Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Inflammation is the initial stage of ankylosing spondylitis (AS), looking for possible inflammatory regulator will have a great significance in AS treatment. Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 (JMJD3) could specifically demethylate the 27th lysine of histones H3(H3K27), which was found in inflammation and many autoimmune diseases. The most important functions of JMJD3 are regulating the differentiation of T cell subsets. JMJD3 specifically de-methylated H3K27 trimethylation in the promoter sequence of the retinoid-acid receptor-related orphan receptor c (RORc) gene, which is considered to be the beginning of Th17 differentiations. As we known, Th17 has been determined its important role in AS inflammation. So this research aims to explore the epigenetic regulation of JMJD3 in AS inflammation through Th17 differentiations.
Methods: A total of 40 AS patients in active stage and 20 healthy controls (25.2¡À4.1 years) participated in the experiments. All patients were met with the modified New York criteria. 20 of them whose BASDAI¡Ý4 were classified into AS-Active group(25.8¡À7.1years), others were classified into AS-Stable group(31.2¡À8.4years). The serum level of IL-17 was detected by ELISA. The proteins were all detected by Western blotting. The mRNA were detected by quantitative PCR .
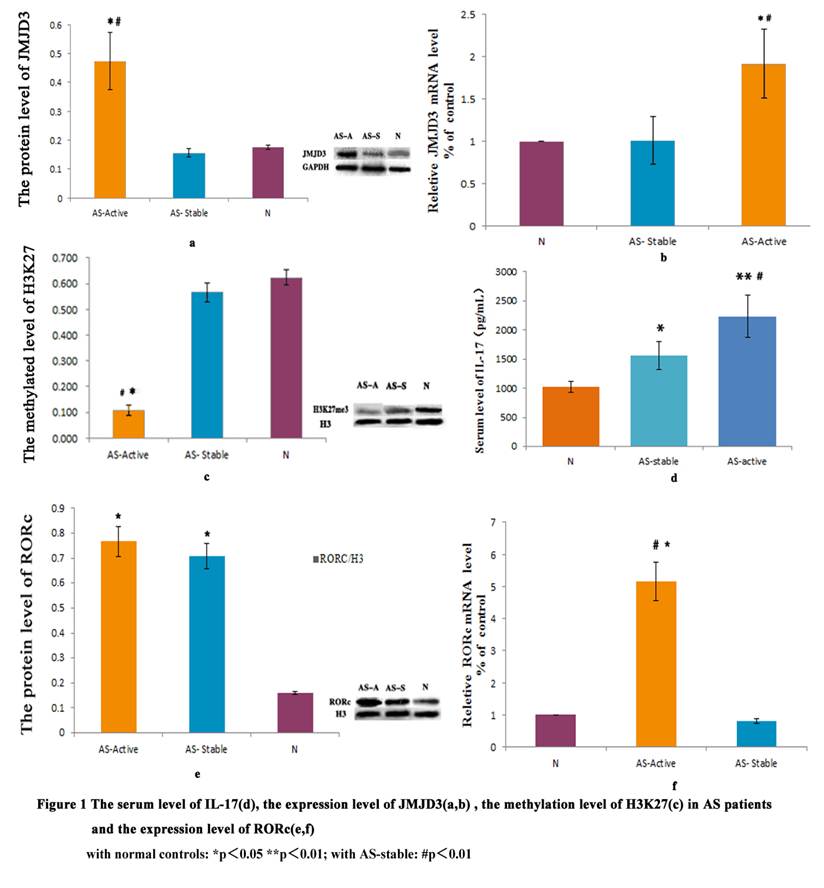
Results: As in Figure1. The serum IL-17 levels were significantly higher in AS- active patients. The level of JMJD3 is significant higher in AS-active. The methylation level of H3K27 was reduced in AS-active than in others. The protein level of RORc is higher in AS-active and AS-stable, but in transcriptional level the AS-active group was higher than other two groups.
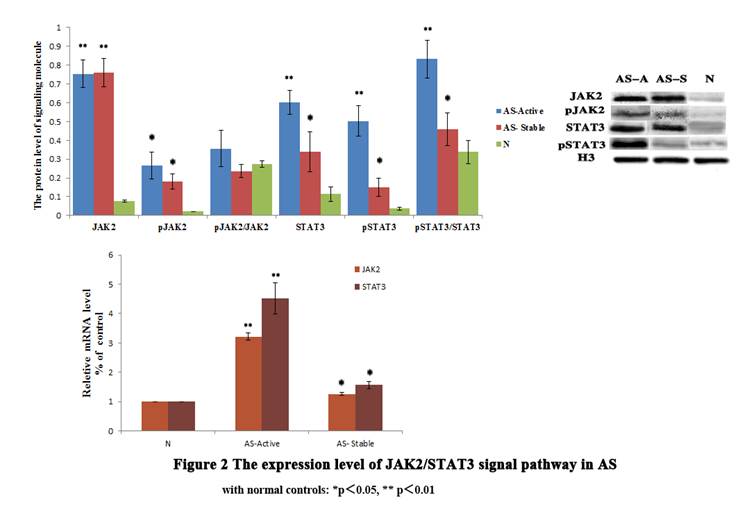
In Figure 2. The protein level and phosphorylated level of JAK2 and STAT3 were higher in AS-active. The transcriptional level were higher too.
Conclusion: Our study found that JMJD3 catalyzes the demethylation of H3K27 might be an important epigenetic mechanisms in AS inflammatory. The highly expression of JMJD3 in active AS patients may leading to the higher expression of RORc, and could activation the signal transduction through JAK2/STAT3 pathway, inducing a large number of IL-17 secretions. That could be the beginning of the differentiation and function of Th17, and JMJD3 maybe the core epigenetic regulator in this inflammation process. These exciting findings have broad implications for finding possible biomarkers in the inflammatory of AS, and may give us a new possible point of view from the epigenetic regulation mechanism of Th17 in the inflammation stage of AS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liu H, Xu Z, Feng X, Feng X, Zhang H, Jiang Q, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zhao Z. JMJD3 Epigenetically Regulate Ankylosing Spondylitis Inflammation through Th17 Differentiation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jmjd3-epigenetically-regulate-ankylosing-spondylitis-inflammation-through-th17-differentiation/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jmjd3-epigenetically-regulate-ankylosing-spondylitis-inflammation-through-th17-differentiation/