Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Innate Immunity
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Persistent production of type I interferons (IFN-Is) is one of the hallmarks of lupus skin disease that is exacerbated by ultraviolet (UV) light. We previously showed IFN-I induction by UV occurs in a cGAS-STING-dependent manner, but the IFN-I signature returns to baseline levels in healthy skin, unlike in lupus. Here, we propose that the immune checkpoint VISTA is a regulator of skin IFN-I production in keratinocytes of therapeutic relevance to lupus.
Methods: Skin biopsies from B6, B6.Vsir-/- (VISTA-deficient), B6.Vsir-/-Sting-/-, KRT14creVsirfl/fl (Vsir-/- in keratinocytes), and cre-Vsirfl/fl female mice (3 mo) were collected prior to, 3 and 24h after UVB (500mJ/cm2). Gene expression was quantified by RNA-seq (Rosalind). Skin infiltrating cells were quantified by flow cytometry. Human keratinocytes were isolated from healthy skin and cultured in vitro. Cells were treated with agonistic anti-VISTA (803) or isotype IgG2a (20ug/ml) prior to UVB (50mJ/cm2), in the presence or absence of IFNa (100U). Expression of IFN-Is and IFN-I stimulated genes (ISGs) were quantified by qPCR (4hr after UV) and IFN-I score derived.
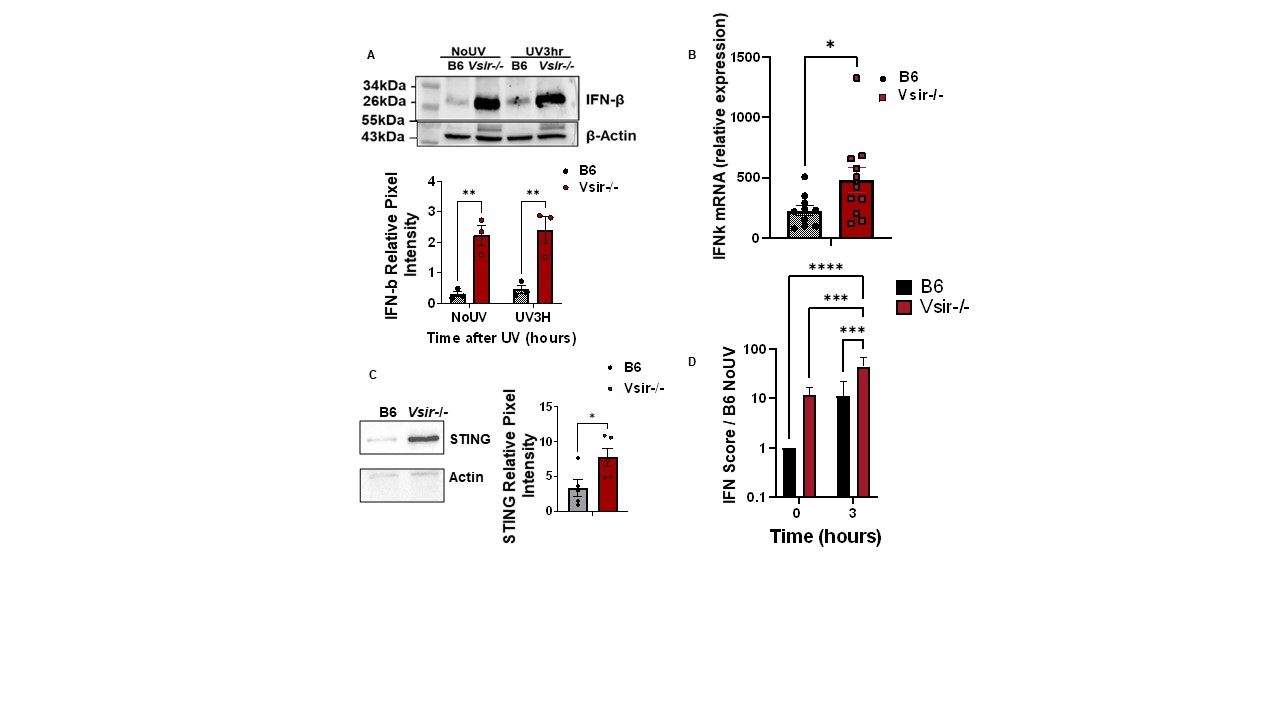
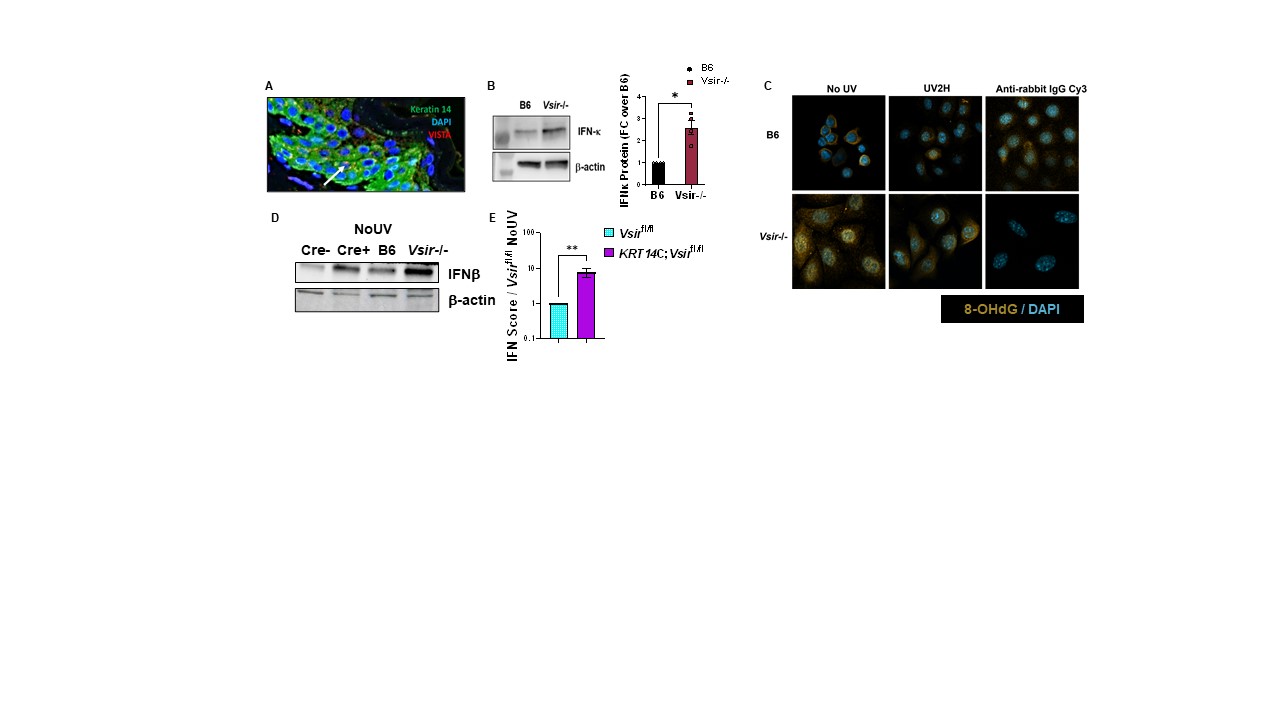
