Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To determine whether clinical tenderness can be considered a sign of inflammatory joint activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis (OA) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: Patients diagnosed with RA, PsA and OA underwent clinical and ultrasound examination of wrists and finger joints. Gray scale signs of synovitis (GS) and Power Doppler signal (PD) were evaluated using a semiquantitative grading system. Radiographs of the hands were scored for erosions, joint space narrowing, osteophytes and malalignment and a binary damage score was calculated. Differences in PD and GS between tender non-swollen (TNS) vs. non-tender non-swollen joints (NTNS) were calculated by Chi-Square test and prediction of tenderness was assessed by sex- and age-adjusted binary logistic regression analysis.
Results: There was no difference in the frequency of PD positivity between TNS and NTNS joints in RA (p=0.18), PsA (p=0.59) or OA (p=0.96) (Fig. 1). However, PD had a significant impact on tenderness in non-swollen joints in patients with a disease duration of less than 2 years, both in RA (OR 2.22, 95%CI 1.12-4.43, p=0.02) and in PsA (OR 3.26, 95%CI 1.21-8.81, p=0.02). The radiographic damage score had a significant impact on tenderness in non-swollen joints in RA (OR 1.8, 95%CI 1.17-2.86, p< 0.01), PsA (OR 1.84, 95%CI 1.18-2.86; p< 0.01) and OA (OR 1.89, 95%CI 1.03-3.46; p=0.04) (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: Tenderness might not always be a sign of active inflammation in RA, PsA and OA. While inflammation may play a role in early disease, tenderness in established disease may be better explained by joint damage and malalignment.
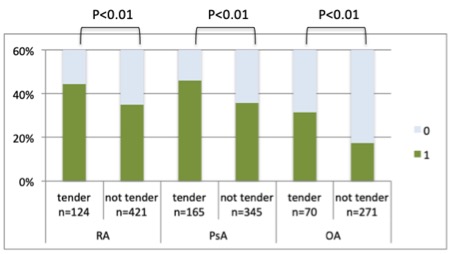 Figure 1. Difference of damage score (0 vs. ≥1) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and osteoarthritis (OA).
Figure 1. Difference of damage score (0 vs. ≥1) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and osteoarthritis (OA).
 Figure 2. Difference of detected erosions (0 vs. ≥1), joint space narrowing (0 vs. ≥1), malalignment (presence/ absence), osteophytes (presence/ absence) and damage score (0 vs. ≥1) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (A), psoriatic arthritis (B) and osteoarthritis (C). Impact of erosions (semiquantitatively), joint space narrowing (semiquantitatively), malalignment, osteophytes and damage score on tenderness in non-swollen joints was calculated by age- and sex-adjusted binary logistic regression.
Figure 2. Difference of detected erosions (0 vs. ≥1), joint space narrowing (0 vs. ≥1), malalignment (presence/ absence), osteophytes (presence/ absence) and damage score (0 vs. ≥1) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (A), psoriatic arthritis (B) and osteoarthritis (C). Impact of erosions (semiquantitatively), joint space narrowing (semiquantitatively), malalignment, osteophytes and damage score on tenderness in non-swollen joints was calculated by age- and sex-adjusted binary logistic regression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Popescu M, Schimpl V, Supp G, Durechova M, Studenic P, Zauner M, Smolen J, Aletaha D, Mandl P, Gessl I. Joint Damage and Malalignment Determine Articular Tenderness More Than Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis or Osteoarthritis in Established Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/joint-damage-and-malalignment-determine-articular-tenderness-more-than-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-or-osteoarthritis-in-established-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/joint-damage-and-malalignment-determine-articular-tenderness-more-than-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-or-osteoarthritis-in-established-disease/
