle and clinical factors was modest. Future studies should investigate whether smoking cessation and weight loss may delay or prevent RA-ILD. Additional factors such as biomarkers may improve prediction of RA-ILD among patients with RA.
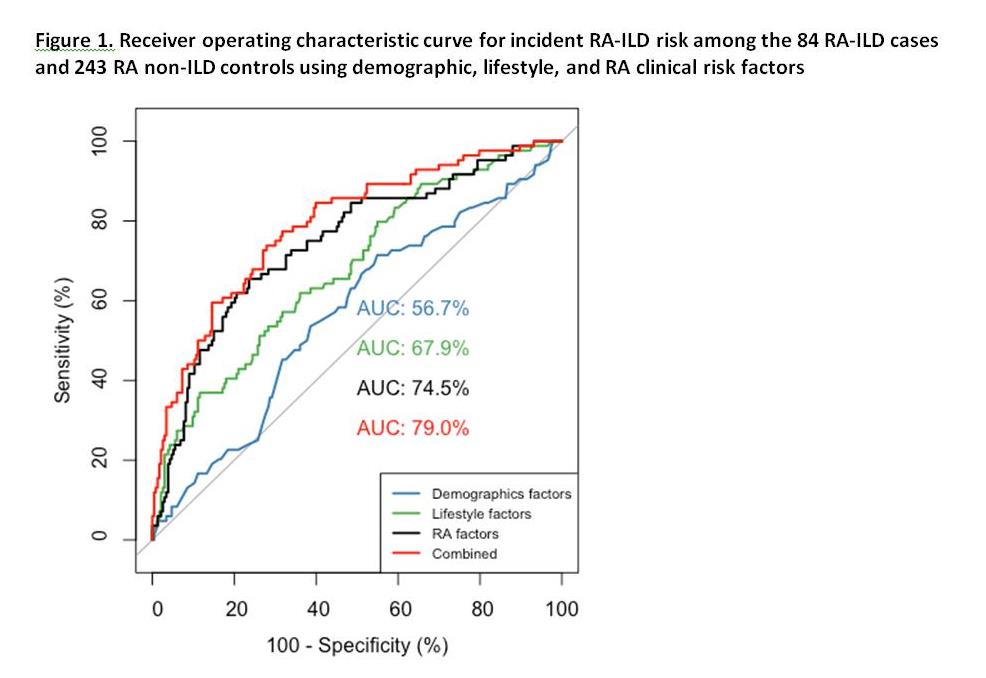 Demographic factors: age, sex, race, education Lifestyle factors: BMI, smoking pack-years RA factors: RA duration, RF status, anti-CCP status, hand bone erosions, rheumatoid nodules, biologic DMARD use, methotrexate use, glucocorticoid use, disease activity (DAS28-CRP), functional status (MDHAQ).
Demographic factors: age, sex, race, education Lifestyle factors: BMI, smoking pack-years RA factors: RA duration, RF status, anti-CCP status, hand bone erosions, rheumatoid nodules, biologic DMARD use, methotrexate use, glucocorticoid use, disease activity (DAS28-CRP), functional status (MDHAQ).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kronzer V, Huang W, Dellaripa P, Huang S, Feathers V, Lu B, Iannaccone C, Gill R, Hatabu H, Nishino M, Crowson C, Davis J, Weinblatt M, Shadick N, Doyle T, Sparks J. Lifestyle and Clinical Risk Factors for Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lifestyle-and-clinical-risk-factors-for-incident-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lifestyle-and-clinical-risk-factors-for-incident-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/