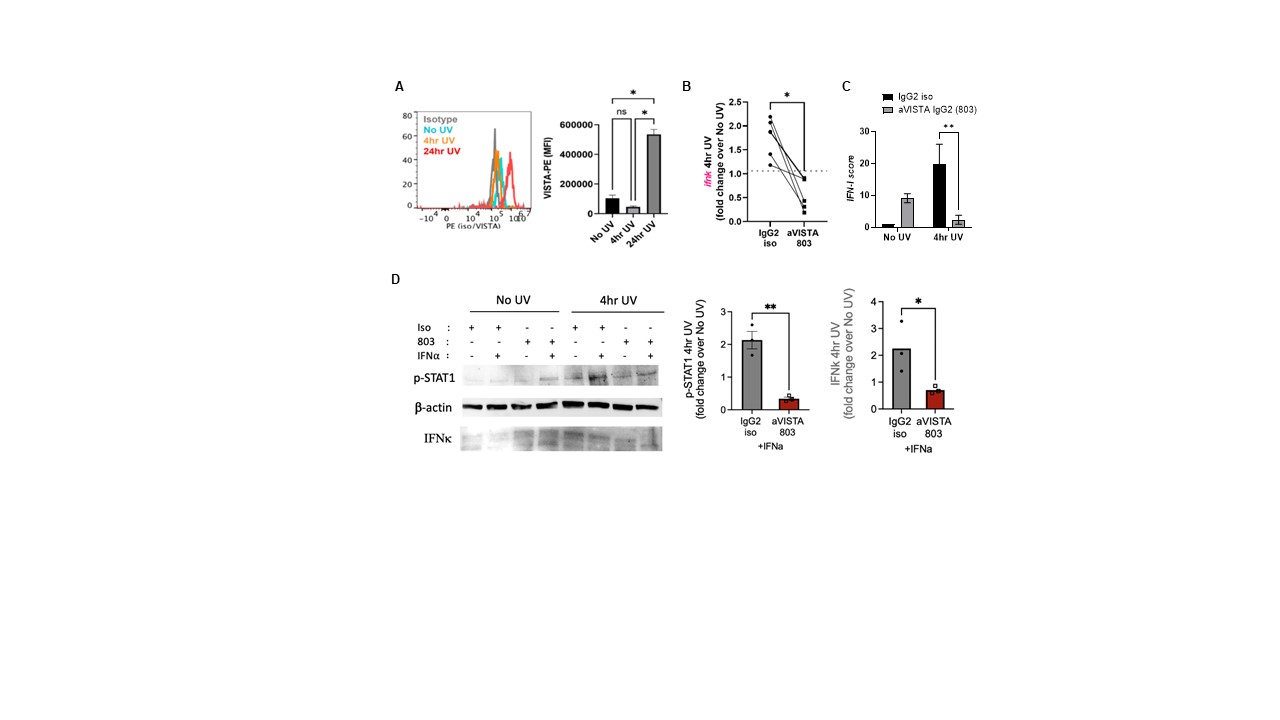
Results: At baseline, B6.Vsir-/- skin had increased IFN-k mRNA, IFN-b protein, as well as total STING protein levels (Fig. 1A-C). RNA-seq revealed increased expression of Sting and upstream cytosolic DNA sensors in VISTA-deficient mouse skin before and after UV. B6.Vsir-/- mice exhibited a 5-fold higher skin IFN-I score after UV compared to B6 mice (Fig.1D). Higher baseline and UV-induced IFN-I response in VISTA-deficient skin was suppressed in the absence of STING (Vsir-/-Sting-/- mice). Moreover, fewer skin-infiltrating neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes were recruited to Vsir-/-Sting-/- vs. STING-sufficient Vsir-/- skin post UV. RNAseq also revealed decreased expression of DNA repair genes like Ogg1, Xpd and Pole in B6.Vsir-/- skin, which are essential for repair of UV-induced DNA damage. VISTA deficient mouse keratinocytes produced 2-fold higher IFN-k at baseline ex vivo and accumulated higher levels of oxidized DNA (8-OHdG) compared with B6 cells (Fig. 2B-C).Mice with a conditional VISTA deletion only in keratinocytes exhibited a 10-fold higher baseline IFN-I signature and increased IFN-b protein levels compared to controls (Fig. 2D-E). Expression of VISTA on human keratinocytes decreased 4 hr after UV, but increased 5-fold 24 