Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Recent evidence suggests that innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) might be involved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis and individuals at risk of RA exhibited an increased frequency of ILC1 (Rodríguez-Carrio J, Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017). JAK3 participates in ILC1 and ILC3 differentiation. Tofacitinib and JAK3 inhibitor, PF-06651600, impair the ability of human intraepithelial ILC1 to produce IFN-γ and the proliferation of ILC1 and ILC3 (Robinette ML, Mucosal immunology. 2018). Our study aims to evaluate the effects of tofacitinib on ILC1 and ILC3 expansion and function in RA.
Methods: Twenty RA patients, who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR RA classification criteria, with active disease, naive to biological agents, were enrolled and started tofacitinib. The study was complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local Ethical Committee. Ten healthy donors (HD) matched for age and sex were also enrolled. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) collected before (T0) and three months after therapy (T1), were cultured to evaluate ILC1 and ILC3 frequencies and the respective production of IFN-γ and IL-17 by flow cytometry analysis. PBMCs of RA patients were in vitro cultured for 48 hours with tofacitinib at increasing concentrations (25nM, 100nMand 400nM) to evaluate the dose effects of tofacitinib on ILCs frequencies. Role of the Study Sponsor: Research was supported by an unrestricted grant by Pfizer.
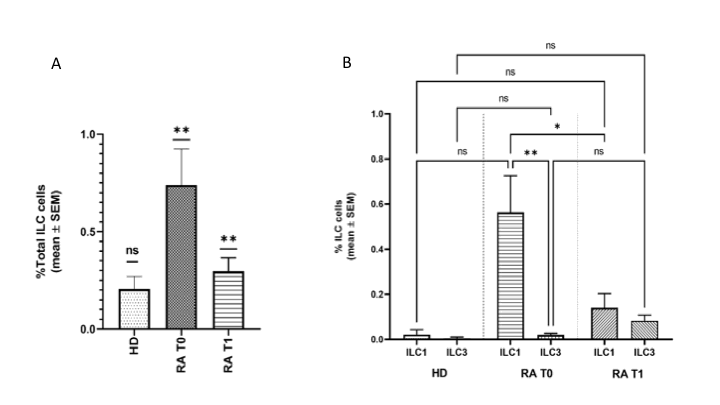
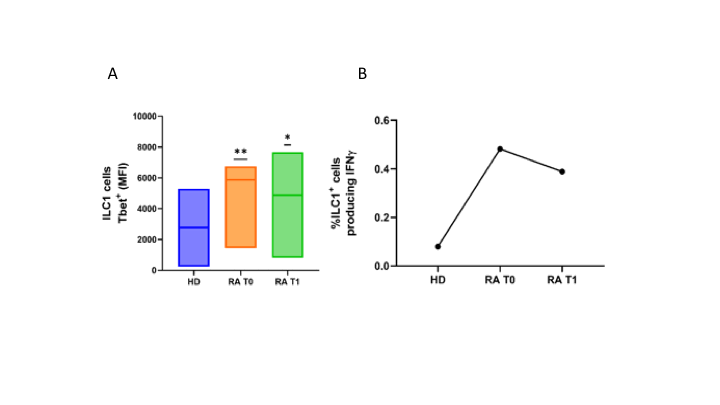
Results: At T0, RA patients showed a significant expansion of peripheral total ILCs and ILC1 (Lin–, CD127+, CD117–, Tbet+) but not ILC3 (Lin–, CD127+, CD117+, RoR γt+), compared to HD. After three months of therapy the overall ILCsfrequency was significantly reduced in RA (Figure 1). Specifically, ILC1 frequency was significantly decreased in association with the reduction of transcriptional factor T-bet expression as well as the ILC1 ability to release IFN-γ (Figure 2). Instead, for ILC3 not significant modifications in frequency, RoR γt expression andIL-17 production were detected at T1. In vitro treatment of PBMCs with increasing concentrations of tofacitinib demonstrated a dose-dependent reduction in the frequency of ILCs compared to untreated cells. In particular, ILC1s resulted more affected, by the in vitro treatment, both in terms of frequency and transcription factors expressioncompared to ILC3, supporting our ex vivo results (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Our preliminary results demonstrate that tofacitinib modulates the innate immune response by reducing the frequency of ILC1 cells and their production of IFN- γ.
A. Peripheral total ILCs frequency in HD and RA patients at T0 and T1; **p <0,01.
B. Frequency of ILC1 and ILC3 in HD and RA patients at T0 and T1; **p <0,01, *p <0,05.
A. Box plot showing comparison between median values of T-bet MFI for HD and RA patients at T0 and T1; **p <0,01, *p <0,05.
B. IFNγ production by ILC1s in HD and RA patients at T0 and T1.
A. Total ILCs frequency
B. Frequency of ILC1
C. Box plot showing MFI expression of Tbet on ILC1s
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
La Barbera L, Lo Pizzo M, Rizzo C, Mohammadnezhad L, Camarda f, Ciccia F, Guggino G. JAK/STAT Inhibition Modifies the Innate Lymphoid Cells 1 Immune Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-stat-inhibition-modifies-the-innate-lymphoid-cells-1-immune-response-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/jak-stat-inhibition-modifies-the-innate-lymphoid-cells-1-immune-response-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/