Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Effectiveness of SC abatacept in patients with polyarticular-course JIA (pJIA) was shown in a 2-year, open-label Phase III international study (NCT01844518). Here we assess potential predictors of Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score 27-CRP (JADAS27-CRP) minimal disease activity (MDA), inactive disease (ID) and remission.
Methods: Patients with pJIA aged 2–17 years received weight-tiered SC abatacept (10–< 25 kg: 50 mg; 25–< 50 kg: 87.5 mg; ≥50 kg: 125 mg) weekly for 4 months.1 JIA-ACR30 responders at Month 4 could receive SC abatacept for another 20 months.1 Potential predictors of response over 11 time points to Month 21 were determined with a multivariate logistic regression (MVR) analysis; Month 4, 13 and 21 data are presented. MVR variables assessed were baseline age, sex, race, weight, geographic region, CRP, MTX use, prior biologic use, number of active joints, number of joints with limitation of motion, physician’s global assessment of disease activity, Childhood HAQ-DI (CHAQ-DI), parental assessment of well-being (PaGA) and JIA-ACR50 or JIA-ACR70 responses at Month 3. Variables were deemed significant if corresponding p values were < 0.05 at ≥6 of the 11 time points. Missing values were imputed as non-responders. Baseline continuous variable cut-offs (high/low) were determined by receiver-operator curve analysis. Outcomes analyzed included JADAS27-CRP MDA (≤3.8), ID (≤1) and remission (JADAS27-CRP ID for ≥6 months) rates. Odds ratios and 95% CIs were computed.
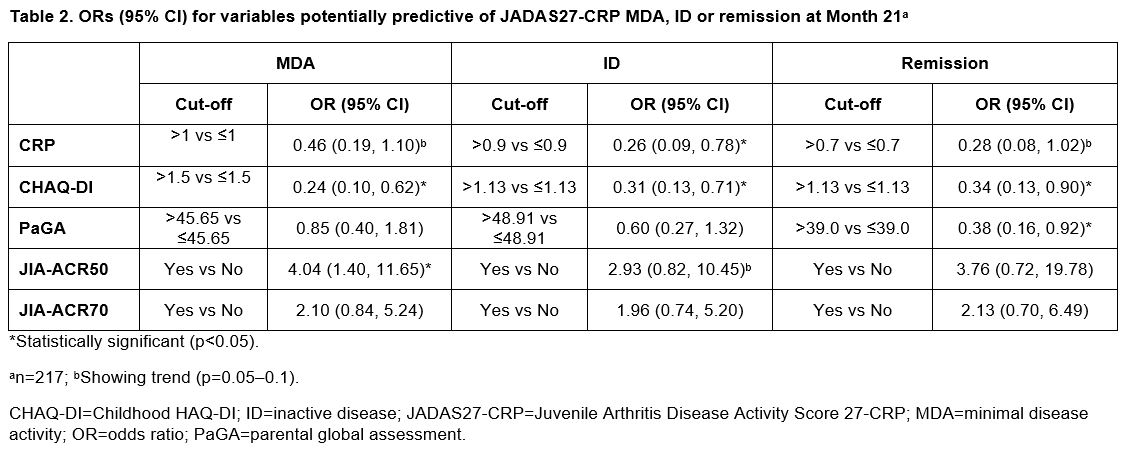
Results: In all treated patients (N=219), median (range) baseline characteristics were: age 11.0 (2.0–17.0) years, CRP 0.2 (0.1–21.1) mg/dL, CHAQ-DI 1.0 (0.0–2.9) and PaGA 47.2 (0.0–95.8). Variables with the highest number of significant p values (≤0.05) were baseline CRP, CHAQ-DI, PaGA, and Month 3 JIA-ACR50 and JIA-ACR70. Baseline CRP, PaGA and CHAQ-DI were predictive of JADAS27-CRP MDA, ID and/or remission at multiple time points (Month 13: Table 1; Month 21: Table 2). JIA-ACR50 response at Month 3 was statistically significant at predicting achievement of JADAS27-CRP MDA at Month 13 (Table 1) and Month 21 (Table 2), and showed a statistical trend at Month 4 (data not shown). JIA-ACR50 response was statistically significant (p< 0.05) at five consecutive time points between Months 10 and 21.
Conclusion: Clinically important JIA-ACR50 response at Month 3 was predictive of the attainment of JADAS27-CRP MDA status at Month 13 and Month 21 in patients aged 2–17 years with pJIA treated with SC abatacept.
Reference:
- Brunner HI, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018;70:1144–1154.
Medical writing: Rachel Rankin (Caudex)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ruperto N, Brunner H, Berman A, Ávila-Zapata F, Horneff G, Alessio M, Becker M, Belot A, Burgos-Vargas R, Boteanu A, Goldenstein-Schainberg C, Scheibel I, Terreri M, Zemel L, Wong R, Askelson M, Nys M, Martini A, Lovell D. JIA-ACR50 Response as a Predictor of Minimal Disease Activity in Patients Aged 2–17 Years with Polyarticular-Course JIA Treated with SC Abatacept [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jia-acr50-response-as-a-predictor-of-minimal-disease-activity-in-patients-aged-2-17-years-with-polyarticular-course-jia-treated-with-sc-abatacept/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jia-acr50-response-as-a-predictor-of-minimal-disease-activity-in-patients-aged-2-17-years-with-polyarticular-course-jia-treated-with-sc-abatacept/