Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Glucocorticoids (GCs) are the most versatile and efficacious anti-inflammatory drugs rheumatologists have available for patients. Unfortunately, prolonged systemic GC exposure leads to unacceptable toxicities, which have reduced GC use in favor of biologics that sacrifice efficacy for improved safety. LFD-200 is an antibody-drug conjugate that limits systemic toxicities through selective delivery of a modified, potent GC payload to immune cells via an antibody to VISTA, a cell surface protein mainly expressed on immune cells. In multiple prior mouse studies, including models of autoimmune disease (e.g., diabetes, asthma, arthritis), LFD-200 is rapidly internalized, resulting in reduced serum GC exposure and increased intracellular exposure in immune cells as well as enhanced efficacy compared to conventional GCs. Safety and pharmacodynamic studies of LFD-200 have now also been conducted in non-human primates (NHPs).
Methods: Three NHP studies evaluating subcutaneously administered LFD-200 were conducted in cynomolgus macaques. Study 1: NHPs received one dose of LFD-200 (5 or 20 mg/kg). The control group received one dose of vehicle followed by 2 doses of dexamethasone (Dex; 3 mg/kg) given 6 and 7 days post vehicle. Ex vivo cytokine stimulation with lipopolysaccharides (LPS) was conducted on pre- and post-dosing tissue samples. Tissue exposure was assessed via immunohistochemistry using an antibody to the payload. Study 2: Toxicology study in which NHPs were dosed every 2 weeks (Q2W) with placebo or LFD-200 at 50 or 250 mg/kg for 4 weeks. Study 3: Same dosing design as Study 1, but with an additional 2 mg/kg in LFD-200 group. Circulating cortisol levels were assessed in Studies 2 and 3 via ELISA or liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.
Results: LFD-200 achieves durable GC exposure in immune cells. A single dose of 5 or 20 mg/kg LFD-200 resulted in GC payload detection in immune tissues for ³7 days post-dose (Figure 1). LFD-200 achieves durable cytokine suppression. Compared to baseline, LFD-200 dosing resulted in up to 75% decrease in LPS-stimulated cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IP-10, TNFa) in whole blood through 4 days post-dose, with up to 43% reduction observed 7 days post-dose. LFD-200 treatment showed no evidence of systemic GC effects. In Study 3, after a single dose of LFD-200, no impact on cortisol levels was observed at any dose or time point tested. Comparatively, dexamethasone suppressed cortisol levels well below baseline for >3 days (Figure 2A). In Study 2, repeated high doses of LFD-200 (50 and 250 mg/kg Q2W) showed no changes in cortisol (Figure 2B) and no histopathological changes in heart, brain, liver, bone, eye, kidney, or intestine (thymic cellularity was decreased at 250 mg/kg).
Conclusion: In these NHP studies, LFD-200 selectively delivered sustained GC levels in immune tissues, resulting in inhibition of ex vivo induced inflammatory cytokines without evidence of systemic toxicity. LFD-200 has the potential to provide a safer, less frequently dosed GC treatment option for patients living with autoimmune or inflammatory diseases.
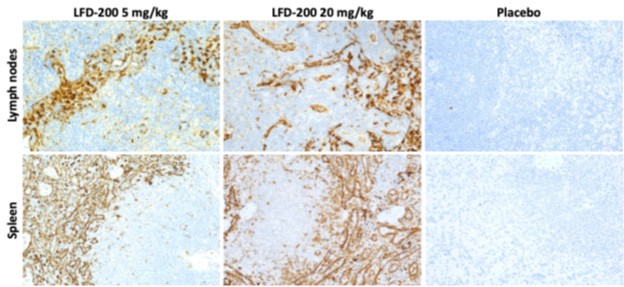 Figure 1: LFD-200 payload accumulation in lymph nodes and spleen. Immunohistochemistry for LFD-200 payload was conducted on lymph nodes and spleen that were collected 7 days after a single dose of 5 or 20 mg/kg LFD-200. Payload-specific antibody staining (brown) was detected in the spleen and lymph node at both doses but was absent in the placebo group. Slides were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue).
Figure 1: LFD-200 payload accumulation in lymph nodes and spleen. Immunohistochemistry for LFD-200 payload was conducted on lymph nodes and spleen that were collected 7 days after a single dose of 5 or 20 mg/kg LFD-200. Payload-specific antibody staining (brown) was detected in the spleen and lymph node at both doses but was absent in the placebo group. Slides were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue).
.jpg) Figure 2: Serum cortisol levels following LFD-200 administration. A) Cortisol levels observed in Study 3 following a single dose (2, 5 or 20 mg/kg) of LFD-200 (n=4/group); the control group received one dose of vehicle followed by two doses of dexamethasone (3 mg/kg) 6 and 7 days post vehicle dosing (4 hrs before the final tissue collection). B) Cortisol levels (collected before each dose) observed in Study 2 following repeated doses of LFD-200 (50 or 250 mg/kg) (n=2 for the vehicle and n=4 for LFD-200). Red and blue arrows indicate LFD-200 and dexamethasone dosing, respectively.
Figure 2: Serum cortisol levels following LFD-200 administration. A) Cortisol levels observed in Study 3 following a single dose (2, 5 or 20 mg/kg) of LFD-200 (n=4/group); the control group received one dose of vehicle followed by two doses of dexamethasone (3 mg/kg) 6 and 7 days post vehicle dosing (4 hrs before the final tissue collection). B) Cortisol levels (collected before each dose) observed in Study 2 following repeated doses of LFD-200 (50 or 250 mg/kg) (n=2 for the vehicle and n=4 for LFD-200). Red and blue arrows indicate LFD-200 and dexamethasone dosing, respectively.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McClure M, Carriere C, Bell K, Williams R, Kuesters G, Sansevere E, Nichols D, Tzianabos A, Rothstein J. LFD-200, an Antibody Drug Conjugate that Selectively Delivers a Glucocorticoid Payload to Immune Cells, Provides Sustained Anti-inflammatory Effects Without Systemic Toxicity in Non-human Primates [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lfd-200-an-antibody-drug-conjugate-that-selectively-delivers-a-glucocorticoid-payload-to-immune-cells-provides-sustained-anti-inflammatory-effects-without-systemic-toxicity-in-non-human-primates/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lfd-200-an-antibody-drug-conjugate-that-selectively-delivers-a-glucocorticoid-payload-to-immune-cells-provides-sustained-anti-inflammatory-effects-without-systemic-toxicity-in-non-human-primates/