hr after UV(Fig. 3A).Pre-treatment of human keratinocytes with an agonistic anti-VISTA antibody (803) suppressed UV-induced IFN-k, Stat1 phosphorylation and IFN-I score, even in keratinocytes with a pre-existing IFN-I signature (Fig. 3C-D).
Conclusion: These studies identify VISTA as a suppressor of IFN-I production in keratinocytes and demonstrate STING-dependent IFN-I production in the absence of VISTA. As oxidized DNA is resistant to degradation in the cytosol where it can serve as a potent trigger of cGAS-STING, VISTA promotion of DNA repair may indirectly suppress STING signals. Antibody-mediated activation of VISTA in keratinocytes demonstrates its potential as a target to suppress IFN-I production in the context of photosensitivity and lupus.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peters Z, Mendyka L, Shan S, Rigby W, Burns C, Noelle R, Skopelja-Gardner S. Keratinocyte VISTA Suppresses Skin IFN-I Production by Regulating DNA Damage Repair and Cytosolic DNA Sensing [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/keratinocyte-vista-suppresses-skin-ifn-i-production-by-regulating-dna-damage-repair-and-cytosolic-dna-sensing/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/keratinocyte-vista-suppresses-skin-ifn-i-production-by-regulating-dna-damage-repair-and-cytosolic-dna-sensing/